Sheltered Instruction is a teaching approach designed to make academic content comprehensible for English language learners while promoting their language development. This method integrates language objectives with content goals, using visual aids, modeling, and scaffolding to support understanding. Discover how Sheltered Instruction can transform Your classroom experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
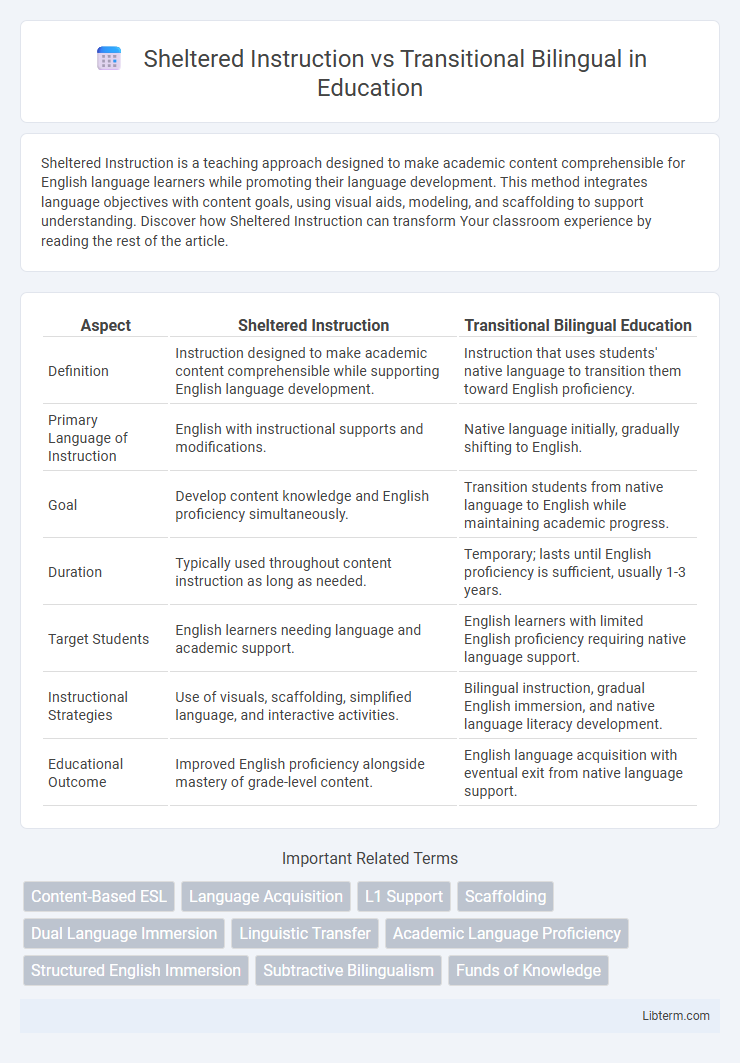
| Aspect | Sheltered Instruction | Transitional Bilingual Education |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instruction designed to make academic content comprehensible while supporting English language development. | Instruction that uses students' native language to transition them toward English proficiency. |
| Primary Language of Instruction | English with instructional supports and modifications. | Native language initially, gradually shifting to English. |
| Goal | Develop content knowledge and English proficiency simultaneously. | Transition students from native language to English while maintaining academic progress. |
| Duration | Typically used throughout content instruction as long as needed. | Temporary; lasts until English proficiency is sufficient, usually 1-3 years. |
| Target Students | English learners needing language and academic support. | English learners with limited English proficiency requiring native language support. |
| Instructional Strategies | Use of visuals, scaffolding, simplified language, and interactive activities. | Bilingual instruction, gradual English immersion, and native language literacy development. |
| Educational Outcome | Improved English proficiency alongside mastery of grade-level content. | English language acquisition with eventual exit from native language support. |
Introduction to Sheltered Instruction and Transitional Bilingual Education
Sheltered Instruction integrates content and language teaching to support English language learners by simplifying academic language and providing visual aids, enabling comprehension across subjects. Transitional Bilingual Education uses students' native language to facilitate learning while gradually increasing English proficiency, aiming for full immersion in English over time. Both approaches prioritize language development but differ in instructional strategies and the role of the native language in the classroom.
Defining Sheltered Instruction: Key Features
Sheltered Instruction is an instructional approach designed to make academic content comprehensible for English Language Learners (ELLs) while promoting English language development. Key features include simplified language, visual aids, and hands-on activities tailored to students' proficiency levels. This method integrates language objectives with content objectives to ensure simultaneous learning of both language and subject matter.
Understanding Transitional Bilingual Education
Transitional Bilingual Education (TBE) focuses on developing students' proficiency in their native language while gradually introducing English language instruction to ensure academic success. It aims to transition students from their home language to English, promoting bilingualism and biliteracy during the process. Unlike Sheltered Instruction, which primarily delivers content in English adapted for English Language Learners (ELLs), TBE maintains a balance between native language support and English acquisition to minimize academic disruption.
Core Goals of Each Educational Approach
Sheltered Instruction aims to make academic content comprehensible for English language learners by integrating language development with subject matter teaching, focusing on building both language proficiency and academic skills simultaneously. Transitional Bilingual Education primarily seeks to develop students' native language literacy while gradually transitioning them to English, emphasizing cognitive development and content mastery in the first language before moving to English instruction. Both approaches target academic achievement but differ in language use strategies, with Sheltered Instruction promoting immediate English immersion and Transitional Bilingual Education supporting bilingualism during the transition.
Instructional Strategies Compared
Sheltered Instruction utilizes strategies like scaffolding, visual aids, and language objectives to make academic content comprehensible for English Language Learners (ELLs) while promoting language development. Transitional Bilingual Instruction, however, emphasizes instruction in the student's native language alongside English, employing code-switching and gradual English language introduction to support content mastery. Both approaches adapt teaching methods to accommodate linguistic needs but differ in language use intensity and focus on bilingual proficiency versus English immersion.
Language Development Outcomes
Sheltered Instruction enhances language development by integrating content and language objectives, promoting academic vocabulary growth and comprehension through contextualized lessons. Transitional Bilingual programs support language development by providing instruction in the student's native language while gradually introducing English, which helps maintain academic progress and builds biliteracy skills. Research shows Sheltered Instruction tends to accelerate English proficiency, whereas Transitional Bilingual approaches better preserve students' first language and cultural identity.
Academic Achievement: Evidence and Research
Research indicates that Sheltered Instruction consistently improves academic achievement for English Language Learners (ELLs) by integrating language development with content mastery, resulting in higher standardized test scores in subjects like math and science. In contrast, Transitional Bilingual programs show mixed outcomes, often delaying English proficiency gains due to initial instruction in the native language, which may impact long-term academic performance. Meta-analyses highlight that Sheltered Instruction's emphasis on scaffolding and language objectives fosters better comprehension and retention, directly correlating with improved academic success among ELL students.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Sheltered Instruction faces challenges such as limited language proficiency support for students, which can hinder comprehension of academic content, and often requires teachers to have specialized training that is not always available. Transitional Bilingual programs struggle with the risk of students losing their native language proficiency and cultural identity while also facing delays in acquiring full English literacy. Both methods may encounter difficulties in balancing content mastery with language development, impacting long-term academic achievement.
Choosing the Right Approach for English Language Learners
Selecting the right approach for English Language Learners depends on factors like language proficiency levels, academic goals, and available resources. Sheltered Instruction emphasizes content mastery through modified language input, ideal for students ready to engage with grade-level material while learning English. Transitional Bilingual programs support native language use initially, promoting gradual English acquisition and cultural connection, which benefits learners needing strong foundational language support.
Future Trends in Multilingual Education
Sheltered Instruction integrates academic content with language development, promoting accessibility for English Language Learners (ELLs) through tailored strategies. Transitional Bilingual Education prioritizes native language proficiency as a foundation for English acquisition, gradually shifting instruction to English. Future trends in multilingual education emphasize hybrid models combining digital tools and culturally responsive teaching to enhance language outcomes and equity for diverse student populations.
Sheltered Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com