Mastering technical skills is essential for career advancement and adapting to rapidly evolving industries. Developing proficiency in areas such as programming, data analysis, and digital tools enhances your efficiency and problem-solving capabilities. Explore the rest of this article to discover strategies for acquiring and refining your technical expertise.
Table of Comparison
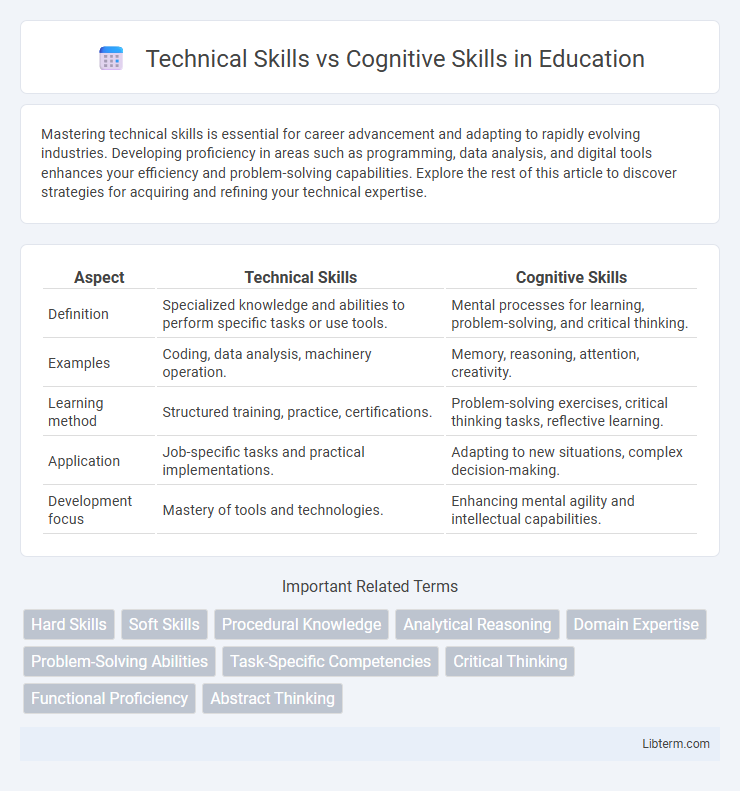
| Aspect | Technical Skills | Cognitive Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specialized knowledge and abilities to perform specific tasks or use tools. | Mental processes for learning, problem-solving, and critical thinking. |
| Examples | Coding, data analysis, machinery operation. | Memory, reasoning, attention, creativity. |
| Learning method | Structured training, practice, certifications. | Problem-solving exercises, critical thinking tasks, reflective learning. |
| Application | Job-specific tasks and practical implementations. | Adapting to new situations, complex decision-making. |
| Development focus | Mastery of tools and technologies. | Enhancing mental agility and intellectual capabilities. |
Understanding Technical Skills: Definition and Scope
Technical skills refer to the specific knowledge and abilities required to perform specialized tasks, such as programming, data analysis, or machinery operation, often acquired through education or training. These skills encompass proficiency in tools, technologies, and methodologies necessary to complete job-related functions efficiently. Understanding the scope of technical skills enables organizations to align employee competencies with technological demands, driving productivity and innovation.
Exploring Cognitive Skills: Key Components
Cognitive skills encompass critical components such as problem-solving, analytical thinking, and memory retention, which drive effective decision-making and complex reasoning. These skills enable individuals to process information, adapt to new situations, and innovate beyond routine technical tasks. Developing strong cognitive abilities enhances overall learning capacity and supports continuous personal and professional growth.
Technical Skills in the Modern Workplace
Technical skills in the modern workplace encompass proficiency in software applications, programming languages, data analysis, and digital tools essential for operational efficiency and innovation. Mastery of technical skills such as coding, cybersecurity, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence enables employees to adapt to rapid technological advancements and competitive market demands. Continuous upskilling in technical domains drives productivity, supports automation, and fosters a culture of technological competence critical for organizational success.
The Importance of Cognitive Skills in Problem-Solving
Cognitive skills such as critical thinking, reasoning, and analytical abilities play a crucial role in effective problem-solving by enabling individuals to process information, identify patterns, and develop innovative solutions. Unlike technical skills, which are task-specific and often procedural, cognitive skills provide the mental framework necessary to adapt to complex and novel challenges across various domains. Mastery of cognitive skills enhances decision-making quality and drives successful outcomes in dynamic and uncertain environments.
Key Differences Between Technical and Cognitive Skills
Technical skills involve specific, teachable abilities related to tasks, such as programming, machinery operation, or data analysis, while cognitive skills refer to mental capabilities like problem-solving, critical thinking, and memory. Technical skills are often measurable and acquired through training or education, whereas cognitive skills are inherent mental processes essential for learning and adapting. The key difference lies in technical skills being task-specific proficiencies, whereas cognitive skills underpin the ability to process information and apply knowledge effectively across various contexts.
How Technical Skills and Cognitive Skills Complement Each Other
Technical skills provide the practical expertise needed to perform specific tasks, while cognitive skills enable problem-solving, critical thinking, and adaptability in complex situations. Together, they create a balanced skill set that enhances productivity and innovation by allowing individuals to apply knowledge effectively and adjust strategies as challenges arise. Mastery of both skill types is essential for success in dynamic work environments, fostering continuous learning and efficient decision-making.
Training Methods for Developing Technical Skills
Training methods for developing technical skills emphasize hands-on practice, simulations, and interactive workshops that replicate real-world scenarios to enhance proficiency. Utilizing tools like software tutorials, coding bootcamps, and technical certifications allows learners to acquire and validate specific industry competencies efficiently. Incorporating project-based learning and continual feedback mechanisms supports skill retention and application in dynamic professional environments.
Strategies for Enhancing Cognitive Skills
Enhancing cognitive skills involves targeted strategies like engaging in problem-solving activities, memory exercises, and critical thinking tasks that stimulate neural pathways and improve mental agility. Incorporating mindfulness practices and continuous learning routines further boosts attention span and information processing capabilities. These approaches complement technical skills by fostering adaptability and innovative thinking essential for complex problem-solving in technical fields.
Industry Demand: Which Skills Are More Valued?
Industry demand increasingly favors cognitive skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and adaptability due to rapid technological advancements and the need for innovative solutions. While technical skills remain essential for operational tasks and specialized roles, employers prioritize cognitive abilities that enable employees to learn new technologies and navigate complex challenges. Data from job market analyses reveal a growing trend where hybrid skill sets combining both technical expertise and strong cognitive skills command higher employability and career growth potential.
Preparing for the Future: Balancing Technical and Cognitive Skills
Preparing for the future demands a strategic balance between technical skills, such as coding, data analysis, and software proficiency, and cognitive skills, including critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity. Organizations prioritize candidates who demonstrate adaptability by integrating advanced digital capabilities with strong cognitive flexibility to navigate rapid technological changes. Mastering this balance enhances employability in evolving industries like artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and biotechnology.
Technical Skills Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com