Teaching modality refers to the method or approach used to deliver educational content, including in-person, online, and hybrid formats. Each modality offers distinct advantages tailored to different learning styles and accessibility needs, impacting student engagement and outcomes. Discover how selecting the right teaching modality can enhance your learning experience by exploring the detailed insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
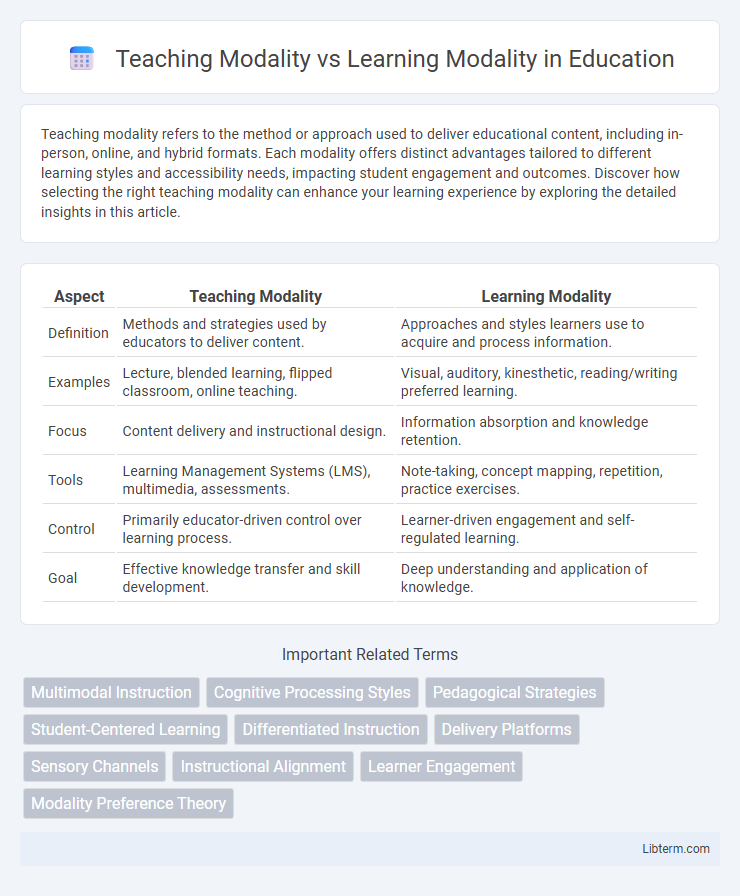
| Aspect | Teaching Modality | Learning Modality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Methods and strategies used by educators to deliver content. | Approaches and styles learners use to acquire and process information. |
| Examples | Lecture, blended learning, flipped classroom, online teaching. | Visual, auditory, kinesthetic, reading/writing preferred learning. |
| Focus | Content delivery and instructional design. | Information absorption and knowledge retention. |
| Tools | Learning Management Systems (LMS), multimedia, assessments. | Note-taking, concept mapping, repetition, practice exercises. |
| Control | Primarily educator-driven control over learning process. | Learner-driven engagement and self-regulated learning. |
| Goal | Effective knowledge transfer and skill development. | Deep understanding and application of knowledge. |
Understanding Teaching Modality: Definition and Types
Teaching modality refers to the structured method or approach an instructor uses to deliver educational content, encompassing types such as in-person, online, hybrid, synchronous, and asynchronous formats. Understanding these modalities is crucial for aligning instructional strategies with diverse learner needs and maximizing engagement. Each modality offers distinct advantages, facilitating adaptability and accessibility in varied educational environments.
What Is Learning Modality? Key Concepts Explained
Learning modality refers to the preferred sensory channel through which an individual absorbs, processes, and retains information, typically categorized into visual, auditory, and kinesthetic modalities. This concept emphasizes how learners interact with educational content, influencing engagement and comprehension levels. Understanding individual learning modalities enables educators to tailor instructional strategies, facilitating more effective knowledge acquisition and skill development.
Major Differences Between Teaching and Learning Modalities
Teaching modality refers to the methods and techniques instructors use to deliver content, such as lectures, online tutorials, or hands-on workshops, while learning modality emphasizes the preferred ways students absorb and process information, including visual, auditory, and kinesthetic styles. Major differences lie in the directionality and control: teaching modalities are instructor-driven strategies designed to present material effectively, whereas learning modalities focus on individual cognitive preferences influencing how information is received and retained. Understanding the divergence between teaching modalities and learning modalities allows for the optimization of instructional design to enhance student engagement and comprehension.
The Importance of Aligning Teaching and Learning Modalities
Aligning teaching modality with learning modality enhances knowledge retention and engagement by matching instructional methods to students' preferred cognitive styles, such as visual, auditory, or kinesthetic learning. Research demonstrates that congruence between teaching approaches and learner modalities significantly improves academic performance and motivation across diverse educational settings. Educators who assess and adapt to learners' modalities foster inclusive environments that optimize comprehension and skill acquisition.
Popular Teaching Modalities in Modern Education
Popular teaching modalities in modern education include face-to-face, online, blended, and flipped classroom approaches, each designed to enhance learner engagement and accommodate diverse learning preferences. Face-to-face teaching facilitates direct interaction and immediate feedback, while online modalities leverage digital platforms to provide flexible, self-paced learning opportunities. Blended and flipped classrooms combine in-person and virtual methods to optimize instructional effectiveness and cater to various learning modalities such as visual, auditory, and kinesthetic.
Common Learning Modalities and Their Characteristics
Common learning modalities include visual, auditory, kinesthetic, and reading/writing, each characterized by distinct sensory preferences influencing how information is absorbed and processed. Visual learners grasp concepts best through images and spatial understanding, auditory learners benefit from listening and verbal instruction, kinesthetic learners excel through hands-on activities and physical engagement, while reading/writing learners prefer interaction with text-based materials. Teaching modality must align with these learning modalities to enhance comprehension and retention, utilizing varied instructional methods such as multimedia presentations, discussions, experiments, and written exercises.
Impact of Mismatched Modalities on Student Outcomes
Mismatch between teaching modality, such as in-person, online, or hybrid, and students' preferred learning modality can significantly impair educational outcomes. Research shows students learn more effectively and retain information longer when the instructional delivery aligns with their cognitive styles--visual, auditory, or kinesthetic. Such mismatches often contribute to decreased engagement, lower academic performance, and increased dropout rates.
Strategies for Effective Modality Integration in the Classroom
Effective modality integration in the classroom hinges on aligning teaching modality with diverse learning modalities to enhance student engagement and comprehension. Utilizing a blend of visual, auditory, and kinesthetic teaching strategies ensures that multimodal learners receive content in formats best suited to their cognitive preferences. Incorporating technologies like interactive whiteboards, videos, and hands-on activities optimizes instructional delivery and adapts to varied learner modalities for improved academic outcomes.
Assessing and Adapting Teaching Approaches for Diverse Learners
Teaching modality refers to the methods and delivery formats educators use to present content, such as in-person, online, or blended learning environments. Learning modality involves the preferred ways students absorb and process information, including visual, auditory, and kinesthetic styles. Assessing these modalities through adaptive teaching strategies enables educators to tailor instruction to diverse learners, enhancing engagement and improving academic outcomes.
Future Trends in Teaching and Learning Modalities
Future trends in teaching and learning modalities emphasize hybrid and personalized approaches, integrating artificial intelligence and virtual reality to create immersive, adaptive educational experiences. Data-driven analytics enable real-time adjustments to teaching strategies and learning paths, improving engagement and retention rates. Emerging technologies support flexible, learner-centered environments that accommodate diverse needs and promote lifelong learning.
Teaching Modality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com