Vocational education provides specialized training focused on practical skills needed for specific trades or occupations, enhancing your employability in competitive job markets. It bridges the gap between traditional education and industry requirements, equipping you with hands-on experience and certifications that employers value. Discover how vocational education can transform your career prospects by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
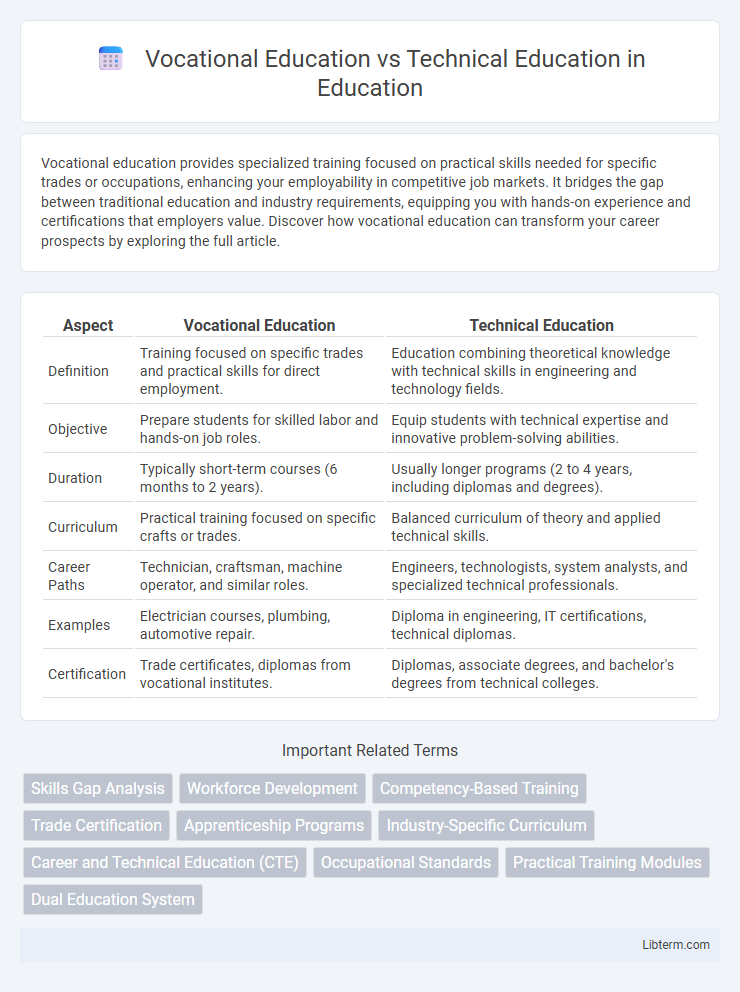
| Aspect | Vocational Education | Technical Education |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Training focused on specific trades and practical skills for direct employment. | Education combining theoretical knowledge with technical skills in engineering and technology fields. |
| Objective | Prepare students for skilled labor and hands-on job roles. | Equip students with technical expertise and innovative problem-solving abilities. |
| Duration | Typically short-term courses (6 months to 2 years). | Usually longer programs (2 to 4 years, including diplomas and degrees). |
| Curriculum | Practical training focused on specific crafts or trades. | Balanced curriculum of theory and applied technical skills. |
| Career Paths | Technician, craftsman, machine operator, and similar roles. | Engineers, technologists, system analysts, and specialized technical professionals. |
| Examples | Electrician courses, plumbing, automotive repair. | Diploma in engineering, IT certifications, technical diplomas. |
| Certification | Trade certificates, diplomas from vocational institutes. | Diplomas, associate degrees, and bachelor's degrees from technical colleges. |
Introduction to Vocational and Technical Education
Vocational education focuses on practical skills and training for specific trades, preparing students for immediate employment in industries such as healthcare, construction, and hospitality. Technical education emphasizes theoretical knowledge combined with applied sciences to develop expertise in areas like engineering, information technology, and advanced manufacturing. Both forms of education aim to enhance workforce readiness but differ in depth of theory and specialization areas.
Defining Vocational Education
Vocational education concentrates on imparting practical skills and hands-on training specific to various trades and occupations, preparing students for immediate employment in sectors such as carpentry, plumbing, and healthcare support. It emphasizes competency-based learning tailored to meet labor market demands, often culminating in certifications or diplomas recognized by industry bodies. Unlike broader technical education, vocational education prioritizes direct job readiness and skill acquisition over theoretical or engineering-focused knowledge.
Understanding Technical Education
Technical education emphasizes the development of specialized skills and practical knowledge in fields such as engineering, information technology, and healthcare, preparing students for specific careers with hands-on training. It integrates theoretical concepts with applied methodologies, enabling learners to operate advanced technologies and machinery effectively. This education path often involves certification programs, apprenticeships, and industry-aligned curricula designed to meet evolving workforce demands.
Key Differences Between Vocational and Technical Education
Vocational education focuses on practical skills and training for specific trades such as carpentry, plumbing, or automotive repair, preparing students for immediate employment in skilled labor markets. Technical education emphasizes theoretical knowledge and applied sciences, often covering areas like engineering technology, computer science, or electronics, which can lead to further academic pursuits or specialized technical roles. The key difference lies in vocational education's hands-on, job-specific approach versus technical education's combination of theory and practice designed for broader technical professions.
Curriculum and Skills Focus
Vocational education curriculum centers on practical skills tailored to specific trades such as carpentry, culinary arts, or cosmetology, emphasizing hands-on training to prepare students directly for the workforce. Technical education offers a more theoretical and analytical approach, focusing on applied sciences and engineering principles, equipping learners with problem-solving skills and technological proficiency. Both education types prioritize skill development but differ in their depth of theoretical knowledge and application scope.
Career Opportunities and Pathways
Vocational education focuses on practical skills for specific trades such as carpentry, plumbing, and culinary arts, leading directly to hands-on job opportunities and apprenticeships. Technical education emphasizes applied sciences and technology-based skills in areas like engineering, IT, and electronics, preparing students for roles in industries such as manufacturing, software development, and telecommunications. Both pathways offer strong career prospects, but vocational education typically leads to immediate trade work, while technical education provides a foundation for advanced technical roles and potential further academic study.
Duration and Learning Environments
Vocational education programs typically range from six months to two years, focusing on hands-on skills for specific trades in real-world work settings like workshops or industry sites. Technical education usually spans two to four years, combining theoretical knowledge with practical training in classrooms, laboratories, and specialized facilities. Both learning environments emphasize experiential learning but differ in program length and depth of technical theory.
Industry Demand and Job Market Trends
Vocational education equips students with practical skills tailored to specific trades, directly aligning with current industry demand for roles such as electricians, plumbers, and automotive technicians. Technical education emphasizes theoretical knowledge combined with applied sciences, preparing graduates for jobs in engineering, IT, and advanced manufacturing sectors where innovation drives market trends. Both pathways address evolving job market needs, with vocational programs rapidly filling skilled labor shortages and technical education supporting technology-driven economic growth.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Track
Vocational education offers practical skills training tailored for specific trades, enabling quick workforce entry but often limits advancement without further education. Technical education provides a strong foundation in engineering or technology principles, fostering innovation and adaptability, yet it may require longer study periods and higher costs. Both tracks enhance employability; vocational paths excel in hands-on proficiency, while technical routes build analytical expertise essential for evolving industries.
Choosing the Right Educational Path
Choosing the right educational path between vocational education and technical education depends on career goals and skill preferences. Vocational education emphasizes hands-on training for specific trades such as carpentry, culinary arts, or cosmetology, leading to immediate employment opportunities. Technical education provides a strong foundation in theoretical knowledge and applied sciences, preparing students for roles in engineering, information technology, or advanced manufacturing.
Vocational Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com