Integrating assistive technology enhances accessibility and empowers individuals with disabilities to engage more fully in various activities. This approach tailors tools like speech-to-text software and adaptive devices to meet unique needs, boosting independence and productivity. Discover how assistive technology integration can transform your environment by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
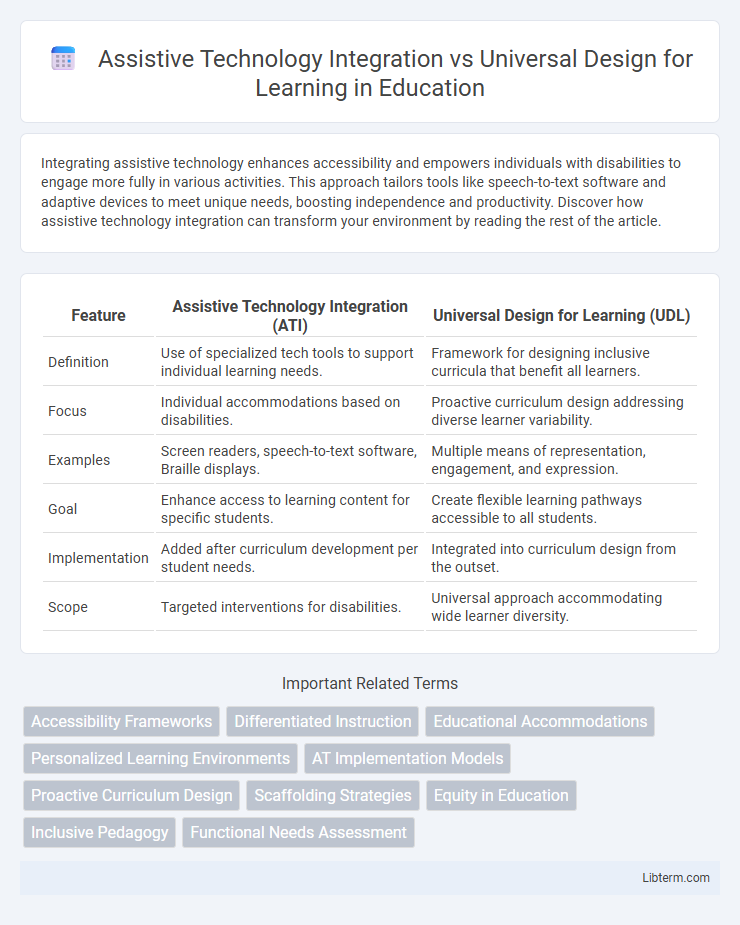
| Feature | Assistive Technology Integration (ATI) | Universal Design for Learning (UDL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of specialized tech tools to support individual learning needs. | Framework for designing inclusive curricula that benefit all learners. |
| Focus | Individual accommodations based on disabilities. | Proactive curriculum design addressing diverse learner variability. |
| Examples | Screen readers, speech-to-text software, Braille displays. | Multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression. |
| Goal | Enhance access to learning content for specific students. | Create flexible learning pathways accessible to all students. |
| Implementation | Added after curriculum development per student needs. | Integrated into curriculum design from the outset. |
| Scope | Targeted interventions for disabilities. | Universal approach accommodating wide learner diversity. |
Understanding Assistive Technology Integration
Assistive Technology Integration involves embedding specialized tools and devices to support students with disabilities in accessing curriculum and participating fully in learning activities. This approach emphasizes personalized accommodations tailored to individual needs, such as speech-to-text software or hearing aids. Effective integration requires collaboration between educators, technology specialists, and students to ensure seamless use that enhances educational outcomes.
Defining Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is an educational framework aimed at improving and optimizing teaching and learning for all people based on scientific insights into how humans learn. UDL emphasizes multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression to accommodate diverse learner needs, ensuring equitable access to education. By integrating flexible learning environments and materials, UDL supports inclusivity and reduces barriers without the need for retrofitting assistive technologies.
Key Principles of Assistive Technology
Assistive Technology integration emphasizes customization and adaptation of tools to support individual learning needs, enabling personalized access to educational content and participation. Key principles include enhancing independence, promoting accessibility, and supporting diverse learning styles through tailored devices or software. This approach contrasts with Universal Design for Learning, which incorporates flexible learning environments and materials designed for all students from the outset.
Core Concepts of Universal Design for Learning
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) centers on creating flexible learning environments that accommodate diverse learner needs by providing multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression. Unlike Assistive Technology Integration, which offers specific tools to support individual learners with disabilities, UDL proactively designs curricula to be accessible and effective for all students from the outset. Key UDL principles emphasize removing barriers through customizable content, varied instructional methods, and inclusive assessments that promote equitable educational opportunities.
Comparing AT Integration and UDL Approaches
Assistive Technology Integration targets specific student needs by providing customized tools to overcome learning barriers, while Universal Design for Learning (UDL) establishes flexible curricula that accommodate diverse learners from the outset. AT focuses on individualized adaptations such as speech-to-text software or alternative keyboards, whereas UDL emphasizes multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression to benefit all students. Both approaches aim to enhance educational accessibility but differ in scope: AT is reactive and tailored, whereas UDL is proactive and systemic.
Benefits of Assistive Technology in Education
Assistive technology enhances educational outcomes by providing personalized tools that accommodate diverse learning needs, such as speech-to-text software and adaptive keyboards. These technologies increase accessibility and independence for students with disabilities, fostering greater engagement and academic success. Integration of assistive technology supports inclusive classrooms by bridging gaps in communication, mobility, and information access.
Advantages of Universal Design for Learning
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) offers inclusive educational frameworks that proactively address diverse learning needs by providing multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression. Unlike Assistive Technology Integration, which often targets specific disabilities individually, UDL promotes accessibility for all students, reducing the need for separate adaptations. This approach enhances overall learning flexibility, improves student engagement, and fosters equitable educational opportunities across varied learning environments.
Overcoming Barriers in Implementation
Assistive Technology Integration targets specific disabilities by customizing tools to support individual learners, effectively overcoming barriers related to physical, sensory, or cognitive challenges. Universal Design for Learning (UDL) employs flexible teaching methods and materials that address diverse learning styles and needs proactively, minimizing barriers before they arise. Combining both approaches enhances inclusivity by providing tailored support while promoting accessible curriculum design, facilitating seamless implementation in educational environments.
Best Practices for Blending AT and UDL
Blending Assistive Technology (AT) and Universal Design for Learning (UDL) requires implementing flexible, inclusive tools that support diverse learning needs while promoting independence. Best practices include selecting AT that complements UDL's multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression, ensuring technology enhances accessibility without creating dependence. Collaboration among educators, specialists, and students is essential to tailor solutions, continuously assess effectiveness, and foster an adaptable learning environment that maximizes participation and achievement for all learners.
Future Directions in Inclusive Education
Emerging trends in inclusive education emphasize the synergy between Assistive Technology Integration and Universal Design for Learning (UDL) to create adaptive learning environments that meet diverse student needs. Future directions include leveraging AI-driven tools and customizable digital platforms to enhance accessibility while promoting autonomy and engagement for all learners. Research increasingly supports the integration of real-time data analytics within UDL frameworks to personalize educational experiences and optimize assistive technology interventions.
Assistive Technology Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com