Simulated practice enhances skill development by providing a risk-free environment where you can refine techniques and decision-making abilities. This method replicates real-world scenarios, promoting experiential learning that boosts confidence and competence. Explore the rest of the article to discover how simulated practice can transform your training approach.
Table of Comparison
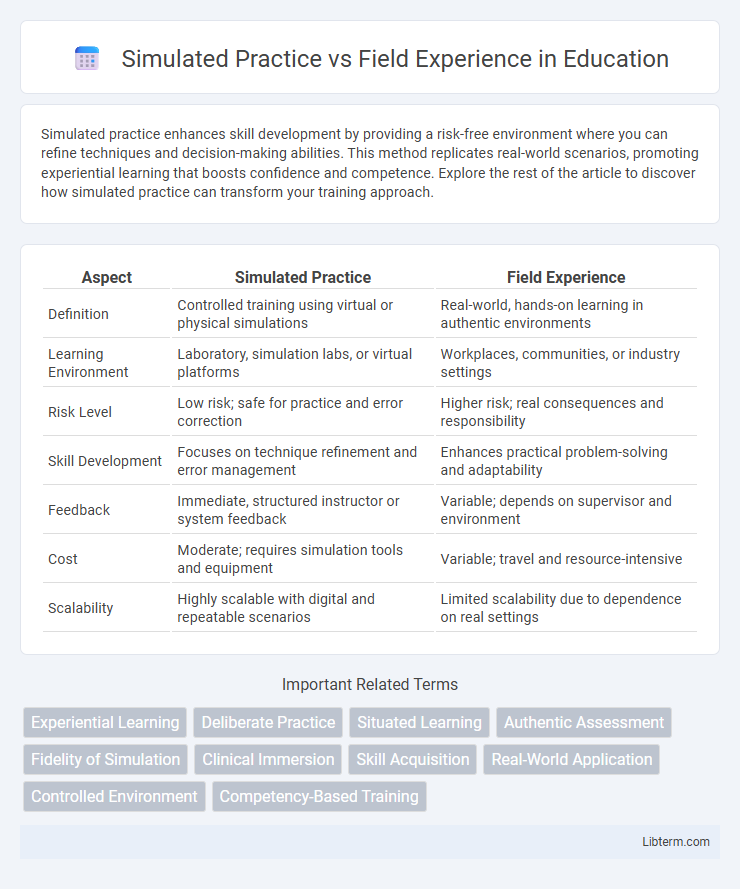
| Aspect | Simulated Practice | Field Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controlled training using virtual or physical simulations | Real-world, hands-on learning in authentic environments |
| Learning Environment | Laboratory, simulation labs, or virtual platforms | Workplaces, communities, or industry settings |
| Risk Level | Low risk; safe for practice and error correction | Higher risk; real consequences and responsibility |
| Skill Development | Focuses on technique refinement and error management | Enhances practical problem-solving and adaptability |
| Feedback | Immediate, structured instructor or system feedback | Variable; depends on supervisor and environment |
| Cost | Moderate; requires simulation tools and equipment | Variable; travel and resource-intensive |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with digital and repeatable scenarios | Limited scalability due to dependence on real settings |
Introduction to Simulated Practice and Field Experience
Simulated practice uses controlled, virtual environments to develop clinical skills, offering risk-free scenarios for learners to practice decision-making and procedural tasks. Field experience immerses students in real-world settings, engaging directly with patients and healthcare professionals to gain hands-on expertise and contextual understanding. Combining both methods enhances competency by balancing theoretical knowledge with practical application.
Defining Simulated Practice
Simulated practice involves the use of virtual environments, mannequins, or role-playing scenarios to replicate real-world situations for skill development and decision-making without actual risk. This method enhances learning by allowing repeated practice, immediate feedback, and controlled conditions tailored to specific competencies. Simulated practice is essential in fields such as healthcare, aviation, and emergency response, where hands-on experience is critical but real-world exposure may be limited or hazardous.
Understanding Field Experience
Field experience offers hands-on immersion in real-world environments, enabling professionals to develop practical skills, adapt to unpredictable situations, and build industry-specific problem-solving abilities. Unlike simulated practice, which provides controlled, risk-free learning scenarios, field experience exposes individuals to authentic challenges and workflows essential for comprehensive professional growth. This direct engagement enhances critical thinking, decision-making, and interpersonal communication within actual work contexts, fostering deeper understanding and lasting competence.
Key Differences Between Simulated Practice and Field Experience
Simulated practice provides controlled, risk-free environments for skill development using virtual scenarios or mannequins, while field experience offers real-world exposure with unpredictable variables and live interactions. Simulations allow repetitive training and immediate feedback, enhancing procedural proficiency, whereas field experience builds adaptive decision-making and interpersonal skills through genuine patient care or work situations. The direct applicability and emotional complexity of field experience contrast with the standardized, measurable nature of simulated practice.
Advantages of Simulated Practice
Simulated practice offers a controlled environment for skill development, allowing learners to repeatedly perform tasks without real-world risks or consequences. This method enhances confidence and proficiency by providing instant feedback and enabling correction of errors in real time. Access to diverse, complex scenarios in simulation promotes critical thinking and adaptability, which may be limited during unpredictable field experience.
Benefits of Field Experience
Field experience provides hands-on learning that enhances practical skills and real-time decision-making, which cannot be fully replicated in simulated practice. Direct interaction with actual work environments fosters a deeper understanding of workplace dynamics, problem-solving under pressure, and effective communication with diverse teams. This immersive exposure significantly improves adaptability and confidence, preparing individuals for real-world challenges.
Challenges of Each Method
Simulated practice often faces challenges related to limited realism and failure to fully replicate unpredictable field variables, which can hinder the development of practical decision-making skills. Field experience presents difficulties such as exposure to uncontrolled environmental risks, inconsistent learning opportunities, and potential ethical concerns involving real-world consequences. Both methods require balancing controlled learning environments with authentic experience to optimize skill acquisition and professional competence.
Integrating Simulation and Fieldwork in Training
Integrating simulation and fieldwork in training enhances skill retention by combining controlled, repeatable scenarios with real-world unpredictability, offering learners both practical exposure and critical decision-making opportunities. Simulation-based training provides a risk-free environment to practice complex procedures, while field experience solidifies these skills through direct application in actual contexts. This balanced approach optimizes learning outcomes, ensuring competence and confidence in handling diverse professional challenges.
Impact on Skill Development and Competency
Simulated practice enhances skill development by providing a controlled environment for repetitive task mastery and immediate feedback, accelerating competency acquisition without real-world risks. Field experience exposes individuals to unpredictable scenarios, fostering adaptive problem-solving and decision-making skills essential for practical competence. Combining both methods optimizes skill refinement and ensures comprehensive competency by balancing theoretical learning with real-world application.
Choosing the Right Approach for Optimal Learning
Selecting between simulated practice and field experience hinges on the learning objectives and context specificity; simulated practice offers a controlled environment to refine technical skills and decision-making without real-world risks, while field experience provides authentic exposure to dynamic situations, enhancing adaptability and situational awareness. Blending both approaches often yields optimal learning outcomes by combining theoretical knowledge with practical application, ensuring skill retention and confidence in real-world scenarios. Educators and trainers must assess learner readiness, resource availability, and risk factors to tailor a balanced training program that maximizes competency development.
Simulated Practice Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com