Humanities explore the diverse aspects of human culture, including history, literature, philosophy, and the arts, providing insight into societal values and human experiences. This field encourages critical thinking and fosters empathy by examining how people across time and cultures understand the world. Discover how studying humanities can enrich Your perspective and enhance your understanding of humanity by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
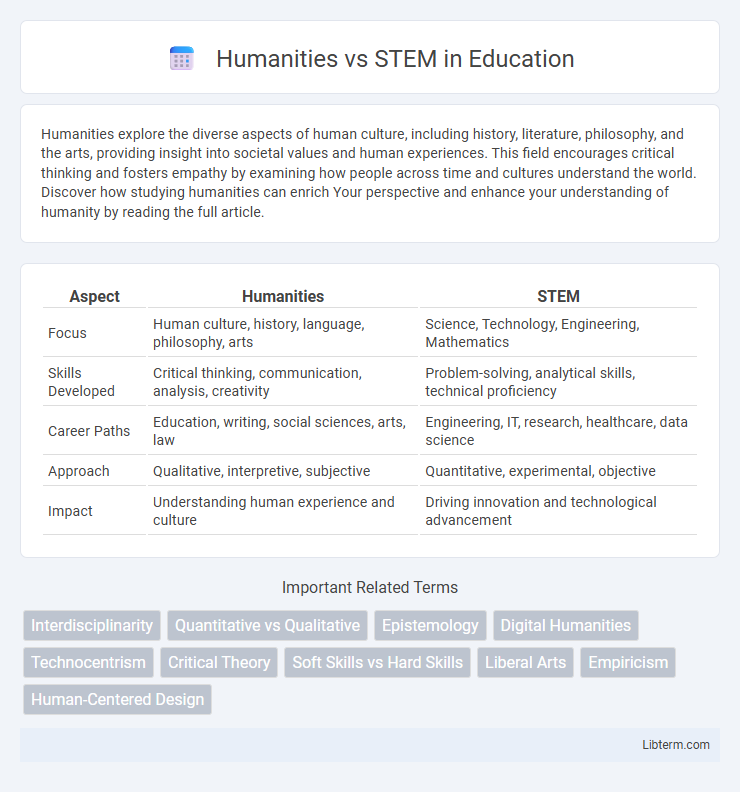
| Aspect | Humanities | STEM |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Human culture, history, language, philosophy, arts | Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, communication, analysis, creativity | Problem-solving, analytical skills, technical proficiency |
| Career Paths | Education, writing, social sciences, arts, law | Engineering, IT, research, healthcare, data science |
| Approach | Qualitative, interpretive, subjective | Quantitative, experimental, objective |
| Impact | Understanding human experience and culture | Driving innovation and technological advancement |
Understanding Humanities and STEM: Key Definitions
Humanities encompass the study of human culture, history, language, and philosophy, aiming to understand human experiences and societal values. STEM refers to Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics, focusing on empirical analysis, innovation, and problem-solving through technical and scientific methods. Understanding humanities and STEM requires recognizing their complementary roles: humanities provide critical thinking and ethical perspectives, while STEM drives technological advancements and quantitative research.
Historical Evolution of Humanities and STEM Fields
The historical evolution of humanities traces back to ancient civilizations where philosophy, literature, and arts shaped cultural foundations, influencing societal values and intellectual inquiry. STEM fields emerged more prominently during the Scientific Revolution, driven by empirical methods and technological advancements that transformed industries and education systems. Over time, humanities and STEM have developed distinct methodologies but increasingly intersect in interdisciplinary research, enhancing innovation and comprehensive understanding of human and technological progress.
Core Differences Between Humanities and STEM Disciplines
Humanities disciplines emphasize critical thinking, cultural analysis, and the exploration of human values through qualitative research methods, focusing on subjects like literature, philosophy, and history. STEM fields prioritize quantitative analysis, empirical experimentation, and technological innovation, covering areas such as mathematics, engineering, and biological sciences. The core difference lies in their methodologies; humanities rely on interpretive reasoning and subjective understanding, whereas STEM depends on objective data and reproducible results.
Interdisciplinary Connections: Bridging Humanities and STEM
Interdisciplinary connections between Humanities and STEM foster innovative solutions by integrating critical thinking, ethical considerations, and cultural perspectives with technical expertise. Collaborative projects in areas like digital humanities, artificial intelligence ethics, and bioengineering highlight how combining literature, philosophy, and social sciences with mathematics, computer science, and engineering enhances problem-solving and creativity. This fusion cultivates well-rounded professionals capable of addressing complex global challenges with both analytical rigor and empathy.
Skills Developed: Analytical vs. Technical Approaches
Humanities develop critical thinking, interpretive analysis, and effective communication skills through the study of culture, history, and philosophy, emphasizing qualitative reasoning and ethical considerations. STEM disciplines cultivate technical expertise, quantitative analysis, and problem-solving abilities by applying mathematical principles, scientific methods, and engineering techniques to real-world challenges. Both fields foster creativity and innovation but differ in their approach, with humanities focusing on contextual understanding and STEM prioritizing empirical data and systematic experimentation.
Societal Impact: Humanities vs. STEM Contributions
Humanities enrich society by fostering critical thinking, cultural awareness, and ethical reasoning, shaping values and social norms through literature, philosophy, and history. STEM fields drive technological advancements and innovation, directly improving healthcare, infrastructure, and environmental sustainability. The synergy between Humanities and STEM enhances comprehensive societal progress by combining human-centered insights with scientific and technical solutions.
Career Pathways in Humanities and STEM
Career pathways in STEM fields include software engineering, data science, biotechnology, and environmental engineering, where technical skills and analytical problem-solving are essential. Humanities careers encompass roles such as journalism, education, public relations, and cultural management, emphasizing critical thinking, communication, and ethical reasoning. Both pathways offer diverse opportunities, with STEM focusing on innovation and technology, while humanities prioritize human experience and societal impact.
The Value Debate: Humanities or STEM Education?
The value debate between humanities and STEM education centers on their distinct contributions to society and individual growth. Humanities foster critical thinking, ethical reasoning, and cultural awareness, essential for addressing complex social issues and enhancing communication skills. STEM disciplines drive innovation, economic development, and technical problem-solving, equipping students with competencies crucial for the modern technological landscape.
Future Trends: The Convergence of Humanities and STEM
The future of education and innovation lies in the convergence of Humanities and STEM, fostering interdisciplinary skills essential for solving complex global challenges. Integrating ethical reasoning, cultural awareness, and critical thinking from the Humanities with technological expertise in STEM fields drives advancements in artificial intelligence, sustainable development, and digital humanities. This fusion enhances creativity and human-centered solutions, preparing a workforce adept in both data-driven science and empathetic human insights.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right path between Humanities and STEM depends on individual interests, career goals, and skill sets. Humanities courses often emphasize critical thinking, cultural understanding, and communication skills, while STEM fields focus on analytical problem-solving, technical expertise, and innovation. Evaluating personal strengths and the future job market demand for sectors such as technology, engineering, arts, and social sciences helps guide an informed decision.
Humanities Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com