Formative data captures real-time insights into learning progress, enabling educators to tailor instruction to student needs effectively. This ongoing assessment method helps identify strengths and areas for improvement before final evaluations. Discover how formative data can transform your educational approach by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
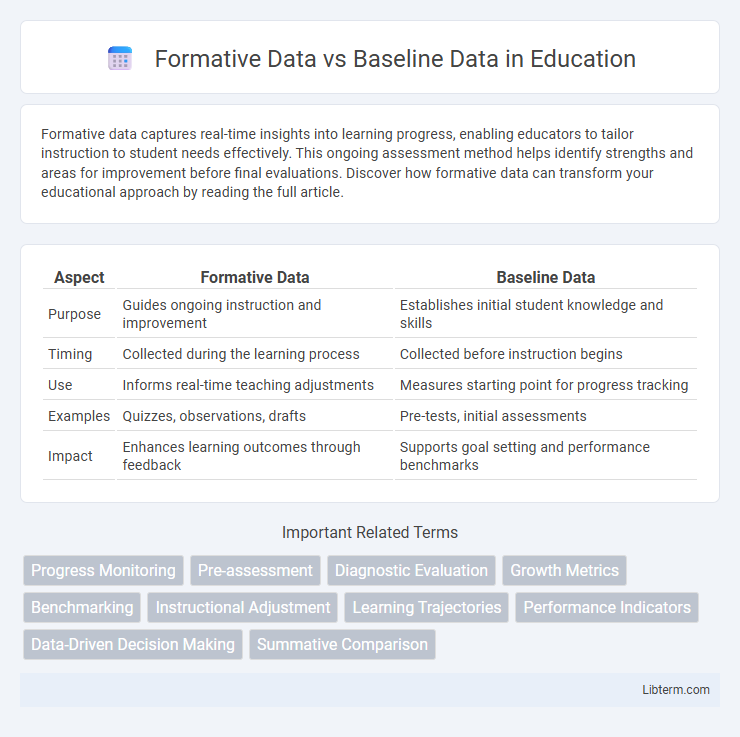
| Aspect | Formative Data | Baseline Data |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Guides ongoing instruction and improvement | Establishes initial student knowledge and skills |
| Timing | Collected during the learning process | Collected before instruction begins |
| Use | Informs real-time teaching adjustments | Measures starting point for progress tracking |
| Examples | Quizzes, observations, drafts | Pre-tests, initial assessments |
| Impact | Enhances learning outcomes through feedback | Supports goal setting and performance benchmarks |
Understanding Formative Data: Key Concepts
Formative data refers to information collected during a process to monitor progress and guide improvements, often used in educational and developmental contexts. It provides real-time feedback that helps identify strengths and areas needing adjustment before final evaluations. Understanding formative data involves recognizing its purpose in enhancing ongoing performance rather than measuring absolute outcomes, distinguishing it from baseline data, which captures initial conditions prior to intervention.
Defining Baseline Data in Research
Baseline data in research refers to the initial set of information collected before any intervention or treatment is applied, establishing a reference point for measuring changes over time. This data is critical for comparative analysis, helping researchers determine the effectiveness of an experimental variable by contrasting subsequent results against these initial metrics. Accurate baseline data ensures validity and reliability in the study's outcomes by controlling for pre-existing conditions and participant characteristics.
Differences Between Formative and Baseline Data
Formative data, collected during an intervention or learning process, provides ongoing insights to adjust strategies and improve outcomes, while baseline data is gathered before any intervention begins to establish a reference point. Baseline data serves as the initial measurement of skills, knowledge, or behaviors, enabling comparison over time, whereas formative data captures progress and trends throughout the implementation phase. The key difference lies in their timing and purpose: baseline data benchmarks starting conditions, and formative data informs real-time decision-making and instructional refinement.
Importance of Formative Data in Program Planning
Formative data plays a crucial role in program planning by providing real-time insights into participant needs, behaviors, and environmental factors, allowing for tailored interventions and adaptive strategies. Unlike baseline data, which offers a static snapshot before program implementation, formative data continuously informs adjustments to enhance program effectiveness and stakeholder engagement. Leveraging formative data improves decision-making, supports iterative improvements, and ensures that program objectives align closely with evolving community dynamics and feedback.
Role of Baseline Data in Outcome Evaluation
Baseline data establishes the initial conditions or benchmark measurements before an intervention begins, serving as a critical reference point for outcome evaluation. It enables evaluators to measure changes and assess the effectiveness of programs by comparing pre- and post-intervention results. Accurate baseline data collection ensures that any observed outcomes can be attributed to the intervention rather than external factors or natural variations.
Methods for Collecting Formative Data
Formative data is gathered through methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, and focus groups designed to provide real-time feedback during a project's development, allowing for iterative improvements. Techniques like usability testing and pilot studies are essential for collecting detailed insights that inform adjustments before final implementation. In contrast, baseline data is typically collected once at the start to establish reference points for later comparison, emphasizing initial conditions rather than ongoing refinement.
Techniques for Gathering Baseline Data
Techniques for gathering baseline data include surveys, observational studies, and standardized assessments, which provide initial measurements of variables before interventions. Data collection methods often involve structured interviews, questionnaires, and computerized tracking to ensure accurate and reliable baseline information. Employing mixed methods enhances the depth and validity of baseline data, enabling precise comparisons with formative data during progress evaluation.
When to Use Formative Data vs Baseline Data
Formative data is used during the development or implementation phase to monitor progress and make real-time adjustments, enhancing the effectiveness of interventions or programs. Baseline data is collected before the start of an intervention to establish a point of reference for measuring future changes and outcomes. Use formative data when ongoing feedback is needed for improvement, while baseline data is crucial for comparing pre- and post-intervention performance.
Common Challenges in Data Collection
Formative data and baseline data often face common challenges in data collection such as inconsistent data quality, limited respondent engagement, and logistical constraints in accessing target populations. Ensuring accurate, timely, and representative data requires standardized measurement tools and rigorous training of data collectors to minimize bias and errors. Data collection environments often introduce variability, necessitating adaptive strategies to maintain reliability and validity across diverse contexts.
Best Practices for Integrating Both Data Types
Integrating formative data and baseline data enhances program evaluation by combining real-time feedback with initial condition assessments, enabling continuous improvement and informed decision-making. Best practices include establishing clear data collection protocols, aligning measurement criteria across both data types, and utilizing integrated data dashboards for comprehensive analysis. Leveraging these methods ensures accurate tracking of progress while maintaining contextual understanding of starting points.
Formative Data Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com