Standardization ensures consistent quality and interoperability across products and services, fostering efficiency and reducing costs. It helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and enhances consumer trust by maintaining uniform standards. Explore the rest of the article to understand how standardization can benefit your business and streamline processes.
Table of Comparison
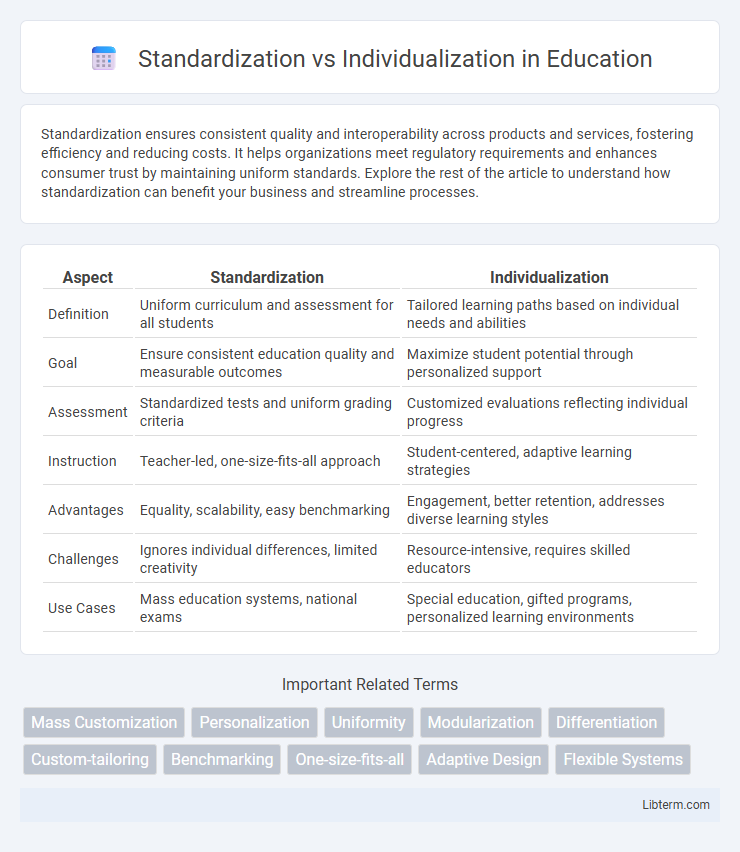
| Aspect | Standardization | Individualization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uniform curriculum and assessment for all students | Tailored learning paths based on individual needs and abilities |
| Goal | Ensure consistent education quality and measurable outcomes | Maximize student potential through personalized support |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and uniform grading criteria | Customized evaluations reflecting individual progress |
| Instruction | Teacher-led, one-size-fits-all approach | Student-centered, adaptive learning strategies |
| Advantages | Equality, scalability, easy benchmarking | Engagement, better retention, addresses diverse learning styles |
| Challenges | Ignores individual differences, limited creativity | Resource-intensive, requires skilled educators |
| Use Cases | Mass education systems, national exams | Special education, gifted programs, personalized learning environments |
Understanding Standardization: Definition and Purpose
Standardization refers to the process of developing and implementing consistent procedures, guidelines, or specifications to ensure uniformity and efficiency across products, services, or processes. It aims to reduce variability, improve quality control, and facilitate interoperability within industries or organizations. By establishing clear benchmarks, standardization enhances reliability, simplifies training, and supports scalability in production and service delivery.
The Concept of Individualization Explained
Individualization emphasizes tailoring products, services, and experiences to meet the unique preferences, needs, and behaviors of each customer, leveraging data analytics and AI technologies for precise customization. Unlike standardization, which offers uniform solutions to achieve economies of scale, individualization drives higher customer satisfaction and loyalty through personalized engagement. This concept is central to modern marketing strategies and product development aiming to enhance user experience and competitive advantage.
Key Differences Between Standardization and Individualization
Standardization involves creating uniform processes and products to ensure consistency, efficiency, and scalability across operations, often resulting in reduced costs and simplified management. Individualization emphasizes tailoring products, services, or experiences to meet unique customer preferences and needs, enhancing personalization and customer satisfaction. Key differences lie in their approach: standardization prioritizes uniformity and mass production, while individualization focuses on customization and flexibility.
Pros and Cons of Standardization
Standardization offers the advantage of consistent quality and simplified processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs across industries such as manufacturing and software development. However, it may lead to reduced flexibility and inhibit innovation by limiting customization options tailored to specific customer needs. Over-reliance on standardization can result in products or services that fail to meet diverse market demands, impacting customer satisfaction and competitiveness.
Advantages and Challenges of Individualization
Individualization enhances customer satisfaction by tailoring products and services to specific needs, improving engagement and brand loyalty. It allows businesses to respond swiftly to diverse market demands, fostering innovation and differentiation. However, individualization poses challenges such as increased production complexity, higher costs, and the need for advanced data analytics to effectively manage personalized experiences.
Standardization in Education and Its Impact
Standardization in education establishes uniform curricula, assessments, and teaching methods to ensure consistent learning outcomes across diverse student populations. This approach facilitates large-scale data analysis and benchmarking, promoting accountability and comparability among schools and districts. However, emphasizing standardized protocols may limit teachers' flexibility to tailor instruction to individual student needs, potentially hindering personalized learning and creativity.
Individualization in Healthcare: Benefits and Limitations
Individualization in healthcare enhances patient outcomes by tailoring treatments to genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, increasing the precision of medical interventions. This personalized approach improves medication efficacy, reduces adverse reactions, and supports preventive care strategies, fostering better long-term health management. However, individualization faces limitations such as higher costs, complexity in data integration, and potential disparities in access to advanced personalized therapies.
Balancing Standardization and Individualization for Optimal Results
Balancing standardization and individualization involves integrating consistent processes with tailored approaches to meet specific needs effectively. Organizations achieve optimal results by standardizing core functions to ensure quality and efficiency while individualizing strategies to address unique client preferences or market conditions. Data-driven insights and adaptive frameworks support this balance, enhancing performance and customer satisfaction simultaneously.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Both Approaches
Case studies reveal that standardization enhances operational efficiency and consistency, exemplified by McDonald's uniform service protocols across global locations. In contrast, individualization drives personalized customer experiences as seen in Amazon's tailored product recommendations and adaptive marketing strategies. Combining both approaches, companies like IKEA implement standardized production with individualized customer choices, balancing cost-effectiveness and customization.
Future Trends: Integrating Standardization and Individualization
Future trends emphasize the integration of standardization and individualization through adaptive technologies like AI-driven customization and modular product designs. Smart manufacturing leverages real-time data to balance consistent quality with personalized variations, enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. The convergence of IoT and machine learning enables scalable personalization within standardized production frameworks, optimizing both cost and user experience.
Standardization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com