Direct instruction is a structured teaching method characterized by clear, explicit teaching of a specific skill or concept through step-by-step demonstrations and guided practice. This approach ensures that learners receive precise explanations and immediate feedback, fostering better understanding and mastery. Explore the rest of the article to discover how direct instruction can enhance your learning outcomes effectively.
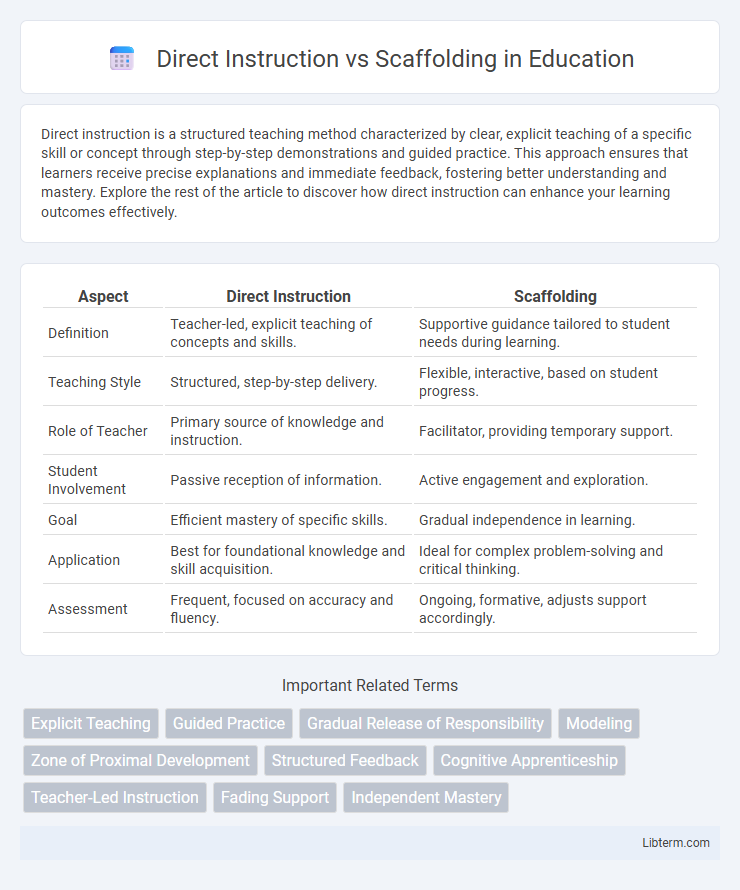
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Direct Instruction | Scaffolding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teacher-led, explicit teaching of concepts and skills. | Supportive guidance tailored to student needs during learning. |
| Teaching Style | Structured, step-by-step delivery. | Flexible, interactive, based on student progress. |
| Role of Teacher | Primary source of knowledge and instruction. | Facilitator, providing temporary support. |
| Student Involvement | Passive reception of information. | Active engagement and exploration. |
| Goal | Efficient mastery of specific skills. | Gradual independence in learning. |
| Application | Best for foundational knowledge and skill acquisition. | Ideal for complex problem-solving and critical thinking. |
| Assessment | Frequent, focused on accuracy and fluency. | Ongoing, formative, adjusts support accordingly. |
Understanding Direct Instruction
Direct Instruction emphasizes explicit teaching with clear, structured lessons and specific learning objectives to ensure mastery of skills. It relies on teacher-led demonstrations, guided practice, and immediate feedback to facilitate efficient knowledge acquisition. This method is particularly effective for foundational skills and content that require precise understanding and step-by-step instruction.
Defining Scaffolding in Education
Scaffolding in education refers to a teaching method where instructors provide temporary support to students, enabling them to achieve higher levels of understanding and skill acquisition than they would independently. This approach gradually removes assistance as learners develop increased competence, fostering autonomy and confidence. Unlike direct instruction, which involves explicit teaching, scaffolding emphasizes guided discovery and incremental learning tailored to individual student needs.
Core Principles of Direct Instruction
Direct Instruction emphasizes explicit teaching through carefully structured lessons, clear learning objectives, and continuous assessment to ensure student mastery. It relies on scripted, systematic presentation of content with frequent practice and immediate feedback to promote retention and skill acquisition. This method contrasts with scaffolding by providing direct, unambiguous guidance rather than gradually removing support based on learner independence.
Key Features of Scaffolding
Scaffolding is a teaching strategy that provides temporary support tailored to students' current skill levels, promoting gradual independence through guided learning. Key features include modeling, questioning, and providing feedback to bridge the gap between existing knowledge and new concepts. This approach emphasizes active learner engagement and adapts support based on continuous assessment of student progress.
Benefits of Direct Instruction
Direct Instruction offers clear, structured teaching that accelerates student learning by providing explicit guidance and immediate feedback. It enhances knowledge retention by breaking complex concepts into manageable steps, ensuring mastery before progressing. This method is particularly effective for learners needing strong foundational skills and consistent reinforcement.
Advantages of Scaffolding Strategies
Scaffolding strategies enhance learning by providing tailored support that adapts to a student's current skill level, fostering deeper understanding and independent problem-solving. This approach encourages active engagement and gradually transfers responsibility to the learner, promoting long-term retention and confidence. Research indicates that scaffolding improves critical thinking skills and accommodates diverse learning styles more effectively than direct instruction alone.
Comparing Effectiveness: Direct Instruction vs Scaffolding
Direct Instruction offers structured, teacher-led lessons that ensure clear, immediate understanding of concepts, making it highly effective for foundational knowledge acquisition. Scaffolding provides personalized support through gradual release of responsibility, fostering deeper comprehension and critical thinking skills over time. Research shows a combination of Direct Instruction and Scaffolding yields optimal learning outcomes by balancing clarity with cognitive engagement.
When to Use Direct Instruction
Direct Instruction is most effective when teaching foundational skills that require clear, explicit guidance, such as phonics in early reading or basic math operations. It is ideal for learners who need structured support to master specific content quickly and accurately. Use Direct Instruction when tasks are new, complex, or when learners have limited prior knowledge and need step-by-step demonstrations to ensure comprehension.
When to Apply Scaffolding Techniques
Scaffolding techniques are most effective when learners face new or complex tasks that require support to build understanding and skills incrementally. These methods are applied in situations where students benefit from guided practice, gradually transferring responsibility as competence increases. Using scaffolding during collaborative learning or problem-solving activities enhances retention and fosters independent learning.
Combining Direct Instruction and Scaffolding for Optimal Learning
Combining Direct Instruction with Scaffolding enhances student learning by providing clear, structured guidance alongside tailored support that gradually fosters independence. Research in educational psychology demonstrates that this hybrid approach accelerates skill acquisition and deepens conceptual understanding by balancing explicit teaching with adaptive assistance. Effective integration of both methods leverages the strengths of modeled instruction and responsive feedback, optimizing cognitive engagement and long-term retention.
Direct Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com