Performance-based budgeting aligns your financial resources with measurable outcomes to maximize efficiency and impact. This approach prioritizes funding based on program effectiveness, ensuring that every dollar spent drives tangible results. Explore the rest of the article to understand how performance-based budgeting can transform your organization's financial strategy.
Table of Comparison
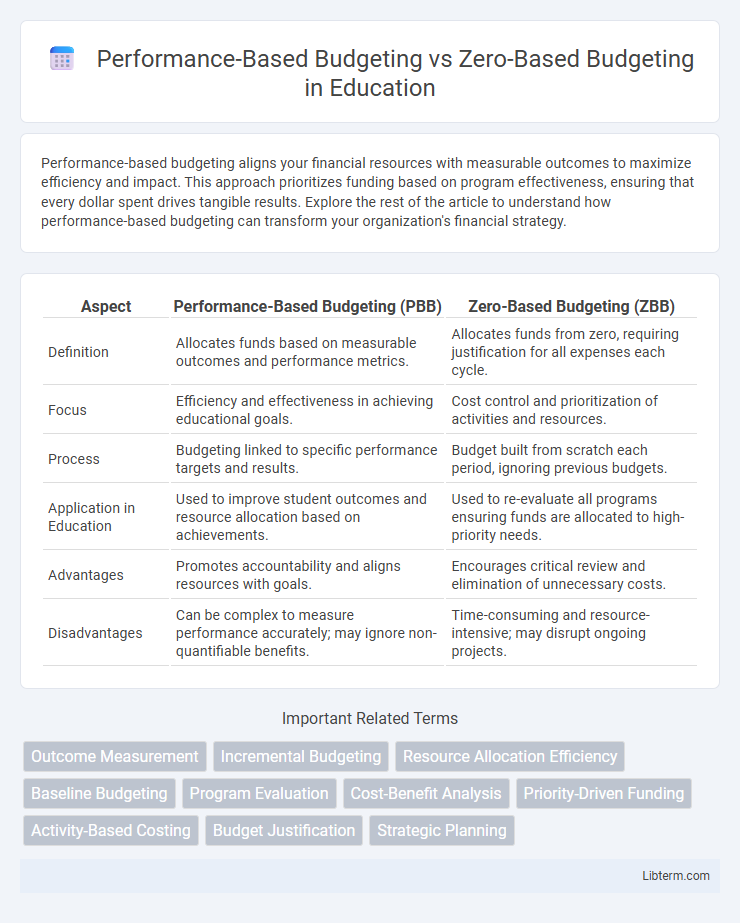
| Aspect | Performance-Based Budgeting (PBB) | Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allocates funds based on measurable outcomes and performance metrics. | Allocates funds from zero, requiring justification for all expenses each cycle. |
| Focus | Efficiency and effectiveness in achieving educational goals. | Cost control and prioritization of activities and resources. |
| Process | Budgeting linked to specific performance targets and results. | Budget built from scratch each period, ignoring previous budgets. |
| Application in Education | Used to improve student outcomes and resource allocation based on achievements. | Used to re-evaluate all programs ensuring funds are allocated to high-priority needs. |
| Advantages | Promotes accountability and aligns resources with goals. | Encourages critical review and elimination of unnecessary costs. |
| Disadvantages | Can be complex to measure performance accurately; may ignore non-quantifiable benefits. | Time-consuming and resource-intensive; may disrupt ongoing projects. |
Introduction to Budgeting Methodologies
Performance-Based Budgeting (PBB) allocates resources based on measurable outcomes and performance metrics to enhance efficiency and accountability in public and private sector budgeting. Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) requires justifying all expenses from a zero base for each new budget cycle, promoting cost reduction and prioritization of activities. Both methodologies aim to optimize budget allocation but differ in focus; PBB emphasizes results while ZBB emphasizes starting anew without historical spending biases.
What is Performance-Based Budgeting?
Performance-Based Budgeting (PBB) is a budgeting approach that allocates funds based on the achievement of specific performance outcomes and measurable results. It links financial resources directly to programs and activities that demonstrate effectiveness in meeting strategic goals, enhancing accountability and resource optimization. PBB uses performance indicators and targets to prioritize funding, ensuring that expenditures contribute to improved organizational performance and public value.
What is Zero-Based Budgeting?
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) is a budgeting method where every expense must be justified from scratch for each new period, starting from a "zero base." Unlike traditional budgeting methods that adjust previous budgets incrementally, ZBB requires detailed analysis and approval of all budget items, ensuring resources are allocated based on current needs and priorities. This approach enhances cost efficiency and aligns spending closely with organizational goals, making it a powerful tool for performance optimization and financial discipline.
Key Principles of Performance-Based Budgeting
Performance-Based Budgeting centers on allocating funds based on the achievement of specific, measurable outcomes, linking resource distribution directly to performance results. This method prioritizes efficiency and accountability by setting clear goals, performance indicators, and regularly evaluating program effectiveness to inform budget decisions. It contrasts with Zero-Based Budgeting by emphasizing ongoing performance metrics rather than justifying every expense from scratch annually.
Core Elements of Zero-Based Budgeting
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) requires each expense to be justified from scratch, emphasizing detailed cost-benefit analysis and priority ranking to allocate resources efficiently. Core elements include decision packages, which are evaluated for necessity and alignment with organizational goals, and a systematic review process that challenges existing budget assumptions. This contrasts with Performance-Based Budgeting, which focuses on funding programs based on measurable outcomes and performance metrics rather than reevaluating all expenses annually.
Comparative Analysis: Performance-Based vs Zero-Based Budgeting
Performance-Based Budgeting allocates resources based on program outcomes and effectiveness, emphasizing accountability and performance metrics to optimize public spending. Zero-Based Budgeting requires building each budget cycle from a "zero base," justifying every expense without reference to previous budgets, fostering cost-efficiency and resource reallocation. Comparing both, Performance-Based Budgeting excels in aligning expenditures with strategic goals, while Zero-Based Budgeting promotes rigorous cost control and eliminates unnecessary expenses through detailed scrutiny.
Advantages of Performance-Based Budgeting
Performance-Based Budgeting (PBB) enhances resource allocation efficiency by linking funding directly to measurable program outcomes, promoting accountability and transparency in public sector management. PBB facilitates data-driven decision-making through continuous performance monitoring, enabling governments and organizations to prioritize high-impact initiatives and eliminate wasteful expenditures. This budgeting approach supports strategic planning by aligning financial resources with organizational goals, thereby improving service delivery and optimizing public value.
Benefits of Zero-Based Budgeting
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) enhances resource allocation by requiring every expense to be justified from scratch, promoting cost efficiency and eliminating unnecessary expenditures. Unlike Performance-Based Budgeting, which relies on previous budgets as a baseline, ZBB drives strategic decision-making by aligning budgets with current organizational priorities and goals. This approach fosters financial discipline and transparency, facilitating better budget control and optimized use of funds.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Budgeting Approach
Performance-based budgeting faces challenges such as difficulty in precisely measuring outcomes and attributing results directly to budget allocations, often leading to oversimplified performance metrics. Zero-based budgeting demands significant time and resources, as every expense must be justified from scratch, which can overwhelm management and delay decision-making processes. Both approaches may struggle with aligning short-term financial constraints with long-term strategic goals, limiting their effectiveness in dynamic organizational environments.
Choosing the Right Budgeting Strategy for Your Organization
Performance-based budgeting allocates resources based on measurable outcomes and aligns spending with organizational goals, fostering accountability and efficient use of funds. Zero-based budgeting requires each expense to be justified from scratch, promoting thorough evaluation of every cost but demanding more time and detailed analysis. Organizations should select performance-based budgeting for continuous improvement and goal alignment, while zero-based budgeting suits scenarios needing rigorous cost control and strategic reevaluation.
Performance-Based Budgeting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com