Standards-Based Progression focuses on mastering specific learning standards before moving on to new content, ensuring a solid foundation in key skills and knowledge. This personalized approach adapts to Your pace, promoting deeper understanding and long-term academic success. Discover how implementing this method can transform educational experiences by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
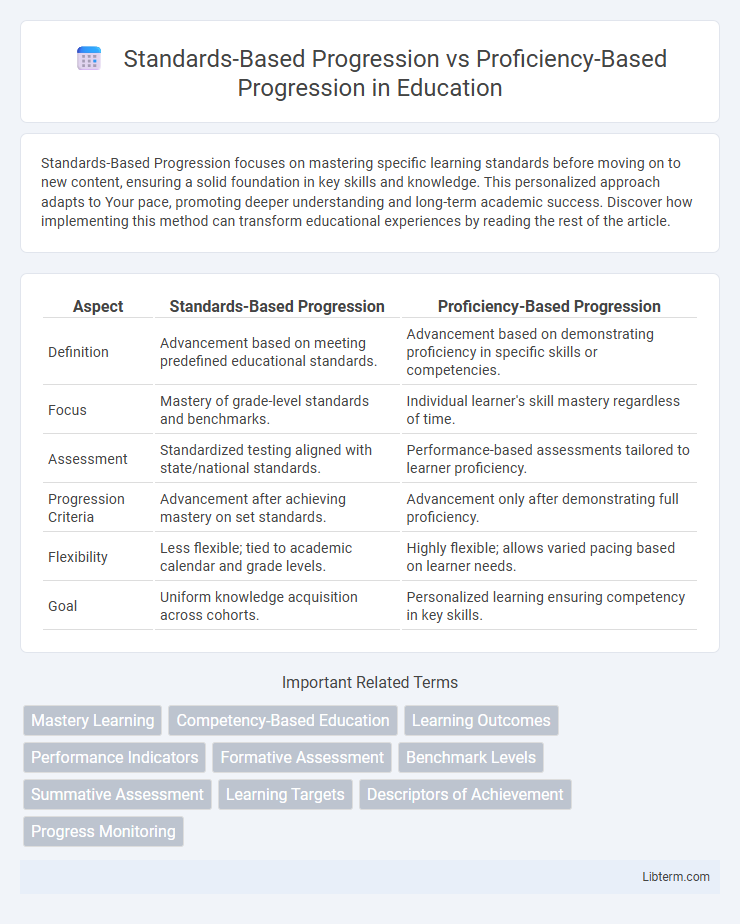
| Aspect | Standards-Based Progression | Proficiency-Based Progression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Advancement based on meeting predefined educational standards. | Advancement based on demonstrating proficiency in specific skills or competencies. |
| Focus | Mastery of grade-level standards and benchmarks. | Individual learner's skill mastery regardless of time. |
| Assessment | Standardized testing aligned with state/national standards. | Performance-based assessments tailored to learner proficiency. |
| Progression Criteria | Advancement after achieving mastery on set standards. | Advancement only after demonstrating full proficiency. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; tied to academic calendar and grade levels. | Highly flexible; allows varied pacing based on learner needs. |
| Goal | Uniform knowledge acquisition across cohorts. | Personalized learning ensuring competency in key skills. |
Understanding Standards-Based Progression
Standards-Based Progression emphasizes mastery of clearly defined learning standards before students advance to the next grade or unit, ensuring that all learners meet essential skills and knowledge benchmarks. This approach aligns assessment directly with specific standards, promoting targeted instruction and personalized learning paths. Prioritizing standards mastery helps educators identify gaps early and tailor support to achieve consistent academic growth.
What is Proficiency-Based Progression?
Proficiency-Based Progression is an educational approach where students advance through curriculum standards only after demonstrating mastery or proficiency of specific skills and knowledge. This method emphasizes personalized learning pacing, allowing learners to build a solid foundation before moving to more advanced content. Proficiency-Based Progression contrasts with time-based models by prioritizing demonstrated competence over seat time, ensuring deeper understanding and skill development.
Key Differences Between the Two Approaches
Standards-Based Progression emphasizes moving forward only after mastering specific academic standards, ensuring students fully grasp content before advancing, while Proficiency-Based Progression allows students to progress upon demonstrating a defined level of skill or competency, often measured through diverse assessments. The former is tightly linked to predefined curriculum benchmarks and pacing guides, whereas the latter focuses on individualized learning paths tailored to each student's readiness and performance. Key differences include the rigidity of progression criteria in Standards-Based systems versus the flexibility and personalized evaluation methods integral to Proficiency-Based models.
Goals of Standards-Based vs Proficiency-Based Systems
Standards-based progression centers on ensuring students meet specific academic standards by the end of a course or grade level, emphasizing consistent achievement across predefined learning objectives. Proficiency-based progression prioritizes students demonstrating mastery of content at their own pace before advancing, promoting individualized learning and deeper comprehension. Both systems aim to improve student outcomes, but standards-based models focus on uniform benchmarks while proficiency-based systems emphasize mastery and personalized timelines.
Assessment Methods Compared
Standards-Based Progression relies on assessment methods that measure student mastery against clearly defined learning standards, using frequent formative and summative evaluations to track individual progress. Proficiency-Based Progression employs assessments that emphasize demonstration of skills and competencies, often incorporating performance tasks, portfolios, and real-world applications to validate proficiency before advancing. Both methods prioritize evidence of learning but differ in the type of assessments used and the criteria for progression, with Standards-Based focusing on meeting specific benchmarks and Proficiency-Based emphasizing overall readiness and application of knowledge.
Impact on Student Learning and Motivation
Standards-based progression emphasizes mastering specific learning goals before advancing, which enhances student understanding and ensures skill competency, leading to improved academic achievement. Proficiency-based progression allows flexible pacing where students advance upon demonstrating proficiency, fostering intrinsic motivation and personalized learning experiences. Both approaches promote deeper engagement by aligning assessment with clear expectations, but proficiency-based models often increase motivation through autonomous progression and timely feedback.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Approach
Standards-Based Progression faces challenges such as rigid benchmarks that may not accommodate individual learning paces, potentially leading to student frustration or disengagement. Proficiency-Based Progression encounters criticism for subjective assessments and difficulties ensuring consistent proficiency levels across diverse classrooms. Both approaches struggle with balancing personalized learning needs and maintaining uniform academic expectations.
Implementation in Schools and Classrooms
Standards-Based Progression in schools focuses on advancing students upon meeting predefined benchmarks aligned with curriculum standards, emphasizing mastery of specific skills and knowledge before moving forward. Proficiency-Based Progression allows students to progress at individualized paces, prioritizing demonstrated competence and deeper understanding rather than seat time, which requires flexible classroom strategies and varied assessment methods. Implementing these models demands comprehensive teacher training, curriculum redesign, and robust data systems to track student achievement and support personalized learning paths effectively.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Case studies in education reveal that standards-based progression emphasizes meeting predefined learning benchmarks before advancing, illustrated by schools like Lindsay Unified School District that tailor pacing to student mastery, improving graduation rates and personalized learning outcomes. Proficiency-based progression, implemented in districts such as Concord School District in New Hampshire, allows students to demonstrate skills at their own pace, resulting in increased student engagement and deeper comprehension as evidenced by improved state assessment scores. Real-world examples highlight that both models promote mastery, but proficiency-based progression often fosters greater student autonomy and adaptability in diverse learning environments.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Educational Context
Choosing between Standards-Based Progression and Proficiency-Based Progression depends on the specific needs of your educational context, including student diversity, curriculum goals, and assessment frameworks. Standards-Based Progression emphasizes advancing students by meeting clearly defined benchmarks at each grade level, ensuring consistency and alignment with state or national standards. Proficiency-Based Progression allows students to move forward upon demonstrating mastery regardless of time, promoting personalized learning and accommodating varied learning paces.
Standards-Based Progression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com