The Chancellor plays a crucial role in shaping economic policies, overseeing government operations, and managing public finances. This position demands a deep understanding of fiscal strategies to ensure sustainable growth and stability. Discover how the Chancellor's decisions impact your financial future by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
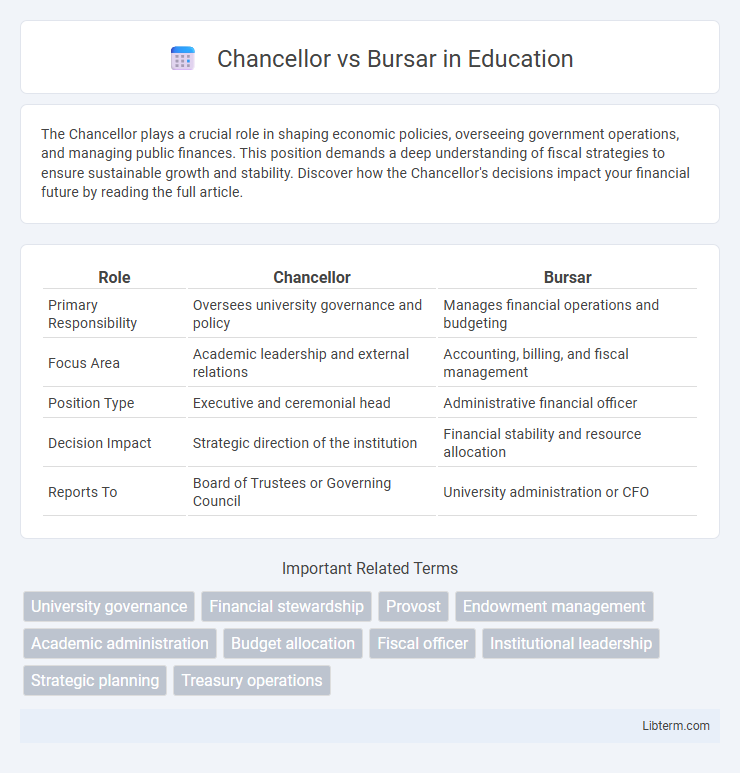
| Role | Chancellor | Bursar |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Oversees university governance and policy | Manages financial operations and budgeting |
| Focus Area | Academic leadership and external relations | Accounting, billing, and fiscal management |
| Position Type | Executive and ceremonial head | Administrative financial officer |
| Decision Impact | Strategic direction of the institution | Financial stability and resource allocation |
| Reports To | Board of Trustees or Governing Council | University administration or CFO |
Understanding the Roles: Chancellor vs Bursar
The Chancellor is the highest-ranking official in a university, responsible for overall strategic leadership, policy-making, and representing the institution publicly. The Bursar manages the university's financial operations, including budgeting, tuition fees, and financial record-keeping. Understanding the distinct roles highlights the Chancellor's focus on governance and vision, while the Bursar handles day-to-day fiscal management.
Core Responsibilities of a Chancellor
The Chancellor serves as the chief executive officer of a university, responsible for setting strategic direction, representing the institution in public and governmental affairs, and ensuring academic and financial integrity. This role includes overseeing policy implementation, fostering institutional growth, and maintaining external partnerships. In contrast, the Bursar primarily manages the financial operations, such as student billing and budget administration, without the broader leadership scope of the Chancellor.
Key Duties of a Bursar
The bursar is primarily responsible for managing a school's financial operations, including billing, tuition collection, and handling student accounts. This role involves overseeing budgeting, maintaining accurate financial records, and ensuring compliance with institutional policies. In contrast, the chancellor typically serves as the chief executive officer of a university, focusing on overall administration, academic leadership, and strategic planning.
Educational Requirements for Each Role
The Chancellor typically requires an advanced degree such as a Ph.D. or Ed.D. in higher education administration, leadership, or a related field, reflecting their executive level of responsibility. A Bursar usually holds a bachelor's degree in finance, accounting, business administration, or economics, with some positions favoring additional certifications in accounting or financial management. Both roles demand specialized knowledge relevant to their institutional duties but differ significantly in educational depth and focus.
Administrative Functions Compared
The Chancellor oversees the overall strategic direction and governance of the institution, focusing on policy-making, external relations, and long-term development plans. The Bursar manages the financial administration, including budgeting, accounting, and ensuring efficient allocation of resources for daily operations. While the Chancellor drives institutional leadership, the Bursar handles fiscal responsibilities critical to maintaining financial stability.
Influence in Institutional Decision-Making
The Chancellor holds significant influence in institutional decision-making, often serving as the chief executive responsible for setting strategic direction and approving major policies. The Bursar primarily manages the financial administration, including budgeting and resource allocation, with influence concentrated on fiscal decisions rather than overall governance. While the Chancellor shapes broad institutional objectives, the Bursar ensures financial viability aligns with those goals, making their roles complementary yet distinct in decision-making impact.
Financial Oversight: Who Handles What?
The Chancellor oversees the overall financial strategy and long-term budget planning of a university, ensuring alignment with institutional goals and compliance with regulatory standards. The Bursar manages daily financial operations such as student billing, tuition collection, and payment processing, serving as the primary point of contact for student financial accounts. This division of responsibilities ensures comprehensive financial oversight, with the Chancellor focusing on macro-level fiscal governance and the Bursar handling micro-level transactional functions.
Career Paths: Advancement Opportunities
Chancellors typically advance through academic administration, gaining experience as deans, provosts, or vice chancellors before leading entire universities, which offers broad strategic leadership opportunities. Bursars progress within financial administration, often starting in accounting or finance roles and moving up to senior financial management positions focused on institutional budgeting and resource allocation. Both career paths provide distinct advancement prospects, with chancellors emphasizing academic governance and bursars specializing in financial stewardship.
Interaction with Students and Faculty
Chancellors primarily interact with faculty through high-level administrative decisions, strategic planning, and fostering academic excellence, while bursars engage directly with students by managing tuition payments, financial aid, and billing inquiries. Faculty collaboration with chancellors often involves policy development and institutional governance, contrasting with the bursar's role in addressing students' financial concerns and facilitating payment processes. Both positions are essential in ensuring smooth operational functions but differ significantly in their day-to-day interactions within the academic community.
Chancellor and Bursar: Collaboration and Distinctions
The Chancellor primarily serves as the chief executive officer of a university, overseeing academic policies, strategic planning, and institutional representation, while the Bursar manages the financial operations, including student billing, tuition payments, and budgeting. Their collaboration is essential for aligning fiscal management with academic priorities, ensuring sustainable resource allocation and compliance with educational regulations. Distinctions between their roles highlight the Chancellor's broad administrative leadership and the Bursar's specialized focus on financial administration and operational efficiency.
Chancellor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com