Waldorf education emphasizes holistic development through creative play, artistic activities, and integrated learning that nurtures the mind, body, and spirit. Its unique approach fosters imagination and critical thinking, preparing students for lifelong learning and personal growth. Discover how Waldorf methods can transform Your educational experience by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
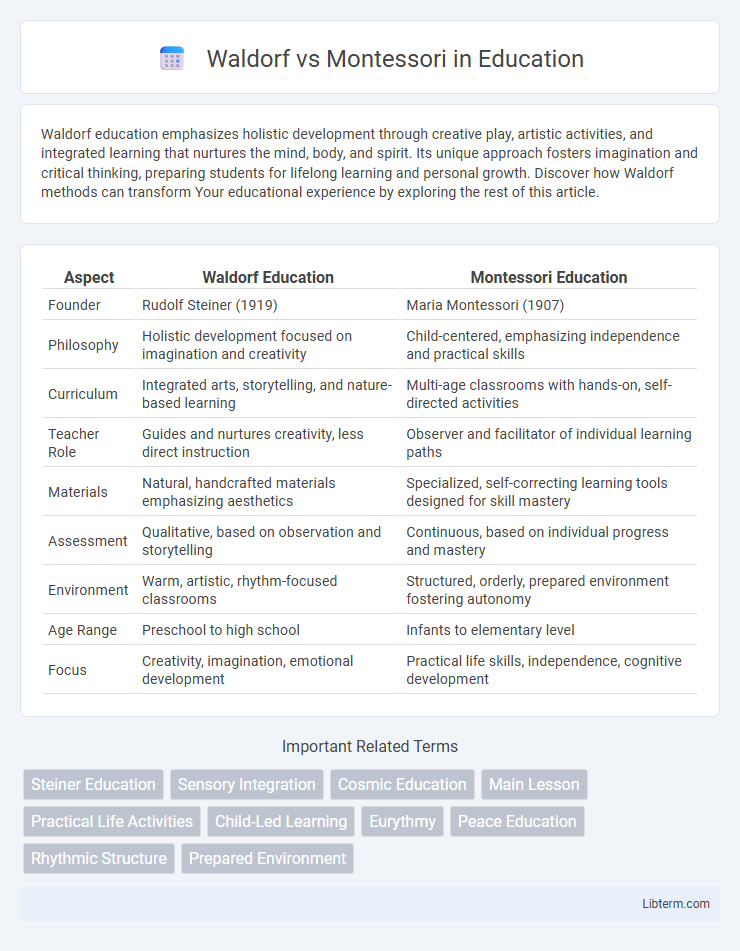
| Aspect | Waldorf Education | Montessori Education |
|---|---|---|
| Founder | Rudolf Steiner (1919) | Maria Montessori (1907) |
| Philosophy | Holistic development focused on imagination and creativity | Child-centered, emphasizing independence and practical skills |
| Curriculum | Integrated arts, storytelling, and nature-based learning | Multi-age classrooms with hands-on, self-directed activities |
| Teacher Role | Guides and nurtures creativity, less direct instruction | Observer and facilitator of individual learning paths |
| Materials | Natural, handcrafted materials emphasizing aesthetics | Specialized, self-correcting learning tools designed for skill mastery |
| Assessment | Qualitative, based on observation and storytelling | Continuous, based on individual progress and mastery |
| Environment | Warm, artistic, rhythm-focused classrooms | Structured, orderly, prepared environment fostering autonomy |
| Age Range | Preschool to high school | Infants to elementary level |
| Focus | Creativity, imagination, emotional development | Practical life skills, independence, cognitive development |
Introduction to Waldorf and Montessori Education
Waldorf education emphasizes imaginative learning, integrating arts and practical activities to nurture creativity and holistic development, founded by Rudolf Steiner in 1919. Montessori education, developed by Maria Montessori in the early 20th century, focuses on child-led, hands-on learning environments designed to foster independence, self-discipline, and critical thinking. Both approaches prioritize individualized learning but differ in curriculum structure and teaching methodologies, with Waldorf leaning toward structured artistic rhythm and Montessori emphasizing freedom within prepared environments.
Core Philosophies: Waldorf vs Montessori
Waldorf education emphasizes holistic development through imaginative play and artistic expression, rooted in Rudolf Steiner's anthroposophy, aiming to nurture creativity, moral values, and social skills. Montessori education, founded by Maria Montessori, focuses on child-led learning with hands-on, sensory materials designed to foster independence, self-discipline, and cognitive development in a prepared environment. The core philosophical difference is Waldorf's emphasis on guided imagination and rhythm, contrasted with Montessori's prioritization of autonomy and structured freedom within a carefully designed space.
Teaching Methods and Classroom Structure
Waldorf education emphasizes imaginative play, storytelling, and arts integrated into a holistic curriculum, promoting creativity and emotional development through a teacher-led approach. Montessori classrooms focus on self-directed learning with hands-on materials, fostering independence and practical life skills in multi-age group settings guided by facilitators. The Waldorf method uses a structured day with rhythmic activities, while Montessori environments encourage free movement and personalized pacing within orderly, child-centered spaces.
Curriculum Focus and Subject Integration
Waldorf education prioritizes a holistic curriculum centered on artistic expression, imagination, and experiential learning, integrating subjects through storytelling, arts, and nature-based activities to nurture creativity and emotional development. Montessori curriculum emphasizes structured, hands-on learning with a focus on practical life skills, sensorial experiences, and individualized pacing, promoting independence and cognitive development through self-directed exploration of math, language, and science. Both approaches integrate subjects but diverge in methods--Waldorf uses thematic, interdisciplinary blocks, while Montessori employs sequential, material-based lessons tailored to each child's learning stages.
Role of the Teacher: Guide vs Facilitator
In Waldorf education, the teacher acts primarily as a guide, shaping the curriculum and learning environment to align with developmental stages and fostering creativity through structured storytelling and artistic activities. Montessori teachers serve as facilitators, providing prepared environments and materials that encourage independent exploration, allowing children to learn at their own pace. The distinct roles reflect Waldorf's emphasis on teacher-led inspiration versus Montessori's focus on student autonomy within guided discovery.
Approach to Creativity and Imagination
Waldorf education emphasizes storytelling, imaginative play, and artistic activities to nurture creativity and foster a deep connection between imagination and emotional development. Montessori promotes creativity through hands-on learning, self-directed exploration, and practical life activities, encouraging children to develop problem-solving skills and independence. Both approaches cultivate creativity but differ in structure: Waldorf integrates imagination with rhythm and narrative, while Montessori emphasizes freedom within a prepared environment.
Individualization and Pace of Learning
Waldorf education emphasizes a holistic, experiential approach that adapts to the developmental stages of each child, fostering creativity and imagination at a natural pace. Montessori education prioritizes individualized learning paths, allowing children to progress independently through hands-on materials and self-directed activities tailored to their unique interests and abilities. Both methods respect individual pace but differ in structure, with Montessori offering more autonomy in daily choices, while Waldorf follows a guided rhythm aligned with age-specific milestones.
Classroom Environment and Materials
Waldorf classrooms emphasize natural, handcrafted materials made from wood, wool, and cotton, creating a warm, home-like atmosphere that fosters creativity and imagination. Montessori environments feature carefully designed, child-sized materials that promote independence and hands-on learning through self-correction and sensory exploration. Both approaches prioritize a calm, organized space but differ in their use of materials and overall classroom aesthetics to support developmental goals.
Social and Emotional Development
Waldorf education emphasizes imaginative play and storytelling to nurture empathy and social skills, promoting a strong sense of community and emotional resilience in children. Montessori encourages self-directed activities and collaborative learning, fostering independence alongside interpersonal respect and emotional intelligence. Both approaches support holistic social and emotional development but differ in structure and methods, catering to diverse learning needs.
Pros, Cons, and Choosing the Right Fit
Waldorf education emphasizes imagination and creativity through arts and storytelling, fostering holistic development but may limit early academic rigor, while Montessori focuses on self-directed learning with hands-on materials, promoting independence yet sometimes lacking in structured social interaction. Pros of Waldorf include nurturing emotional growth and rhythm, whereas cons involve delayed formal reading and math instruction; Montessori's pros feature individualized pacing and practical life skills, with cons including less emphasis on group activities. Choosing the right fit depends on a child's learning style and family values, prioritizing either imaginative freedom or autonomous, experiential learning environments.
Waldorf Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com