Peer feedback enhances your learning by providing diverse perspectives and constructive criticism that fosters growth and improvement. Engaging in this collaborative process helps refine your skills and deepen your understanding of the subject matter. Explore the full article to discover effective strategies for giving and receiving peer feedback that elevate your academic or professional performance.
Table of Comparison
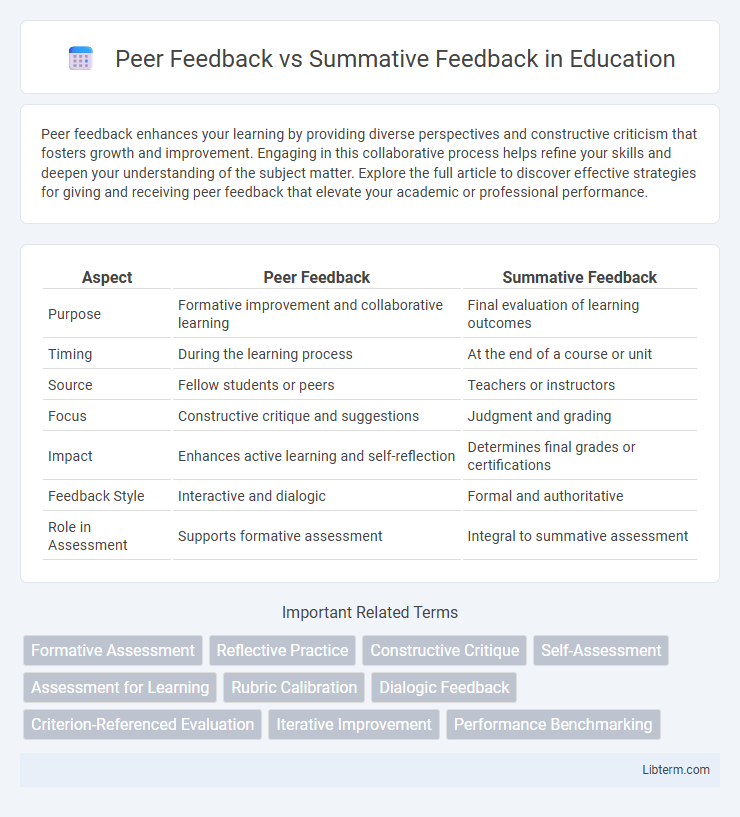
| Aspect | Peer Feedback | Summative Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Formative improvement and collaborative learning | Final evaluation of learning outcomes |
| Timing | During the learning process | At the end of a course or unit |
| Source | Fellow students or peers | Teachers or instructors |
| Focus | Constructive critique and suggestions | Judgment and grading |
| Impact | Enhances active learning and self-reflection | Determines final grades or certifications |
| Feedback Style | Interactive and dialogic | Formal and authoritative |
| Role in Assessment | Supports formative assessment | Integral to summative assessment |
Introduction to Peer Feedback and Summative Feedback
Peer feedback involves learners providing evaluative comments and constructive criticism to their peers, fostering engagement and active learning. Summative feedback, typically delivered by instructors at the end of an assessment, offers a summary judgment on performance to measure learning outcomes. Both types of feedback serve distinct roles in educational settings, with peer feedback promoting ongoing improvement and summative feedback certifying achievement.
Defining Peer Feedback: Concepts and Purpose
Peer feedback involves learners providing constructive comments and evaluations to each other's work, fostering active engagement and critical thinking. This formative assessment method aims to promote collaborative learning, self-reflection, and skill improvement prior to final evaluations. Distinct from summative feedback, peer feedback emphasizes ongoing development rather than final judgment.
Understanding Summative Feedback: Key Characteristics
Summative feedback provides a comprehensive evaluation of student performance at the end of an instructional period, focusing on overall achievement against set standards. It typically includes grades or scores that summarize learning outcomes, offering clear indicators of mastery or areas needing improvement. This type of feedback is often used for reporting purposes and decision-making about progression or certification.
Benefits of Peer Feedback in Learning Environments
Peer feedback enhances learning environments by promoting active engagement and critical thinking among students, enabling them to articulate understanding and address misconceptions collaboratively. It fosters a supportive community where learners develop communication and self-assessment skills, leading to improved retention and academic performance. Compared to summative feedback, peer feedback offers timely, formative insights that encourage continuous improvement and motivation throughout the learning process.
Advantages of Summative Feedback for Assessment
Summative feedback provides a clear and comprehensive evaluation of student performance at the end of an instructional period, enabling teachers to assign grades that reflect overall achievement. It offers standardized criteria that support consistent assessment and help identify knowledge gaps for future improvement. This type of feedback also aids in benchmarking student progress against curriculum standards and learning objectives.
Limitations of Peer Feedback: Challenges and Barriers
Peer feedback often faces challenges such as varying levels of student expertise, which can lead to inconsistent quality and accuracy in evaluations. Students may also experience discomfort or bias when providing critiques to peers, affecting the objectivity and effectiveness of the feedback. Furthermore, lack of training in constructive feedback techniques and time constraints pose significant barriers to maximizing the benefits of peer assessment.
Drawbacks of Summative Feedback: Common Criticisms
Summative feedback often faces criticism for providing limited opportunities for learner improvement, as it is typically delivered after the completion of a task, making real-time adjustments impossible. This form of feedback can cause increased anxiety and decreased motivation due to its high-stakes nature, focusing primarily on final outcomes rather than the learning process. Furthermore, summative assessments may not accurately reflect individual progress or diverse learning styles, potentially overlooking nuanced student needs.
Comparing Effectiveness: Peer vs. Summative Feedback
Peer feedback enhances learner engagement and fosters critical thinking by encouraging active participation and collaborative evaluation. Summative feedback, typically provided by instructors post-assessment, offers authoritative insights but often lacks immediacy and personalized interaction. Studies indicate peer feedback can be equally effective in improving performance and motivation when combined with clear guidelines and instructor oversight.
Best Practices for Integrating Both Feedback Types
Integrating peer feedback with summative feedback enhances student learning by combining formative insights and final evaluations to support continuous improvement. Best practices include establishing clear rubrics for peer assessments to ensure consistency, training students to provide constructive, objective feedback, and aligning summative feedback criteria with peer feedback objectives for coherence. Incorporating timely peer feedback before summative assessments helps identify learning gaps early, enabling targeted instruction and increased student engagement.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Feedback Approach
Selecting the right feedback approach depends on the learning objectives and context, with peer feedback fostering collaborative skills and immediate improvement, while summative feedback provides comprehensive evaluation of overall performance. Peer feedback enhances critical thinking and communication among students, making it ideal for formative learning phases. Summative feedback serves best for final assessments, offering a clear measure of achievement against established standards.
Peer Feedback Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com