Experiential learning immerses you in hands-on activities, fostering deeper understanding and long-lasting knowledge retention. This approach bridges theory and practice, enabling real-world skills development that traditional methods often overlook. Discover how embracing experiential techniques can transform your educational journey in the full article.
Table of Comparison
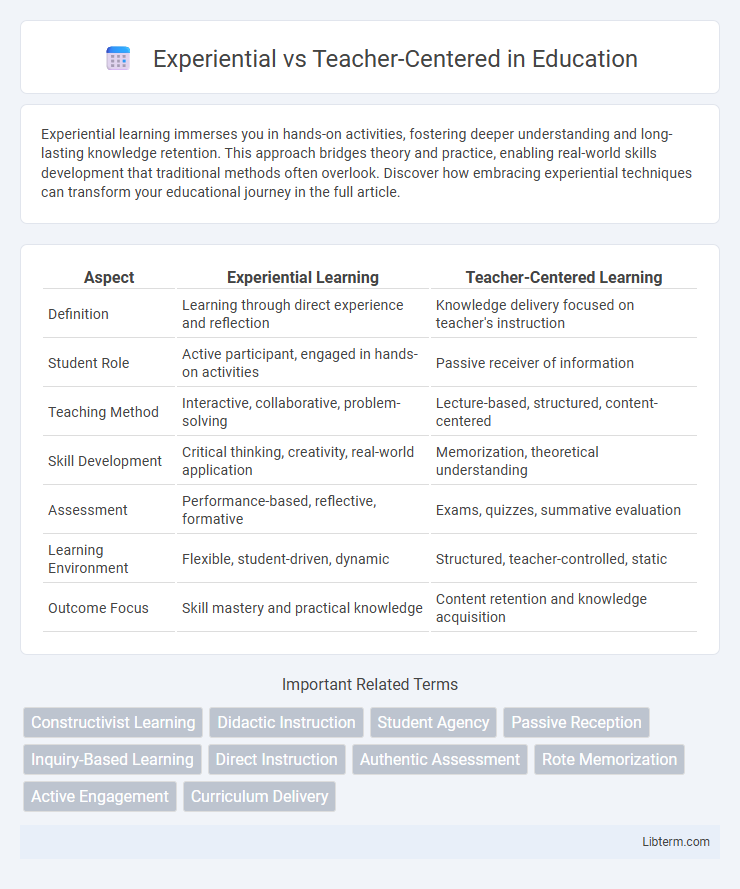
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Teacher-Centered Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection | Knowledge delivery focused on teacher's instruction |
| Student Role | Active participant, engaged in hands-on activities | Passive receiver of information |
| Teaching Method | Interactive, collaborative, problem-solving | Lecture-based, structured, content-centered |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, creativity, real-world application | Memorization, theoretical understanding |
| Assessment | Performance-based, reflective, formative | Exams, quizzes, summative evaluation |
| Learning Environment | Flexible, student-driven, dynamic | Structured, teacher-controlled, static |
| Outcome Focus | Skill mastery and practical knowledge | Content retention and knowledge acquisition |
Introduction to Experiential and Teacher-Centered Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes active participation and hands-on experiences, allowing learners to engage directly with the material for deeper understanding and skill development. Teacher-centered learning prioritizes the instructor's role as the primary source of knowledge, where information is transmitted through lectures, focusing on content delivery and memorization. Both approaches serve distinct educational goals, with experiential learning fostering critical thinking and real-world application, while teacher-centered methods provide structured guidance and foundational knowledge.
Defining Experiential Learning
Experiential learning is defined as an educational approach where students engage directly in hands-on experiences, promoting active participation and real-world application of knowledge. This method contrasts with teacher-centered learning, which emphasizes passive reception of information through lectures and textbooks. Key components of experiential learning include reflection, critical thinking, and problem-solving, fostering deeper understanding and long-term retention.
Understanding Teacher-Centered Approaches
Teacher-centered approaches prioritize direct instruction where the teacher controls the learning environment and delivers content to students, emphasizing memorization and repetition for knowledge retention. This model positions the teacher as the primary source of authority and expertise, structuring lessons around clear objectives and standardized assessments. Understanding teacher-centered methods involves recognizing their effectiveness in establishing foundational skills, particularly in large classrooms or when specific content mastery is required.
Key Differences Between the Two Methods
Experiential learning emphasizes active participation, allowing students to learn through hands-on experiences and reflection, while teacher-centered methods prioritize direct instruction and lecture-based delivery. Experiential approaches foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills by engaging learners in real-world scenarios, whereas teacher-centered models focus on knowledge transmission and content mastery. The key difference lies in learner engagement: experiential learning is learner-driven and interactive, whereas teacher-centered learning is instructor-driven and passive.
Benefits of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning enhances student engagement by promoting hands-on activities that deepen understanding and retention of material. This method fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills through real-world application, contrasting with passive absorption typical of teacher-centered approaches. Increased collaboration and personal reflection during experiential learning contribute to improved communication skills and learner autonomy.
Advantages of Teacher-Centered Instruction
Teacher-centered instruction offers clear structure and efficient content delivery, facilitating consistent coverage of curriculum standards within limited time frames. This approach allows educators to leverage their expertise to clarify complex concepts and maintain classroom discipline effectively. The method supports standardized assessment preparation, ensuring measurable learning outcomes and uniformity across diverse student groups.
Challenges in Implementing Both Approaches
Experiential learning faces challenges such as the need for extensive resources and facilitator expertise to design immersive, real-world activities, which can strain institutional budgets and schedules. Teacher-centered approaches often struggle with passive student engagement and limited adaptability to diverse learning styles, hindering deep understanding and skill development. Both methods require careful balance and integration of technology, curriculum design, and assessment strategies to overcome these obstacles and enhance educational effectiveness.
Impact on Student Engagement and Achievement
Experiential learning significantly boosts student engagement by actively involving learners in hands-on activities that promote critical thinking and real-world problem-solving skills. Teacher-centered approaches often limit student participation, leading to lower motivation and reduced academic achievement compared to experiential methods. Research shows that experiential learning environments correlate with higher retention rates and improved academic performance across diverse subjects.
Choosing the Right Approach for Different Learners
Experiential learning emphasizes active engagement, hands-on activities, and real-world problem-solving, which suits learners who thrive in interactive, practical environments. Teacher-centered approaches focus on structured lectures and direct instruction, benefiting students who prefer clear guidance and systematic information delivery. Selecting the right approach depends on assessing individual learning styles, cognitive preferences, and the educational context to maximize comprehension and retention.
Future Trends in Educational Methodologies
Experiential learning prioritizes hands-on, student-driven activities that enhance critical thinking and creativity, aligning with future trends emphasizing personalized education and real-world problem-solving skills. Teacher-centered approaches, while still relevant for foundational knowledge dissemination, are increasingly supplemented by technology-infused, interactive methods to cater to diverse learning styles. Emerging methodologies focus on hybrid models combining experiential tactics with digital tools to foster engagement, adaptability, and lifelong learning competencies in evolving educational landscapes.
Experiential Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com