Social learning enhances knowledge retention by leveraging interactions and shared experiences among individuals. It fosters collaboration and critical thinking, driving meaningful engagement and skill development. Discover how embracing social learning can transform your educational or professional growth in the full article.
Table of Comparison
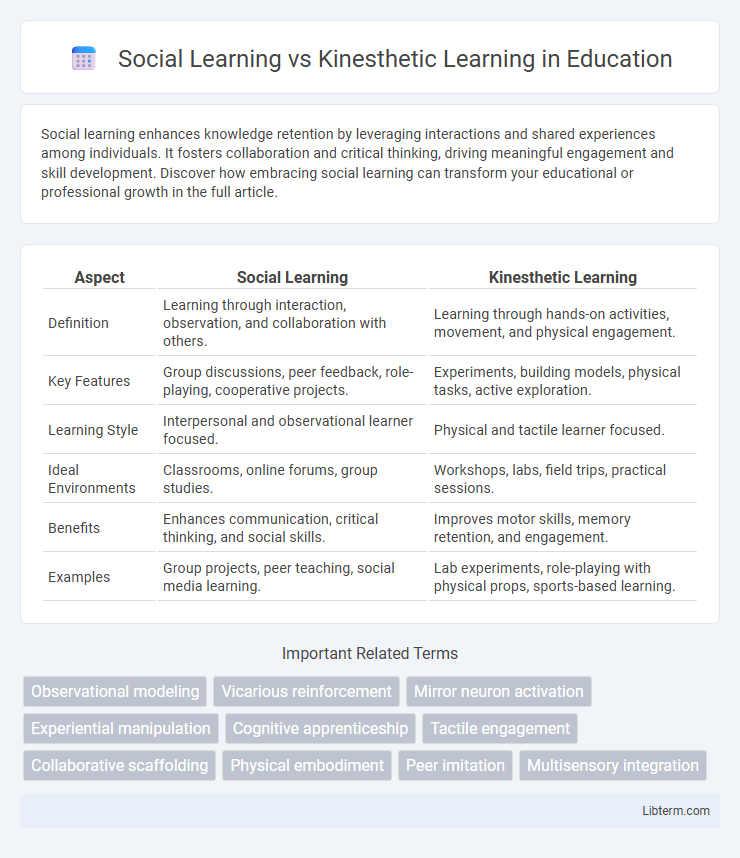
| Aspect | Social Learning | Kinesthetic Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through interaction, observation, and collaboration with others. | Learning through hands-on activities, movement, and physical engagement. |
| Key Features | Group discussions, peer feedback, role-playing, cooperative projects. | Experiments, building models, physical tasks, active exploration. |
| Learning Style | Interpersonal and observational learner focused. | Physical and tactile learner focused. |
| Ideal Environments | Classrooms, online forums, group studies. | Workshops, labs, field trips, practical sessions. |
| Benefits | Enhances communication, critical thinking, and social skills. | Improves motor skills, memory retention, and engagement. |
| Examples | Group projects, peer teaching, social media learning. | Lab experiments, role-playing with physical props, sports-based learning. |
Understanding Social Learning: Key Concepts
Social learning emphasizes learning through observation, imitation, and interaction within social contexts, leveraging group dynamics and shared experiences to enhance knowledge acquisition. Key concepts include modeling behavior, social reinforcement, and cognitive development influenced by peer and mentor interactions. This approach contrasts with kinesthetic learning, which prioritizes tactile and physical engagement to grasp new skills through hands-on activities.
What is Kinesthetic Learning? An Overview
Kinesthetic learning, also known as tactile learning, involves acquiring knowledge through physical activities and hands-on experiences rather than passive listening or observation. This learning style emphasizes movement, touch, and manipulation of objects to better understand concepts and retain information. Kinesthetic learners benefit from activities like role-playing, building models, and interactive experiments, which engage their sensory and motor skills for enhanced cognitive processing.
Core Differences Between Social and Kinesthetic Learning
Social learning emphasizes interaction, collaboration, and observation within group settings to acquire knowledge, relying heavily on communication and imitation. Kinesthetic learning centers on hands-on experiences, physical activity, and movement to understand concepts, engaging the body's sense of touch and proprioception. The core difference lies in social learning's dependence on interpersonal experiences versus kinesthetic learning's focus on physical engagement and direct manipulation of materials.
Benefits of Social Learning in Education
Social learning enhances collaboration, communication, and critical thinking skills by engaging students in group activities and discussions. It promotes diverse perspectives, leading to deeper understanding and improved problem-solving abilities. Through peer interaction, social learning also fosters motivation and accountability, supporting long-term retention and academic success.
Advantages of Kinesthetic Learning Approaches
Kinesthetic learning approaches offer distinct advantages by engaging the body in the learning process, which enhances memory retention and understanding through physical activity. This hands-on method supports the development of motor skills and coordination while promoting active problem-solving and critical thinking. Kinesthetic learning also benefits learners who struggle with traditional auditory or visual methods by providing tactile and movement-based experiences that align with their natural learning preferences.
Challenges Associated with Each Learning Style
Social learning faces challenges such as reliance on interaction quality, where ineffective group dynamics or lack of engagement can hinder knowledge transfer and motivation. Kinesthetic learning struggles with limited access to hands-on materials or environments, making it difficult for learners to fully grasp concepts through physical activity alone. Both styles require tailored resources and support to overcome barriers and maximize effective learning outcomes.
Ideal Environments for Social vs Kinesthetic Learners
Ideal environments for social learners involve collaborative spaces that encourage group discussions, peer interactions, and cooperative projects, fostering communication and teamwork. Kinesthetic learners thrive in hands-on settings equipped with tactile materials, movement opportunities, and experiential activities that engage their sense of touch and physical involvement. Tailoring classroom design to include flexible seating, interactive stations, and real-world simulations maximizes learning outcomes for both styles by addressing their distinct sensory and social needs.
Strategies to Support Social Learning
Strategies to support social learning include collaborative group projects, peer teaching, and interactive discussions that promote shared knowledge construction. Utilizing technology such as social media platforms and online forums enhances engagement and facilitates real-time communication among learners. Structured feedback and role-playing activities further reinforce social interaction and experiential understanding in diverse learning environments.
Techniques to Enhance Kinesthetic Learning
Techniques to enhance kinesthetic learning include incorporating hands-on activities such as experiments, role-playing, and building models that engage the body's movement and tactile senses. Using physical objects and real-world scenarios helps learners internalize concepts through muscle memory and active participation. Integrating movement breaks and interactive games also boosts retention and understanding by aligning learning with natural motor skills.
Combining Social and Kinesthetic Methods for Maximum Impact
Combining social learning and kinesthetic learning leverages active group engagement and physical movement to enhance knowledge retention and skill acquisition. Collaborative activities such as role-playing, group projects, and hands-on experiments stimulate both interpersonal communication and tactile experience, fostering deeper understanding. This integrated approach maximizes learner motivation and promotes practical application of concepts in real-world contexts.
Social Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com