High-stakes testing significantly impacts students' academic paths and school evaluations by determining advancement, graduation, and funding. These tests often create pressure that affects teaching methods and student learning experiences. Explore the rest of the article to understand the broader implications and debates surrounding high-stakes assessments.
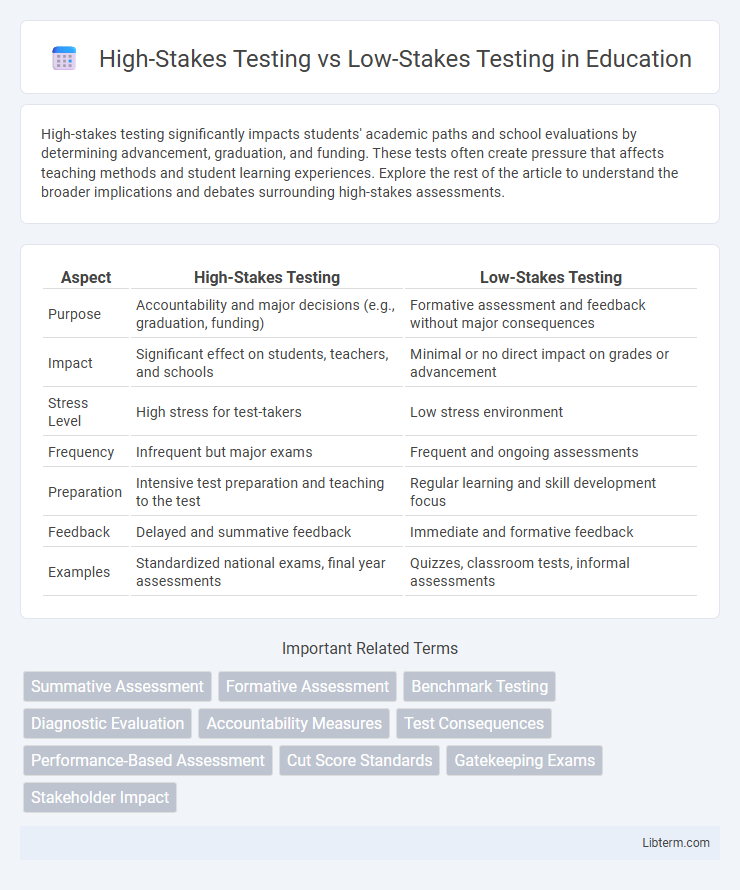
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | High-Stakes Testing | Low-Stakes Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Accountability and major decisions (e.g., graduation, funding) | Formative assessment and feedback without major consequences |
| Impact | Significant effect on students, teachers, and schools | Minimal or no direct impact on grades or advancement |
| Stress Level | High stress for test-takers | Low stress environment |
| Frequency | Infrequent but major exams | Frequent and ongoing assessments |
| Preparation | Intensive test preparation and teaching to the test | Regular learning and skill development focus |
| Feedback | Delayed and summative feedback | Immediate and formative feedback |
| Examples | Standardized national exams, final year assessments | Quizzes, classroom tests, informal assessments |
Understanding High-Stakes and Low-Stakes Testing
High-stakes testing involves assessments that have significant consequences for students, educators, or schools, such as determining graduation eligibility or funding allocations. Low-stakes testing carries minimal or no immediate consequences, often used for formative assessments to guide instruction and provide feedback. Understanding the distinct purposes and impacts of high-stakes versus low-stakes testing is essential for educators aiming to balance accountability with supportive learning environments.
Key Differences Between High-Stakes and Low-Stakes Assessments
High-stakes testing significantly influences critical decisions such as student promotion, graduation, or teacher evaluations, while low-stakes testing primarily serves formative purposes like guiding instruction and providing feedback without drastic consequences. High-stakes assessments often require standardized testing environments with rigorous security measures, whereas low-stakes assessments allow greater flexibility in administration and focus on growth and learning processes. The data from high-stakes tests typically impact policy and accountability, in contrast to low-stakes tests which emphasize individual progress and skill development.
The Purpose and Goals of High-Stakes Tests
High-stakes tests are designed primarily to make critical decisions regarding student progress, graduation eligibility, and educator accountability, emphasizing performance standards and accountability measures. These assessments aim to ensure that students meet predetermined proficiency levels essential for academic advancement and workforce readiness. High-stakes testing also serves policy enforcement purposes, motivating schools and districts to align instruction with standardized criteria to improve overall educational outcomes.
The Role of Low-Stakes Tests in Learning
Low-stakes tests play a crucial role in enhancing learning by reducing stress and encouraging consistent knowledge retrieval, which strengthens memory retention. These assessments provide timely feedback, allowing students to identify knowledge gaps without the pressure of significant consequences. Research shows that integrating low-stakes testing into educational strategies improves long-term academic performance and fosters a growth mindset.
Impact of High-Stakes Testing on Student Performance
High-stakes testing significantly influences student performance by increasing anxiety and pressure, which often hampers genuine learning and critical thinking skills. These tests emphasize rote memorization and narrowly defined curricula, limiting opportunities for creative problem-solving and deeper understanding. Research consistently shows that high-stakes environments can widen achievement gaps, disproportionately affecting students from disadvantaged backgrounds.
Psychological and Emotional Effects of Testing Stakes
High-stakes testing often induces significant stress and anxiety in students due to the pressure of consequences tied to their performance, potentially leading to decreased motivation and increased test anxiety. In contrast, low-stakes testing typically fosters a more supportive environment that encourages learning and reduces psychological distress by minimizing fear of failure. Research indicates that while high-stakes assessments can negatively impact student well-being, low-stakes testing promotes resilience and a growth mindset, enhancing overall emotional health during the evaluation process.
Advantages and Disadvantages of High-Stakes Testing
High-stakes testing offers the advantage of providing clear, objective measures of student achievement and accountability for educators, often leading to increased motivation and focused curriculum alignment. However, disadvantages include heightened stress for students and teachers, potential narrowing of the curriculum, and risks of teaching to the test rather than fostering deeper learning. The pressure associated with high-stakes assessments can also contribute to inequities, disproportionately affecting students from disadvantaged backgrounds.
Benefits and Limitations of Low-Stakes Testing
Low-stakes testing promotes a stress-reduced learning environment by providing frequent feedback without significant consequences, enhancing student motivation and engagement. It facilitates formative assessment, allowing educators to identify knowledge gaps and tailor instruction effectively, thereby improving long-term retention. However, low-stakes tests may lack the rigor needed to accurately measure mastery and can be undervalued by students, potentially reducing their impact on learning outcomes.
Best Practices for Balancing Assessment Strategies
Effective balancing of high-stakes and low-stakes testing involves integrating frequent formative assessments to provide ongoing feedback and support student growth while reserving summative high-stakes tests for critical decision-making points. Educators should employ data-driven strategies to analyze results from both types of tests, ensuring that assessments align with learning objectives and promote student engagement without causing excessive stress. Implementing diverse assessment methods and fostering a culture of continuous improvement helps optimize learning outcomes and maintains a fair evaluation environment.
Future Trends in Educational Testing Approaches
Emerging educational testing approaches increasingly emphasize adaptive high-stakes testing combined with frequent low-stakes formative assessments to personalize learning and reduce test anxiety. Advances in artificial intelligence and data analytics enable real-time feedback and predictive insights, enhancing both summative and formative evaluation accuracy. Future trends point toward integrating biometric data and gamified testing environments to create more engaging, valid, and reliable assessments tailored to diverse learner profiles.
High-Stakes Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com