Restorative justice practices focus on repairing harm through inclusive dialogue between victims, offenders, and the community, fostering accountability and healing. These methods emphasize empathy, mutual respect, and collaborative problem-solving to rebuild trust and promote long-term positive outcomes. Discover how restorative justice can transform conflict resolution and improve Your community relationships by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
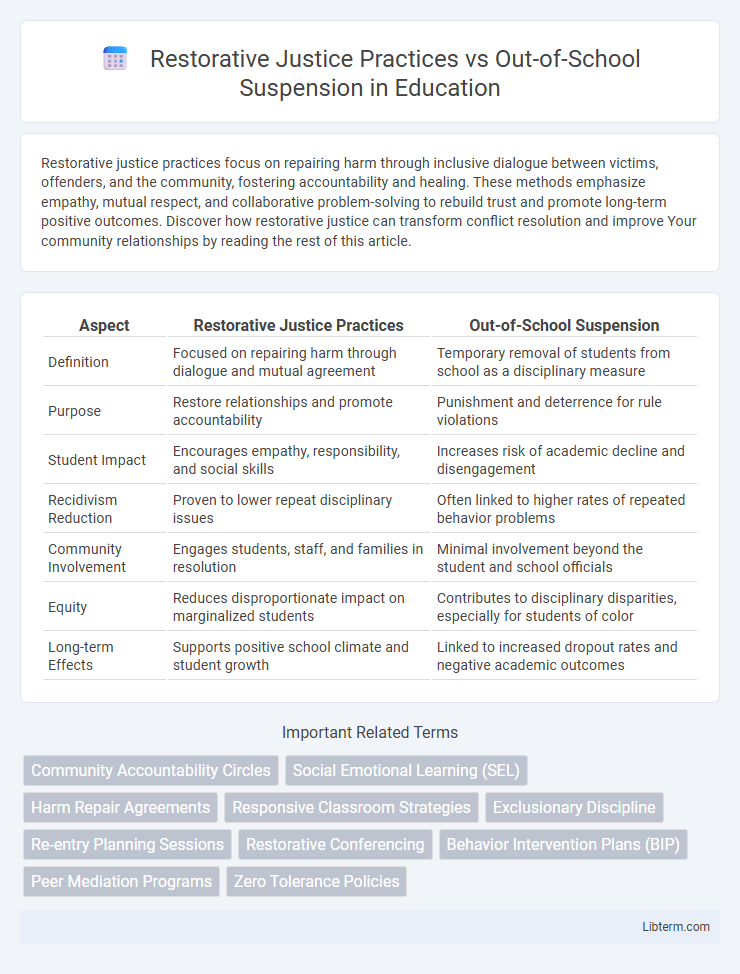
| Aspect | Restorative Justice Practices | Out-of-School Suspension |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focused on repairing harm through dialogue and mutual agreement | Temporary removal of students from school as a disciplinary measure |
| Purpose | Restore relationships and promote accountability | Punishment and deterrence for rule violations |
| Student Impact | Encourages empathy, responsibility, and social skills | Increases risk of academic decline and disengagement |
| Recidivism Reduction | Proven to lower repeat disciplinary issues | Often linked to higher rates of repeated behavior problems |
| Community Involvement | Engages students, staff, and families in resolution | Minimal involvement beyond the student and school officials |
| Equity | Reduces disproportionate impact on marginalized students | Contributes to disciplinary disparities, especially for students of color |
| Long-term Effects | Supports positive school climate and student growth | Linked to increased dropout rates and negative academic outcomes |
Understanding Restorative Justice Practices
Restorative Justice Practices emphasize repairing harm through dialogue and community involvement rather than exclusion, fostering accountability and empathy among students. This approach reduces reliance on Out-of-School Suspension, which often leads to academic setbacks and increased dropout rates. Implementing restorative strategies supports a positive school climate by addressing conflicts constructively and promoting long-term behavioral improvements.
Out-of-School Suspension: Traditional Approach
Out-of-school suspension (OSS) remains a traditional disciplinary method used to address student misconduct by temporarily removing them from the educational environment, often for serious infractions like violence or repeated rule violations. OSS can result in negative academic outcomes, including increased absenteeism, grade retention, and a higher risk of dropout, as students miss critical instructional time. Research indicates that reliance on OSS may contribute to the school-to-prison pipeline and disproportionately impact students of color and those with disabilities.
Key Differences Between Restorative and Punitive Discipline
Restorative justice practices emphasize repairing harm through dialogue and community involvement, fostering accountability and empathy among students, whereas out-of-school suspension relies on exclusion as a punitive measure that often exacerbates disengagement and academic decline. Restorative discipline encourages reconciliation and behavioral change by addressing the root causes of misconduct, while punitive discipline focuses on punishment without facilitating emotional or social repair. These fundamental differences highlight restorative justice's role in promoting long-term positive outcomes compared to the short-term control achieved through suspension.
Impacts on Student Behavior and School Climate
Restorative justice practices significantly reduce repeat behavioral issues by promoting accountability and empathy, contributing to improved student behavior and stronger school climate. Unlike out-of-school suspension, which removes students from the educational environment and often exacerbates disengagement and dropout rates, restorative approaches foster inclusion and community building. Schools implementing restorative justice report decreased disciplinary referrals and increased feelings of safety and belonging among students and staff.
Academic Outcomes: Restorative Justice vs. Suspension
Restorative justice practices foster improved academic outcomes by promoting accountability, empathy, and community engagement, leading to higher attendance rates and reduced repeat offenses. In contrast, out-of-school suspension often correlates with decreased academic performance, increased dropout rates, and loss of instructional time. Schools implementing restorative approaches report better student behavior and academic achievement compared to those relying heavily on suspension.
Reducing Recidivism and Repeat Offenses
Restorative justice practices significantly reduce recidivism rates by fostering accountability, empathy, and community involvement, contrasting with out-of-school suspension which often exacerbates disengagement and repeat offenses. Studies indicate that schools implementing restorative approaches see a decrease in repeat disciplinary actions by up to 40%, while suspension policies correlate with higher dropout rates and subsequent delinquency. Emphasizing conflict resolution and relationship-building, restorative justice addresses root causes of behavior, promoting long-term behavioral change more effectively than exclusionary discipline methods.
Addressing Equity and Racial Disparities in Discipline
Restorative justice practices reduce racial disparities by promoting inclusive dialogue and accountability, contrasting with out-of-school suspension, which disproportionately affects students of color and exacerbates educational inequities. Schools implementing restorative justice report improved attendance, reduced recidivism, and enhanced student-teacher relationships, directly addressing systemic bias in disciplinary actions. Data from the U.S. Department of Education highlights that Black students face suspension rates three times higher than their white peers, underscoring the urgent need for restorative approaches to foster equitable school environments.
Teacher and Administrator Perspectives
Teachers and administrators often view restorative justice practices as effective alternatives to out-of-school suspension by promoting accountability and repairing harm rather than solely punishing students. Educators report that restorative approaches enhance student-teacher relationships and reduce repeat disciplinary incidents, fostering a more positive school climate. Conversely, many find out-of-school suspension disrupts learning but remains a necessary disciplinary tool in severe cases, despite concerns about its negative impact on student engagement and equity.
Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
Restorative justice practices face implementation challenges such as insufficient staff training, resistance from stakeholders, and inconsistent application across schools, which can hinder their effectiveness compared to traditional out-of-school suspension. Best practices include comprehensive professional development, clear policy frameworks, ongoing evaluation, and active community involvement to foster accountability and support behavior change. Ensuring equity and culturally responsive approaches enhances the success of restorative justice while reducing reliance on exclusionary discipline methods.
Future Directions for School Discipline Reform
Restorative justice practices offer a promising alternative to out-of-school suspension by promoting accountability, empathy, and community healing, leading to reduced recidivism and improved student relationships. Emerging research highlights the effectiveness of restorative approaches in decreasing exclusionary discipline and addressing root causes of behavioral issues without compromising school safety. Future directions for school discipline reform emphasize scaling restorative programs, integrating culturally responsive methods, and investing in educator training to foster equitable and supportive school environments.
Restorative Justice Practices Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com