Education Savings Accounts (ESAs) offer a flexible and tax-advantaged way to save for your child's future educational expenses, including tuition, books, and other qualified costs. Contributions grow tax-free, and withdrawals for eligible expenses are not subject to federal income tax, maximizing the value of your investment. Explore the details in the rest of this article to understand how an ESA can benefit your family's education planning.
Table of Comparison
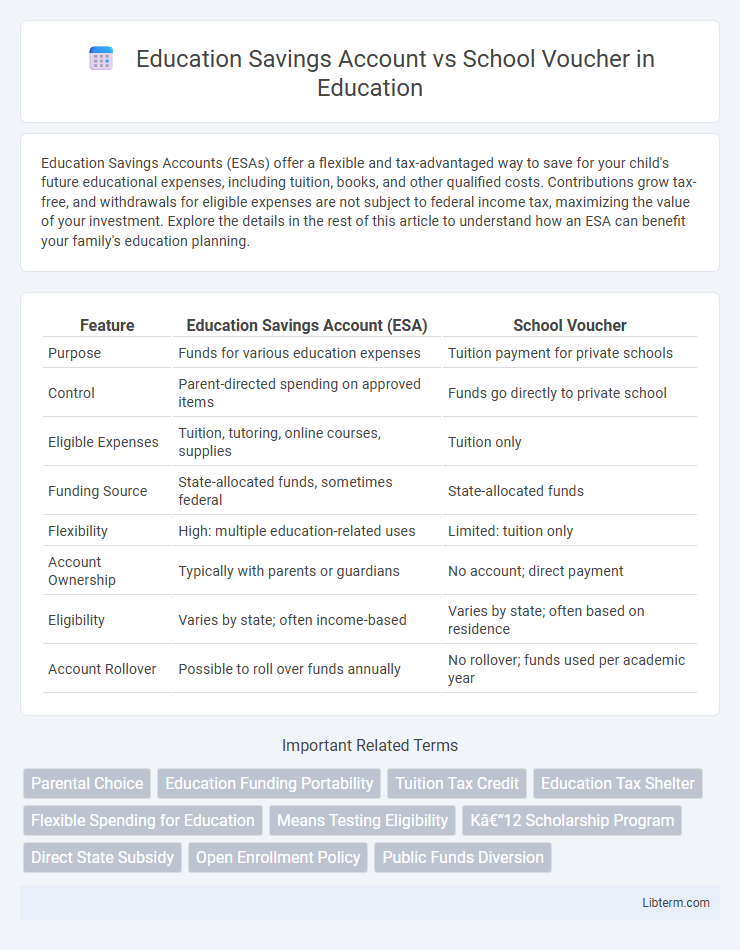
| Feature | Education Savings Account (ESA) | School Voucher |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Funds for various education expenses | Tuition payment for private schools |
| Control | Parent-directed spending on approved items | Funds go directly to private school |
| Eligible Expenses | Tuition, tutoring, online courses, supplies | Tuition only |
| Funding Source | State-allocated funds, sometimes federal | State-allocated funds |
| Flexibility | High: multiple education-related uses | Limited: tuition only |
| Account Ownership | Typically with parents or guardians | No account; direct payment |
| Eligibility | Varies by state; often income-based | Varies by state; often based on residence |
| Account Rollover | Possible to roll over funds annually | No rollover; funds used per academic year |
Understanding Education Savings Accounts (ESAs)
Education Savings Accounts (ESAs) provide families with state-funded resources to customize their child's education through various approved services such as private tuition, tutoring, and educational therapies. Unlike school vouchers, which directly pay for private school tuition, ESAs offer greater flexibility by allowing funds to be used for multiple educational expenses within a controlled and accountable framework. ESAs empower parents to tailor learning experiences to meet individual student needs while maintaining oversight to ensure appropriate usage aligned with state education standards.
What Are School Vouchers?
School vouchers are government-funded scholarships that allow parents to use public education funds toward tuition at private or charter schools, providing more school choice options. These vouchers aim to increase competition among schools and improve educational outcomes by giving families the flexibility to select environments that best meet their child's needs. Unlike Education Savings Accounts (ESAs), school vouchers typically restrict the use of funds exclusively to private school tuition, without covering broader educational expenses.
Key Differences: ESA vs School Voucher
Education Savings Accounts (ESAs) provide families with a fixed amount of public funds deposited into an account to pay for a variety of approved educational expenses, including private school tuition, tutoring, and online courses. School vouchers specifically allocate public funding to cover tuition at private schools, limiting spending primarily to tuition costs. ESAs offer broader flexibility and control over education spending, whereas school vouchers are more restrictive and focused solely on private school tuition.
How ESAs Work: Benefits and Limitations
Education Savings Accounts (ESAs) provide families with state-allocated funds to customize their children's education by paying for private school tuition, tutoring, and educational materials, offering greater flexibility compared to traditional school vouchers. ESAs promote personalized learning by allowing expenditures beyond just tuition, but their limitations include varying state regulations and potential funding disparities that may affect equitable access. While ESAs empower parental choice and innovation, concerns about accountability and the impact on public school funding remain central to the debate.
School Voucher Programs: Pros and Cons
School voucher programs provide families with government-funded scholarships to attend private schools, enhancing school choice and promoting competition that may improve educational quality. Critics argue these programs can divert essential funds from public schools, potentially undermining public education and increasing socioeconomic disparities. Research on their effectiveness is mixed, with some studies showing improved student outcomes and others indicating minimal or negative impacts on academic achievement.
Impact on Public Education Funding
Education Savings Accounts (ESAs) allow parents to withdraw public funds for approved educational expenses, often reducing the amount allocated directly to public schools. School vouchers redirect public education funds to private schools, potentially decreasing enrollment and funding for public institutions. Both policies can lead to significant shifts in public education budgets, affecting resources available for traditional public schools and impacting overall funding equity.
Parental Choice: Opportunities and Restrictions
Education Savings Accounts (ESAs) provide parents with flexible control over a designated amount of public funds to pay for various educational expenses, including private school tuition, tutoring, and educational therapies, enhancing personalized education choices. School vouchers offer a more restrictive option, directing funds specifically toward private school tuition, limiting how parents can use the allocated money. Both programs expand parental choice but vary significantly in flexibility and the scope of permissible expenditures.
Eligibility Criteria for ESAs and Vouchers
Education Savings Accounts (ESAs) typically require families to meet specific income or residency requirements, with eligibility often tied to factors such as student disability status, low-income status, or attendance at failing public schools. School vouchers generally have broader eligibility that may include all students within a certain district or state, but some programs prioritize low-income or special-needs students to increase access to private education. Both ESAs and vouchers are designed to provide educational choice, but ESAs allow families more control over spending on various educational expenses, subject to stricter eligibility verification.
Academic Outcomes: ESA vs Voucher Studies
Studies comparing Education Savings Accounts (ESA) and school vouchers reveal mixed academic outcomes. Research indicates ESAs offer families increased flexibility to customize education, often correlating with higher student performance in standardized tests. In contrast, voucher programs show more variable results, with some studies reporting modest gains and others showing negligible improvements in academic achievement.
Which Option Is Right for Your Family?
Education Savings Accounts (ESAs) offer families flexible control over education funds, allowing expenditures on tuition, tutoring, and online courses, while school vouchers typically cover tuition at private schools only. Choosing the right option depends on your family's specific educational goals, financial needs, and preferred level of spending freedom. Evaluating state-specific availability, eligibility criteria, and the range of qualified expenses helps determine whether ESA or a school voucher better aligns with your child's unique learning requirements.
Education Savings Account Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com