Separation can be a complex and emotionally challenging process affecting both personal and legal aspects of your life. Understanding the key steps involved in separation, including division of assets, child custody, and legal rights, helps you navigate this difficult time with clarity. Explore the detailed guidance in this article to manage separation effectively.
Table of Comparison
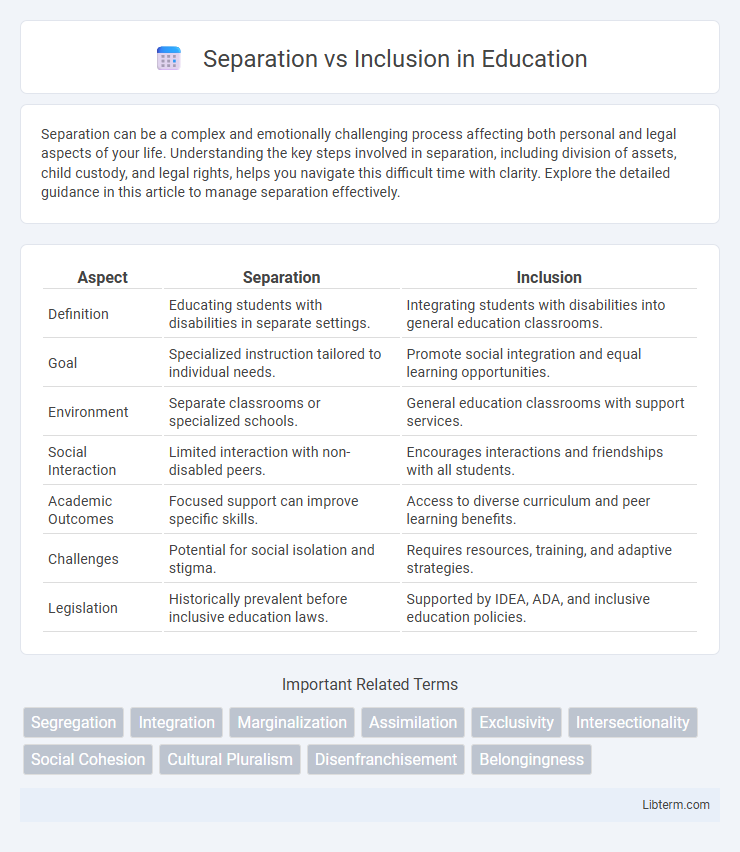
| Aspect | Separation | Inclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Educating students with disabilities in separate settings. | Integrating students with disabilities into general education classrooms. |
| Goal | Specialized instruction tailored to individual needs. | Promote social integration and equal learning opportunities. |
| Environment | Separate classrooms or specialized schools. | General education classrooms with support services. |
| Social Interaction | Limited interaction with non-disabled peers. | Encourages interactions and friendships with all students. |
| Academic Outcomes | Focused support can improve specific skills. | Access to diverse curriculum and peer learning benefits. |
| Challenges | Potential for social isolation and stigma. | Requires resources, training, and adaptive strategies. |
| Legislation | Historically prevalent before inclusive education laws. | Supported by IDEA, ADA, and inclusive education policies. |
Defining Separation and Inclusion
Separation refers to the practice of isolating individuals or groups based on specific characteristics, such as race, ability, or socioeconomic status, which often leads to unequal access to resources and opportunities. Inclusion emphasizes integrating diverse individuals into mainstream settings, ensuring equitable participation, support, and representation for all members regardless of differences. Key principles of inclusion involve embracing diversity, fostering collaboration, and eliminating barriers to equal access and engagement.
Historical Context of Separation and Inclusion
The historical context of separation is rooted in segregation policies, such as Jim Crow laws and apartheid, which institutionalized racial, social, and educational divides globally. Inclusion emerged as a response to these exclusionary practices during the civil rights movements, emphasizing equal access, diversity, and integration across education, workplaces, and communities. Modern inclusion efforts prioritize dismantling systemic barriers and promoting equity to rectify the long-term impacts of historical separation.
Psychological Effects of Separation
Separation often triggers heightened stress, anxiety, and feelings of abandonment, negatively impacting emotional stability and mental health. Prolonged separation can lead to increased symptoms of depression and difficulty forming secure attachments. Understanding these psychological effects is crucial for developing effective support systems and therapeutic interventions.
Benefits of Inclusive Environments
Inclusive environments foster diverse perspectives that enhance creativity and problem-solving within teams. Research shows that organizations with inclusive cultures experience increased employee engagement, leading to higher retention rates and improved performance. Additionally, inclusive settings promote equal opportunity, reducing bias and supporting the growth of all individuals regardless of background.
Barriers to Achieving Inclusion
Barriers to achieving inclusion often stem from systemic discrimination, inaccessible environments, and ingrained social attitudes that favor separation. Physical obstacles like lack of adaptive infrastructure and technological support further hinder equal participation for marginalized groups. Overcoming these challenges requires targeted policies, inclusive design, and continuous community engagement to dismantle exclusionary practices.
Cultural Perspectives on Inclusion
Cultural perspectives on inclusion emphasize respecting and integrating diverse beliefs, customs, and values within social and organizational settings rather than enforcing separation based on differences. Inclusive approaches highlight the value of multiculturalism and intercultural dialogue to foster equity, belonging, and mutual understanding among varied cultural groups. Research shows that culturally inclusive practices improve social cohesion, reduce prejudice, and enhance the well-being of marginalized communities.
Separation vs Inclusion in Education
Separation in education refers to the practice of educating students with disabilities in separate classrooms or schools, often leading to limited social interaction with peers without disabilities. Inclusion emphasizes integrating students with diverse needs into general education classrooms, promoting equal access to curriculum and fostering social development alongside typically developing peers. Research shows inclusive education improves academic outcomes and social skills for students with disabilities while benefiting all students by encouraging diversity and empathy.
Workplace Dynamics: Inclusion vs Separation
Workplace dynamics shift significantly when comparing separation and inclusion, as inclusion fosters diverse perspectives and collaborative innovation, enhancing overall productivity. Separation, conversely, often leads to social silos and reduced knowledge sharing, impairing team cohesion and limiting organizational growth. Inclusive environments encourage employee engagement and psychological safety, which are critical for creativity and retention in competitive industries.
Social Impact of Inclusive Communities
Inclusive communities foster social cohesion by promoting diversity and equal participation, reducing discrimination and social isolation. They enhance economic opportunities and educational outcomes for marginalized groups, contributing to overall societal well-being. The social impact of inclusion extends to improved mental health and stronger interpersonal relationships across diverse populations.
Strategies for Moving from Separation to Inclusion
Effective strategies for moving from separation to inclusion involve implementing comprehensive diversity training programs that foster empathy and cultural awareness among employees. Organizations can adopt inclusive policies, such as equitable hiring practices and creating accessible environments, to dismantle barriers and promote participation from all individuals. Leveraging mentorship and affinity groups also facilitates social integration and supports continuous dialogue around inclusivity principles.
Separation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com