Flipped classroom models transform traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online for students to access at their own pace, freeing up classroom time for interactive, hands-on activities. This approach enhances student engagement and deepens understanding by allowing more personalized support and collaborative learning during in-person sessions. Discover how flipping your classroom can revolutionize your educational experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
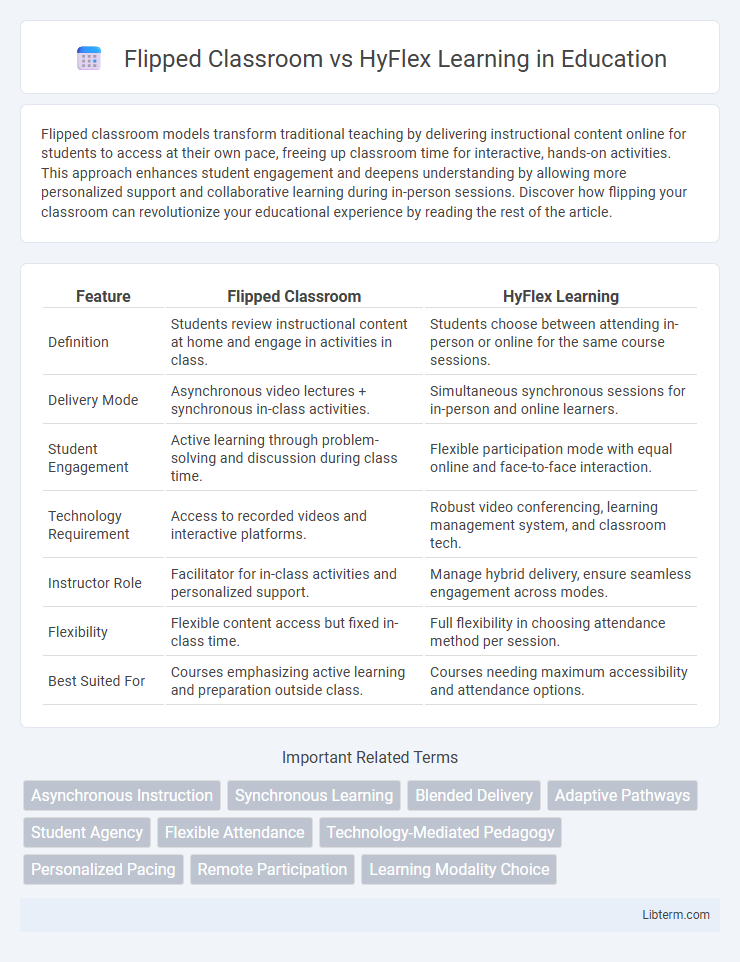
| Feature | Flipped Classroom | HyFlex Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students review instructional content at home and engage in activities in class. | Students choose between attending in-person or online for the same course sessions. |
| Delivery Mode | Asynchronous video lectures + synchronous in-class activities. | Simultaneous synchronous sessions for in-person and online learners. |
| Student Engagement | Active learning through problem-solving and discussion during class time. | Flexible participation mode with equal online and face-to-face interaction. |
| Technology Requirement | Access to recorded videos and interactive platforms. | Robust video conferencing, learning management system, and classroom tech. |
| Instructor Role | Facilitator for in-class activities and personalized support. | Manage hybrid delivery, ensure seamless engagement across modes. |
| Flexibility | Flexible content access but fixed in-class time. | Full flexibility in choosing attendance method per session. |
| Best Suited For | Courses emphasizing active learning and preparation outside class. | Courses needing maximum accessibility and attendance options. |
Introduction to Flipped Classroom and HyFlex Learning
Flipped Classroom transforms traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online outside of class, allowing in-person time for interactive, hands-on activities that enhance student engagement and comprehension. HyFlex Learning combines face-to-face and online modalities simultaneously, providing students the flexibility to choose their mode of participation based on personal circumstances or learning preferences. Both models aim to increase accessibility and student-centered learning but differ fundamentally in structure and delivery, addressing diverse educational needs.
Definition and Core Principles
Flipped Classroom is an instructional strategy where students review lecture materials at home and engage in interactive activities during class time, promoting active learning and personalized support. HyFlex Learning combines face-to-face and online instruction, allowing students to choose their mode of participation while maintaining consistent course content and learning outcomes. Both models emphasize flexibility, student engagement, and adaptability to diverse learning preferences and environments.
Key Differences in Instructional Design
Flipped Classroom centers on pre-class content delivery through videos and readings, enabling in-class time for active, collaborative learning activities that deepen understanding. HyFlex Learning integrates both in-person and online participation simultaneously, offering flexible attendance options and requiring parallel instructional design to accommodate synchronous and asynchronous learners. The core difference lies in Flipped Classroom's sequential content engagement versus HyFlex's simultaneous dual-mode access, demanding distinct approaches in content scheduling, technology use, and learner interaction strategies.
Student Engagement and Participation
Flipped Classroom promotes active student engagement by requiring learners to review lecture materials independently, allowing in-class time for interactive discussions and problem-solving activities that enhance participation. HyFlex Learning combines in-person and online modalities, offering flexible engagement options but potentially diluting real-time participation due to varied attendance modes. Research indicates Flipped Classroom models generally yield higher sustained engagement and improved collaboration compared to HyFlex environments, where student involvement can fluctuate based on individual pacing and technological access.
Flexibility and Accessibility
Flipped Classroom enhances flexibility by allowing students to access lecture materials anytime before class, promoting self-paced learning and deeper in-class engagement. HyFlex Learning maximizes accessibility by offering simultaneous in-person and online participation, catering to diverse student needs and schedules. Both models improve educational flexibility, but HyFlex uniquely bridges physical and virtual spaces for inclusive access.
Technology Requirements and Integration
Flipped Classroom relies heavily on pre-recorded video lectures and digital platforms such as Learning Management Systems (LMS) to distribute content and track student progress, requiring stable internet access and multimedia devices. HyFlex Learning demands more advanced technology infrastructure including synchronous video conferencing tools, interactive collaborative software, and robust Wi-Fi to support simultaneous in-person and remote participation. Seamless integration of hardware like cameras, microphones, and classroom capture systems is critical in HyFlex environments to ensure equitable engagement across modalities.
Teacher Roles and Responsibilities
In Flipped Classroom models, teachers primarily act as facilitators who design pre-class instructional content and guide student-centered activities during class to enhance engagement and comprehension. In HyFlex Learning environments, instructors bear the dual responsibility of delivering synchronous instruction to both in-person and remote learners, managing technology integration, and ensuring equitable participation across modalities. Effective HyFlex teaching demands advanced skills in real-time interaction, content adaptability, and continuous assessment to maintain instructional quality for diverse learning settings.
Challenges and Limitations
Flipped Classroom faces challenges such as student resistance to pre-class preparation and unequal access to technology, which can hinder engagement and participation. HyFlex Learning struggles with increased complexity in course design, requiring instructors to balance in-person and online students simultaneously while ensuring equitable learning experiences. Both models demand significant time investment from educators to develop effective materials and manage diverse student needs, potentially impacting instructional quality.
Impact on Learning Outcomes
Flipped Classroom enhances learning outcomes by promoting active engagement and allowing students to absorb content at their own pace before applying knowledge in interactive settings. HyFlex Learning offers flexibility by combining in-person and online modalities, catering to diverse learner preferences and increasing accessibility. Studies show Flipped Classroom improves conceptual understanding, while HyFlex learning supports higher retention rates and student satisfaction through adaptable participation modes.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Institution
Selecting between Flipped Classroom and HyFlex Learning hinges on institutional goals, infrastructure, and student needs. Flipped Classroom emphasizes pre-class content engagement, fostering active, face-to-face discussions, ideal for smaller, interactive settings. HyFlex Learning offers simultaneous in-person and online participation, requiring robust technology, and suits institutions prioritizing flexibility and diverse learner access.
Flipped Classroom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com