Self-contained classrooms provide a structured environment tailored to meet the unique learning needs of students requiring specialized instruction. These settings promote individualized attention and consistent routines that help enhance academic and social skills effectively. Discover how self-contained classrooms can support your child's educational journey by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
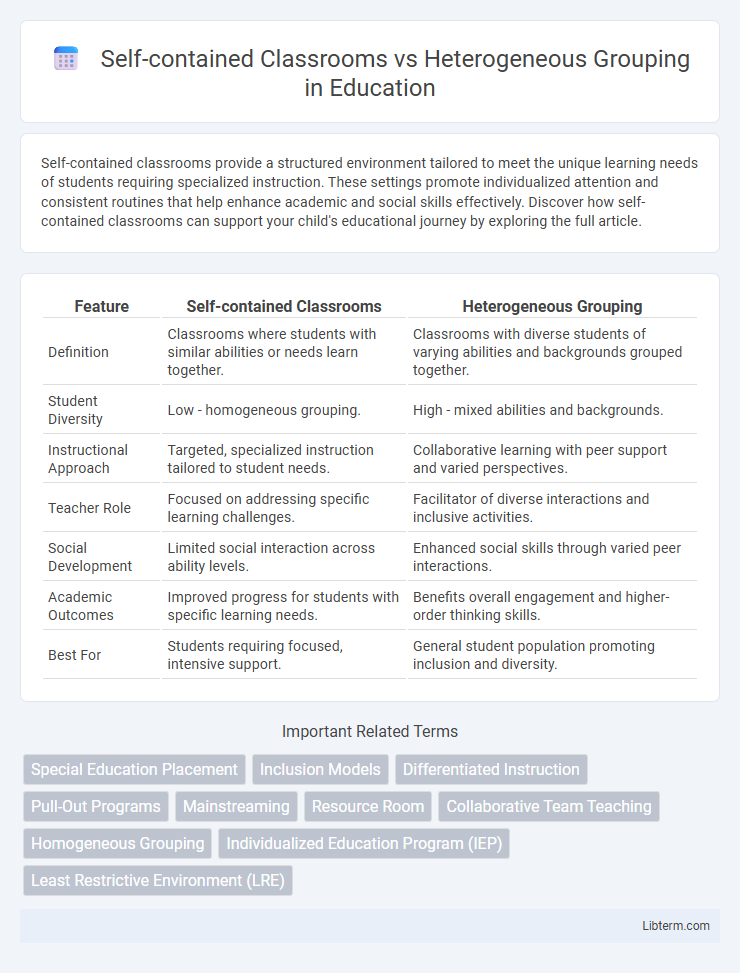
| Feature | Self-contained Classrooms | Heterogeneous Grouping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Classrooms where students with similar abilities or needs learn together. | Classrooms with diverse students of varying abilities and backgrounds grouped together. |
| Student Diversity | Low - homogeneous grouping. | High - mixed abilities and backgrounds. |
| Instructional Approach | Targeted, specialized instruction tailored to student needs. | Collaborative learning with peer support and varied perspectives. |
| Teacher Role | Focused on addressing specific learning challenges. | Facilitator of diverse interactions and inclusive activities. |
| Social Development | Limited social interaction across ability levels. | Enhanced social skills through varied peer interactions. |
| Academic Outcomes | Improved progress for students with specific learning needs. | Benefits overall engagement and higher-order thinking skills. |
| Best For | Students requiring focused, intensive support. | General student population promoting inclusion and diversity. |
Introduction to Classroom Grouping Models
Self-contained classrooms organize students by similar academic levels or needs, fostering tailored instruction and consistent peer interaction. Heterogeneous grouping mixes diverse learners within a single classroom, promoting peer learning and social development across varied abilities. These classroom grouping models impact instructional strategies, student engagement, and overall educational outcomes.
Defining Self-contained Classrooms
Self-contained classrooms are educational settings where students with similar learning needs or disabilities are grouped together and receive instruction from a specialized teacher in a separate classroom. These classrooms focus on tailored curriculum, individualized instruction, and targeted support to address specific academic and behavioral needs. Self-contained classrooms differ from heterogeneous grouping, which integrates students with diverse abilities and learning styles in a single classroom for inclusive education.
Understanding Heterogeneous Grouping
Heterogeneous grouping organizes students of diverse ability levels, learning styles, and backgrounds within the same classroom to promote peer learning and social development. This instructional strategy encourages collaboration, critical thinking, and differentiated instruction tailored to varied student needs. Research shows heterogeneous groups enhance academic achievement and social skills by leveraging diverse perspectives and fostering inclusive learning environments.
Academic Outcomes: Comparing Both Approaches
Self-contained classrooms often lead to higher academic achievement for students with special needs due to personalized instruction and tailored pacing, promoting mastery of core subjects. In contrast, heterogeneous grouping encourages peer learning and exposure to diverse perspectives, which can enhance social skills and cognitive flexibility but may result in varied academic outcomes depending on group dynamics. Research indicates that while self-contained settings foster individualized academic growth, heterogeneous grouping benefits overall classroom engagement and motivation, suggesting a need for strategic implementation based on student profiles.
Social and Emotional Development in Each Setting
Self-contained classrooms foster a stable environment where students with similar needs can build strong peer relationships, promoting consistent social interactions and emotional security. Heterogeneous grouping enhances social skills by encouraging diverse interactions, empathy, and adaptability among students with varying abilities and backgrounds. Both settings impact social and emotional development differently: self-contained classrooms provide targeted support for emotional regulation, while heterogeneous groups develop broader social competencies and inclusion.
Teacher Roles and Instructional Strategies
Self-contained classrooms require teachers to adopt multifaceted roles as primary instructors, specialists, and behavior managers within a consistent student group, allowing for personalized, differentiated instruction tailored to individual needs. In heterogeneous grouping, teachers facilitate diverse learning environments by implementing collaborative, peer-assisted learning strategies that leverage varied abilities and promote social interaction. Effective instructional strategies in self-contained settings often emphasize mastery and remediation, whereas heterogeneous groups benefit from flexible grouping and scaffolded support to address a broad spectrum of skill levels.
Inclusivity and Diversity Considerations
Self-contained classrooms provide tailored support for students with specific learning needs, fostering an environment optimized for individualized instruction and inclusivity. Heterogeneous grouping promotes diversity by integrating students of varied abilities and backgrounds, enhancing social interaction and collaborative learning experiences. Balancing both approaches ensures equitable access to education while addressing unique student requirements and encouraging inclusive peer engagement.
Challenges and Limitations of Self-contained Classrooms
Self-contained classrooms often face challenges such as limited peer interaction and reduced exposure to diverse learning styles, which can hinder social development and academic growth. These classrooms may also struggle with resource allocation and individualized instruction due to the wide range of student needs contained within a single setting. Furthermore, self-contained environments can inadvertently isolate students from the broader school community, limiting opportunities for cooperative learning and skill generalization.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Heterogeneous Grouping
Heterogeneous grouping promotes diverse learning experiences by combining students of varying abilities, which enhances peer learning and social development but may challenge teachers in addressing individual needs effectively. It fosters collaborative skills and reduces stigmatization associated with ability grouping, yet can lead to slower curriculum pacing and frustration for both advanced and struggling students. Balancing group dynamics requires strategic instruction to ensure equitable participation and maximize the benefits of diverse learning environments.
Choosing the Right Classroom Model: Key Factors to Consider
Choosing the right classroom model involves evaluating student diversity, academic needs, and resource availability. Self-contained classrooms provide targeted instruction for students with similar learning profiles, enhancing specialized support and consistency. Heterogeneous grouping promotes peer interaction and diverse perspectives, fostering social skills and collaborative learning, essential for inclusive education environments.
Self-contained Classrooms Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com