Traditional education emphasizes structured curricula, teacher-led instruction, and classroom settings to build foundational knowledge and skills. It fosters discipline, social interaction, and a systematic approach to learning, often preparing students for standardized assessments and academic progression. Explore the rest of the article to discover how traditional education impacts your learning journey and its evolving role in today's world.
Table of Comparison
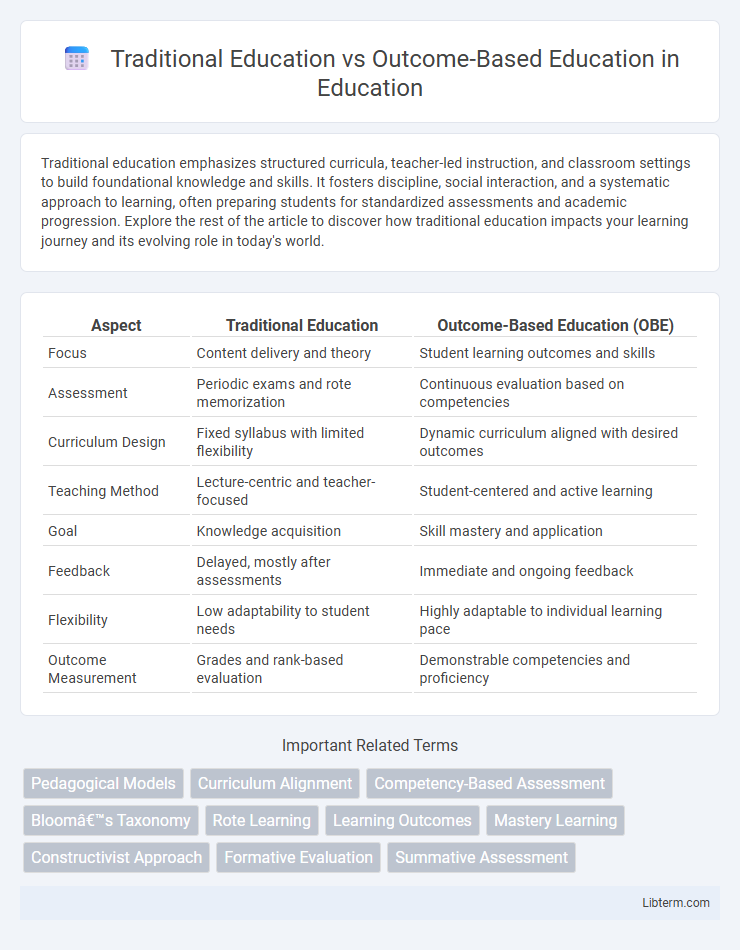
| Aspect | Traditional Education | Outcome-Based Education (OBE) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Content delivery and theory | Student learning outcomes and skills |
| Assessment | Periodic exams and rote memorization | Continuous evaluation based on competencies |
| Curriculum Design | Fixed syllabus with limited flexibility | Dynamic curriculum aligned with desired outcomes |
| Teaching Method | Lecture-centric and teacher-focused | Student-centered and active learning |
| Goal | Knowledge acquisition | Skill mastery and application |
| Feedback | Delayed, mostly after assessments | Immediate and ongoing feedback |
| Flexibility | Low adaptability to student needs | Highly adaptable to individual learning pace |
| Outcome Measurement | Grades and rank-based evaluation | Demonstrable competencies and proficiency |
Introduction to Traditional Education and Outcome-Based Education
Traditional education emphasizes teacher-centered instruction, fixed curricula, and standardized testing to assess student knowledge. Outcome-Based Education (OBE) focuses on clearly defined learning outcomes, student-centered teaching, and continuous assessment to ensure mastery of specific skills and competencies. Both approaches shape educational experiences but differ fundamentally in their methodologies and assessment strategies.
Historical Evolution of Educational Models
Traditional education, rooted in centuries-old methods, emphasized rote memorization and teacher-centered instruction aligned with industrial-age demands. Outcome-Based Education (OBE) emerged in the late 20th century as a response to globalization, prioritizing measurable skills and competencies to ensure students meet specific learning standards. This shift reflects a significant evolution from content-focused curricula to learner-centered models that adapt to the needs of modern economies and diverse student populations.
Core Principles of Traditional Education
Traditional education centers on a fixed curriculum designed to deliver standardized knowledge through direct instruction and memorization. It emphasizes teacher authority, uniform assessment methods, and structured learning environments to maintain consistency and discipline. The core principle lies in prioritizing content mastery and chronological progression over individual learner outcomes or competencies.
Defining Outcome-Based Education (OBE)
Outcome-Based Education (OBE) defines learning through clearly specified outcomes that students must achieve by the end of a course or program, emphasizing mastery of skills and knowledge rather than time spent in class. Unlike traditional education, which often centers on content coverage and instructor-led delivery, OBE prioritizes measurable student performance and competency. This approach aligns curriculum design, teaching methods, and assessments directly with desired learning outcomes, fostering accountability and continuous improvement in educational quality.
Curriculum Design: Content-Centered vs Learner-Centered Approaches
Traditional education emphasizes a content-centered curriculum design, focusing on standardized syllabi and fixed knowledge delivery. Outcome-based education prioritizes a learner-centered approach, tailoring content to achieve specific competencies and real-world skills. This shift enhances adaptability and aligns learning outcomes with individual student needs and market demands.
Assessment and Evaluation Methods Compared
Traditional education primarily relies on summative assessments such as exams and quizzes to measure student learning at the end of a course, often emphasizing memorization and recall. Outcome-Based Education (OBE) adopts continuous, formative assessments including projects, portfolios, and performance tasks that align directly with predefined learning outcomes to evaluate students' practical skills and conceptual understanding. OBE's evaluation methods prioritize mastery of competencies and real-world application, enabling personalized feedback and adaptive learning paths for improved educational effectiveness.
Role of Teachers and Learners in Each Model
In traditional education, teachers primarily serve as knowledge transmitters who direct learning, while learners adopt a passive role by receiving information and memorizing content. Outcome-Based Education shifts this dynamic by positioning teachers as facilitators and mentors who guide learners to achieve specific competencies and skills. Learners actively engage in self-directed learning, critical thinking, and application of knowledge to meet clearly defined outcomes.
Advantages and Limitations of Traditional Education
Traditional education emphasizes structured curricula, teacher-led instruction, and standardized assessments, providing clear benchmarks and consistency across learning environments. It fosters discipline and foundational knowledge through repetitive practice and memorization, which helps students develop strong basic skills. However, traditional education often limits critical thinking and adaptability, struggles to address diverse learning needs, and may not adequately prepare students for real-world problem-solving or evolving career demands.
Benefits and Challenges of Outcome-Based Education
Outcome-Based Education (OBE) emphasizes measurable learning outcomes, fostering student accountability and aligning curriculum with industry requirements for improved employability. The benefits of OBE include personalized learning paths, enhanced critical thinking skills, and clear assessment criteria that promote continuous improvement. Challenges involve the need for extensive faculty training, potential rigidity in curriculum design, and difficulties in assessing complex competencies beyond standardized metrics.
Future Trends and Implications for Educational Reform
Future trends in educational reform emphasize a shift from Traditional Education's content delivery model to Outcome-Based Education's competency-focused framework, highlighting personalized learning and measurable skill acquisition. This transition supports adaptive curricula reinforcing critical thinking, problem-solving, and lifelong learning skills critical in the evolving job market. Integrating technology and data analytics will further optimize learning outcomes and facilitate continuous system improvements aligned with workforce demands.
Traditional Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com