The implicit curriculum refers to the unspoken or hidden lessons, values, and norms that students learn indirectly through the educational environment and interactions rather than formal instruction. This subtle transmission of social and cultural expectations shapes Your overall educational experience and personal development. Explore the rest of the article to understand how the implicit curriculum influences learning outcomes and classroom dynamics.
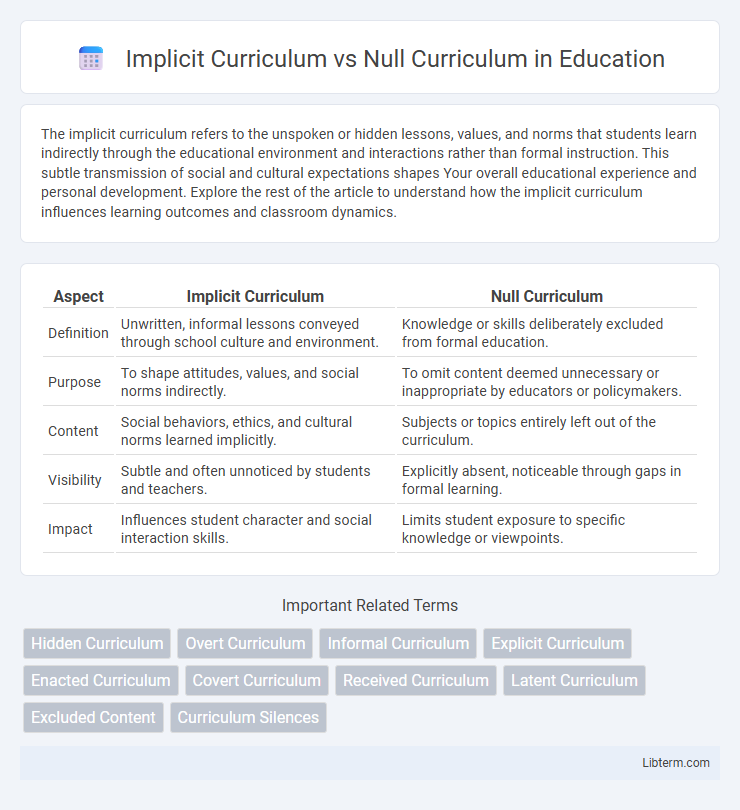
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Implicit Curriculum | Null Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unwritten, informal lessons conveyed through school culture and environment. | Knowledge or skills deliberately excluded from formal education. |
| Purpose | To shape attitudes, values, and social norms indirectly. | To omit content deemed unnecessary or inappropriate by educators or policymakers. |
| Content | Social behaviors, ethics, and cultural norms learned implicitly. | Subjects or topics entirely left out of the curriculum. |
| Visibility | Subtle and often unnoticed by students and teachers. | Explicitly absent, noticeable through gaps in formal learning. |
| Impact | Influences student character and social interaction skills. | Limits student exposure to specific knowledge or viewpoints. |
Understanding Implicit Curriculum: Definition and Characteristics
Implicit curriculum refers to the unwritten, unofficial lessons, values, and perspectives students learn in school that are not part of the formal curriculum. It includes social norms, attitudes, and behaviors conveyed through classroom interactions, teacher attitudes, and institutional culture. Understanding implicit curriculum involves recognizing its powerful role in shaping student identity, social skills, and ethical frameworks beyond academic content.
Exploring Null Curriculum: What Is Left Unsaid
The null curriculum refers to the knowledge and skills intentionally or unintentionally omitted from educational programs, highlighting what is left unsaid or unexplored within formal instruction. Unlike the implicit curriculum, which conveys unspoken values and norms through the learning environment, the null curriculum emphasizes the gaps and absences that shape students' understanding by what they do not learn. This exploration reveals how omissions influence students' perceptions, critically affecting educational equity and the comprehensiveness of knowledge transmission.
Key Differences Between Implicit and Null Curriculum
Implicit curriculum encompasses the lessons and values students learn indirectly through school culture and teacher attitudes, influencing social norms and behaviors. Null curriculum refers to the content and topics deliberately omitted or excluded from the formal curriculum, reflecting societal or institutional priorities and biases. The key difference lies in implicit curriculum's subtle, unintended transmission of knowledge versus null curriculum's conscious absence of specific subjects or materials.
The Role of Teachers in Shaping Implicit Curriculum
Teachers play a pivotal role in shaping the implicit curriculum through their attitudes, behaviors, and interactions, which convey values and social norms beyond formal lesson plans. Their expectations and classroom management strategies subtly influence students' socialization, motivation, and identity formation. Recognizing this influence allows educators to consciously foster an inclusive and supportive learning environment that addresses equity and cultural responsiveness.
Societal Impacts of the Null Curriculum
The null curriculum, representing what is deliberately excluded from formal education, profoundly shapes societal values by signaling which knowledge and perspectives are deemed unimportant or unacceptable. This omission can perpetuate societal inequalities and reinforce dominant cultural narratives by marginalizing minority viewpoints and critical topics such as social justice, environmental issues, or marginalized histories. Consequently, the null curriculum influences collective consciousness and social identity, affecting public discourse, civic engagement, and policy priorities.
Hidden Messages: How Implicit Curriculum Influences Students
Implicit curriculum conveys hidden messages through unspoken norms, values, and attitudes embedded within the school environment, influencing students' social behavior and worldview beyond formal lessons. These underlying lessons impact students' ethical development, sense of belonging, and attitudes towards authority, often reinforcing societal expectations and cultural biases. In contrast, the null curriculum--the content intentionally left out--silences certain perspectives, shaping students' understanding by omission and indirectly reflecting educational priorities and power structures.
Unintended Consequences of Omitting Topics (Null Curriculum)
Omitting topics in the null curriculum leads to significant unintended consequences, such as reinforcing systemic biases and perpetuating knowledge gaps that hinder student critical thinking and cultural awareness. The absence of diverse perspectives or controversial subjects implicitly communicates societal values and norms, shaping students' worldview without explicit teaching. This silent endorsement can marginalize certain groups and limit the development of comprehensive, inclusive educational outcomes.
Addressing Bias in Implicit and Null Curricula
Addressing bias in implicit and null curricula requires identifying hidden messages and omitted content that perpetuate stereotypes and exclusion. Implicit curriculum conveys societal norms through unspoken lessons, while null curriculum excludes critical topics, both reinforcing systemic biases if unexamined. Proactive curriculum audits and inclusive policymaking help mitigate these biases, promoting equity and diversity in educational environments.
Strategies for Making the Implicit and Null Curriculum Visible
Strategies for making the implicit curriculum visible include comprehensive teacher training to identify underlying values and attitudes conveyed in classroom interactions and instructional materials. To address the null curriculum, educators conduct systematic curriculum audits to uncover omitted but essential knowledge and skills, ensuring these gaps are intentionally integrated into lesson planning. Engaging diverse stakeholders such as students, parents, and community members provides critical perspectives that reveal hidden biases and neglected content within both implicit and null curricula.
Implications for Educational Policy and Curriculum Design
Implicit curriculum shapes students' values and social norms through unspoken lessons embedded in school culture, affecting equity and inclusivity in education policy. Null curriculum, the content deliberately or unintentionally excluded from instruction, highlights biases and gaps that policymakers must address to ensure comprehensive educational experiences. Effective curriculum design requires balancing explicit objectives with awareness of implicit and null curricula to foster holistic student development and promote social justice.
Implicit Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com