The Direct Method emphasizes immersive language learning by focusing on speaking and listening skills through real-life conversations. It avoids translation and grammar rules, promoting natural language acquisition by encouraging learners to think and respond in the target language. Discover how this approach can transform your language learning experience by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
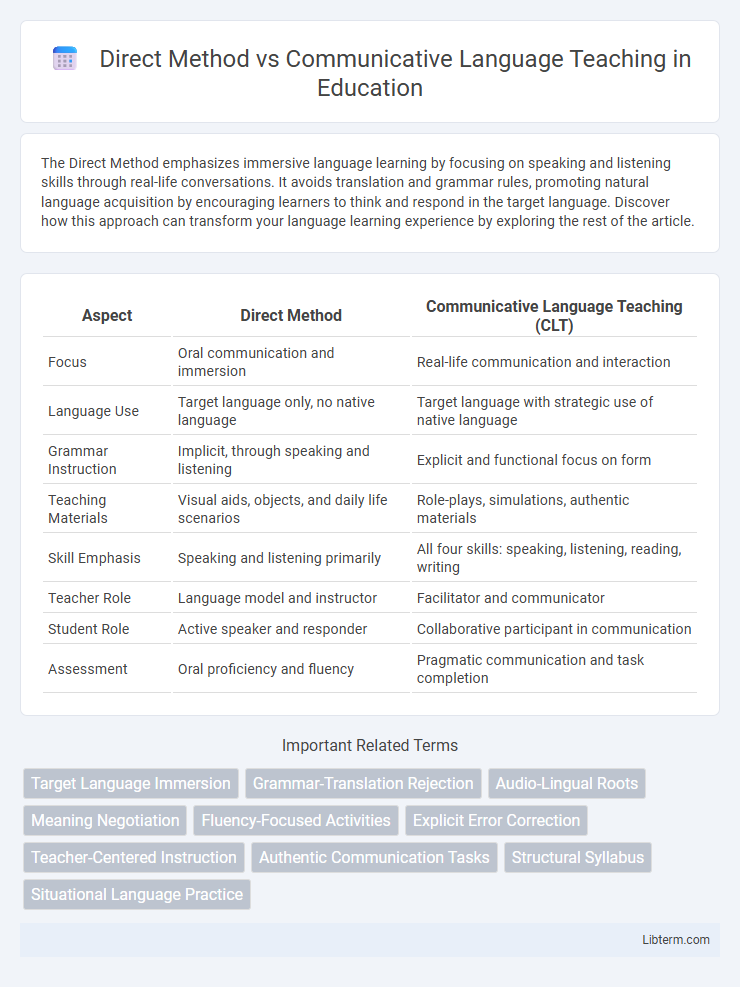
| Aspect | Direct Method | Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Oral communication and immersion | Real-life communication and interaction |
| Language Use | Target language only, no native language | Target language with strategic use of native language |
| Grammar Instruction | Implicit, through speaking and listening | Explicit and functional focus on form |
| Teaching Materials | Visual aids, objects, and daily life scenarios | Role-plays, simulations, authentic materials |
| Skill Emphasis | Speaking and listening primarily | All four skills: speaking, listening, reading, writing |
| Teacher Role | Language model and instructor | Facilitator and communicator |
| Student Role | Active speaker and responder | Collaborative participant in communication |
| Assessment | Oral proficiency and fluency | Pragmatic communication and task completion |
Introduction to Language Teaching Methods
The Direct Method emphasizes immersive, natural language learning through speaking and listening without translation, focusing on vocabulary and grammar in context. Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) prioritizes interaction and real-life communication, integrating speaking, listening, reading, and writing to develop communicative competence. Both methods aim to improve language proficiency but differ in their approach to grammar instruction and classroom dynamics.
Overview of the Direct Method
The Direct Method emphasizes immersive language instruction by using target language exclusively, focusing on oral communication and everyday vocabulary without translation. It encourages spontaneous use of language, promoting listening and speaking skills through question-answer exchanges and visual aids. This approach contrasts with grammar-focused methods as it prioritizes natural language acquisition and contextual learning.
Principles of Communicative Language Teaching
Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) prioritizes interaction and real-life communication, emphasizing fluency and meaningful language use over rote memorization or explicit grammar instruction. This approach encourages learner-centered activities, authentic materials, and the development of all language skills through contextually relevant practice. Unlike the Direct Method, which focuses on direct association between words and objects, CLT fosters negotiation of meaning and learner autonomy to promote communicative competence in diverse social contexts.
Historical Development and Origins
The Direct Method originated in the late 19th century as a reaction against grammar-translation, emphasizing immersive oral practice and avoiding native language use. Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) emerged in the 1970s, influenced by linguists like Dell Hymes, focusing on real-life communication and functional language use rather than rote memorization. Both methods reflect shifts in language pedagogy from structural accuracy toward interactive competence.
Classroom Techniques in the Direct Method
The Direct Method emphasizes immersive language acquisition through speaking and listening activities that avoid translation, relying heavily on question-and-answer exchanges, demonstrations, and visual aids to teach vocabulary and grammar intuitively. Classroom Techniques include daily use of the target language, thematic vocabulary introduction, and prioritizing oral skills via interactive drills and natural speech patterns. This approach fosters spontaneous communication by encouraging students to think and respond directly in the target language without referring to their native tongue.
Communicative Activities and Strategies
Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) emphasizes real-life communicative activities such as role-plays, information gap tasks, and group discussions, fostering spontaneous language use and interaction. Unlike the Direct Method, which relies heavily on repetition and drilling, CLT promotes learner-centered strategies that enhance fluency and pragmatic competence through meaningful exchanges. Effective communicative strategies include task-based learning, collaborative problem-solving, and authentic material integration, all aimed at developing learners' ability to use language contextually and socially.
Strengths of the Direct Method
The Direct Method emphasizes immersive language learning through speaking and listening in real-life contexts, enhancing fluency and pronunciation. It fosters natural language acquisition by avoiding translation and grammar explanations, which strengthens intuitive understanding. Learners develop spontaneous communication skills and improve retention through constant oral practice and immediate feedback.
Advantages of Communicative Language Teaching
Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) emphasizes real-life communication and interaction, enhancing learners' speaking and listening skills more effectively than the Direct Method. CLT supports contextual learning through authentic materials and meaningful tasks, promoting deeper language retention and practical usage. This approach fosters learner autonomy and confidence by encouraging collaborative activities and problem-solving in conversational settings.
Key Differences Between the Methods
The Direct Method emphasizes immersive language learning through speaking and listening without translation, focusing on everyday vocabulary and proper pronunciation, whereas Communicative Language Teaching prioritizes interaction and using language in real-life contexts to develop communicative competence. The Direct Method typically avoids grammar explanations, relying on contextual cues, while Communicative Language Teaching integrates grammar instruction within meaningful communication activities. Assessment in the Direct Method centers on oral proficiency, while Communicative Language Teaching evaluates the ability to effectively convey and interpret messages in diverse situations.
Choosing the Right Method for Learners
Choosing the right method for language learners depends on their communicative goals, learning style, and context; the Direct Method emphasizes immersive, spoken language practice ideal for beginners seeking natural conversation skills, while Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) focuses on interactive, real-life communication scenarios that benefit intermediate to advanced learners aiming to develop fluency and pragmatic competence. Assessment of learner needs, cultural environment, and available resources guides educators in selecting between these approaches for maximum language acquisition effectiveness. Tailoring instruction with a blend of Direct Method's emphasis on oral skills and CLT's strategic interaction enhances learner engagement and proficiency in diverse settings.
Direct Method Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com