A well-designed classroom environment enhances student engagement and fosters effective learning by incorporating natural light, comfortable seating, and organized learning materials. Flexible layouts and interactive displays support different teaching styles and promote collaboration among students, creating a positive and inclusive atmosphere. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips for optimizing your classroom environment.
Table of Comparison
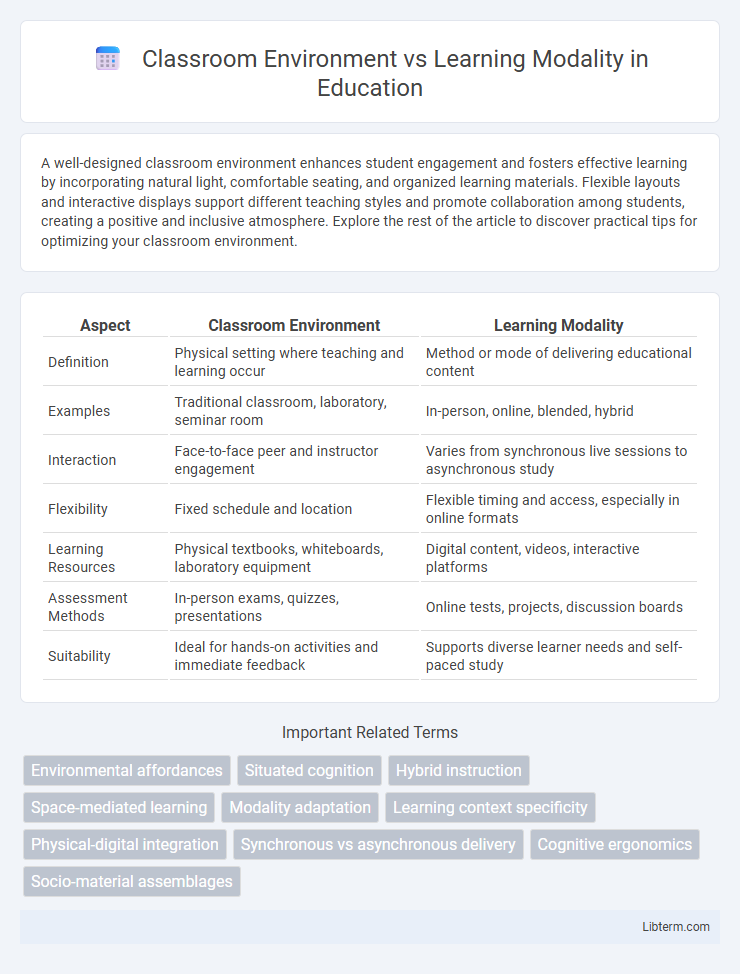
| Aspect | Classroom Environment | Learning Modality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical setting where teaching and learning occur | Method or mode of delivering educational content |
| Examples | Traditional classroom, laboratory, seminar room | In-person, online, blended, hybrid |
| Interaction | Face-to-face peer and instructor engagement | Varies from synchronous live sessions to asynchronous study |
| Flexibility | Fixed schedule and location | Flexible timing and access, especially in online formats |
| Learning Resources | Physical textbooks, whiteboards, laboratory equipment | Digital content, videos, interactive platforms |
| Assessment Methods | In-person exams, quizzes, presentations | Online tests, projects, discussion boards |
| Suitability | Ideal for hands-on activities and immediate feedback | Supports diverse learner needs and self-paced study |
Introduction to Classroom Environment and Learning Modality
Classroom environment significantly influences student engagement and academic performance by shaping the physical, social, and psychological aspects of learning spaces. Learning modality refers to the method through which instruction is delivered, such as face-to-face, online, or blended formats, each catering to diverse learner preferences and needs. Understanding the interplay between classroom environment and learning modality is essential for optimizing educational outcomes and fostering effective knowledge acquisition.
Defining Classroom Environment: Key Elements
Classroom environment encompasses the physical setting, social dynamics, and psychological atmosphere that influence student engagement and learning outcomes. Key elements include seating arrangement, lighting, classroom decor, and availability of learning resources, all of which contribute to creating an inclusive and stimulating space. Effective classroom environments foster collaboration, motivation, and student-centered learning, directly impacting academic performance and well-being.
Types of Learning Modalities Explained
Learning modalities encompass various instructional methods such as visual, auditory, kinesthetic, and reading/writing, each catering to different student preferences and cognitive processes. The classroom environment plays a crucial role in effectively implementing these modalities by providing appropriate resources, technology, and physical arrangements that enhance engagement and knowledge retention. Understanding and integrating diverse learning modalities promote personalized education, leading to improved academic outcomes and student motivation.
Physical Classroom vs Virtual Classroom Dynamics
Physical classroom environments facilitate direct interaction through face-to-face communication, which enhances social cues and immediate feedback critical for active learning and collaboration. Virtual classroom dynamics rely heavily on digital tools and platforms that enable flexible scheduling and access but can limit non-verbal communication and spontaneous peer interactions. Research shows that engagement levels and learning outcomes in physical classrooms often benefit from tangible presence, whereas virtual settings demand structured facilitation and technological proficiency to maximize educational effectiveness.
How Environment Influences Student Engagement
Classroom environment significantly shapes student engagement by providing physical and psychological stimuli that enhance focus and motivation. Factors such as lighting, seating arrangement, and noise levels directly impact attention spans and participation rates in both traditional and virtual learning modalities. Creating adaptive spaces that align with specific learning modalities encourages active involvement and improves overall academic outcomes.
Impact of Learning Modality on Academic Performance
Learning modality significantly shapes academic performance by determining how students engage with material and instructors. Studies show that blended and active learning modalities often enhance comprehension and retention compared to traditional classroom settings. Personalized learning environments that adapt modality to student needs promote higher achievement and motivation.
Teacher Roles Across Different Modalities and Environments
Teacher roles shift significantly across classroom environments and learning modalities, adapting instructional strategies to maximize student engagement and comprehension. In traditional classrooms, educators facilitate direct interaction and immediate feedback, while in virtual settings, they function as digital guides, leveraging technology to foster collaboration and self-paced learning. Hybrid models require teachers to balance synchronous and asynchronous methods, ensuring equitable access and personalized support for diverse learner needs.
Student Collaboration: Environment vs Modality
Classroom environment significantly influences student collaboration by providing physical spaces designed for group interaction, such as round tables and breakout areas that encourage face-to-face communication. In contrast, learning modality affects collaboration through digital tools and platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, or Google Classroom, which facilitate virtual teamwork and real-time interaction despite geographical barriers. Effective student collaboration often combines an engaging classroom environment with interactive learning modalities to enhance communication, participation, and group problem-solving skills.
Technological Integration in Various Learning Contexts
Technological integration in classroom environments enhances learning modalities by enabling interactive and personalized experiences through digital tools such as smartboards, learning management systems, and virtual reality. Diverse learning contexts, including hybrid, remote, and traditional settings, leverage technology to support collaborative activities, real-time feedback, and access to multimedia resources. Effective use of technology fosters student engagement, accommodates diverse learning preferences, and improves educational outcomes across various instructional formats.
Choosing the Optimal Combination for Effective Learning
Classroom environment and learning modality play crucial roles in student engagement and knowledge retention, with evidence indicating that tailored combinations enhance cognitive outcomes. Research in educational psychology reveals that active learning techniques paired with collaborative classroom settings significantly improve critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Selecting the optimal blend, such as hybrid models incorporating both in-person interaction and digital resources, maximizes flexibility while maintaining instructional efficacy.
Classroom Environment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com