Project-Based Learning empowers students to actively engage in real-world challenges, fostering critical thinking and collaboration skills. This hands-on approach deepens understanding by connecting theory with practical application, enhancing retention and motivation. Explore the article to discover how Project-Based Learning can transform your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
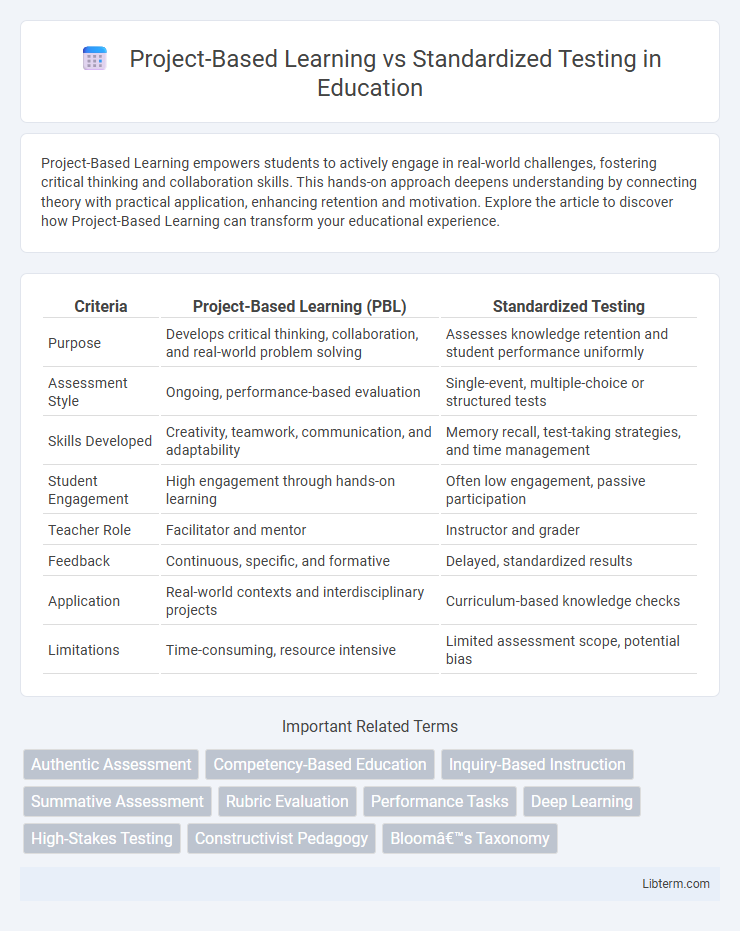
| Criteria | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Standardized Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Develops critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem solving | Assesses knowledge retention and student performance uniformly |
| Assessment Style | Ongoing, performance-based evaluation | Single-event, multiple-choice or structured tests |
| Skills Developed | Creativity, teamwork, communication, and adaptability | Memory recall, test-taking strategies, and time management |
| Student Engagement | High engagement through hands-on learning | Often low engagement, passive participation |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and mentor | Instructor and grader |
| Feedback | Continuous, specific, and formative | Delayed, standardized results |
| Application | Real-world contexts and interdisciplinary projects | Curriculum-based knowledge checks |
| Limitations | Time-consuming, resource intensive | Limited assessment scope, potential bias |
Understanding Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes hands-on, real-world problem solving, enhancing critical thinking and retention through active engagement. Unlike Standardized Testing, which measures rote memorization and recall under timed conditions, PBL fosters deep conceptual understanding and collaboration. Research shows students in PBL environments demonstrate improved creativity, communication skills, and long-term knowledge application compared to those assessed primarily by standardized exams.
What Is Standardized Testing?
Standardized testing refers to a uniform assessment method where all test-takers answer the same questions under consistent conditions, enabling objective comparison of performance across diverse populations. These tests measure specific academic skills or knowledge, often used for accountability and benchmarking in educational systems. Critics argue standardized testing can limit creativity and fail to capture critical thinking and problem-solving abilities emphasized in project-based learning.
Key Differences Between PBL and Standardized Testing
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes hands-on, real-world problem solving that fosters critical thinking, collaboration, and creativity, diverging from the rigid structure of standardized testing that prioritizes memorization and uniform assessment metrics. PBL assessments are dynamic, involving formative feedback and student-driven exploration, while standardized tests rely on summative evaluations with predetermined answers to gauge knowledge. The key difference lies in PBL's focus on process and application of knowledge, contrasted with standardized testing's emphasis on quantifiable outcomes and conformity.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Project-Based Learning significantly enhances student engagement and motivation by fostering active participation, creativity, and real-world problem-solving skills, which standardize testing often fails to address. Unlike standardized tests that emphasize rote memorization and conformity, PBL encourages collaborative learning and critical thinking, leading to deeper understanding and sustained interest in the subject matter. Research indicates students involved in PBL demonstrate higher intrinsic motivation and improved academic performance due to meaningful, personalized learning experiences.
Measuring Academic Success
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes assessing students through real-world problem solving and critical thinking, offering a comprehensive measure of academic success beyond rote memorization. Standardized testing quantifies knowledge through uniform metrics, often focusing on specific content mastery and skill proficiency under timed conditions. While PBL captures deeper understanding and application, standardized tests provide comparability and scalability in assessing academic performance across large populations.
Skill Development: Critical Thinking vs Memorization
Project-Based Learning fosters critical thinking by engaging students in real-world problems that require analysis, evaluation, and creative solutions, thereby enhancing practical skill development. In contrast, Standardized Testing emphasizes memorization and recall of factual information, often limiting opportunities for deep understanding and innovative problem-solving. This emphasis on rote learning can hinder the cultivation of higher-order thinking skills essential for adapting to complex, dynamic environments.
Flexibility in Curriculum and Assessment
Project-Based Learning offers greater flexibility in curriculum design by allowing educators to tailor content to students' interests and real-world applications, fostering deeper engagement. Unlike Standardized Testing, which relies on uniform assessments that measure specific knowledge points, Project-Based Learning emphasizes diverse evaluation methods such as presentations, portfolios, and collaborative projects, accommodating various learning styles. This adaptability enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills, making curriculum and assessment more responsive to individual student needs and educational goals.
Impact on Teacher Roles
Project-Based Learning transforms teacher roles from information deliverers to facilitators and mentors, encouraging personalized guidance and collaboration. Standardized testing shifts teacher focus toward test preparation and curriculum alignment, often limiting instructional creativity and responsiveness. This divergence profoundly impacts teacher autonomy, professional development, and classroom dynamics.
Real-World Applications and Relevance
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes real-world applications by engaging students in hands-on, collaborative projects that mirror authentic challenges found in professional environments. Unlike standardized testing, which primarily assesses rote memorization and theoretical knowledge, PBL fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and adaptability skills essential for dynamic workplace settings. This approach enhances relevance by connecting academic content to practical scenarios, thereby increasing student motivation and retention through meaningful, context-driven experiences.
Future Implications for Education Reform
Project-Based Learning (PBL) fosters critical thinking, creativity, and real-world problem-solving skills essential for the evolving workforce, contrasting with the narrow focus of standardized testing on memorization and rote learning. Shifting education reform towards PBL can enhance student engagement and better prepare learners for a dynamic, technology-driven economy. Emphasizing PBL over standardized testing supports the development of adaptive competencies necessary for future career success and lifelong learning.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com