Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and deep understanding by encouraging students to explore questions and problems actively. This approach promotes curiosity and empowers learners to construct knowledge through investigation rather than passive consumption. Discover how integrating inquiry-based strategies can transform Your educational experience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
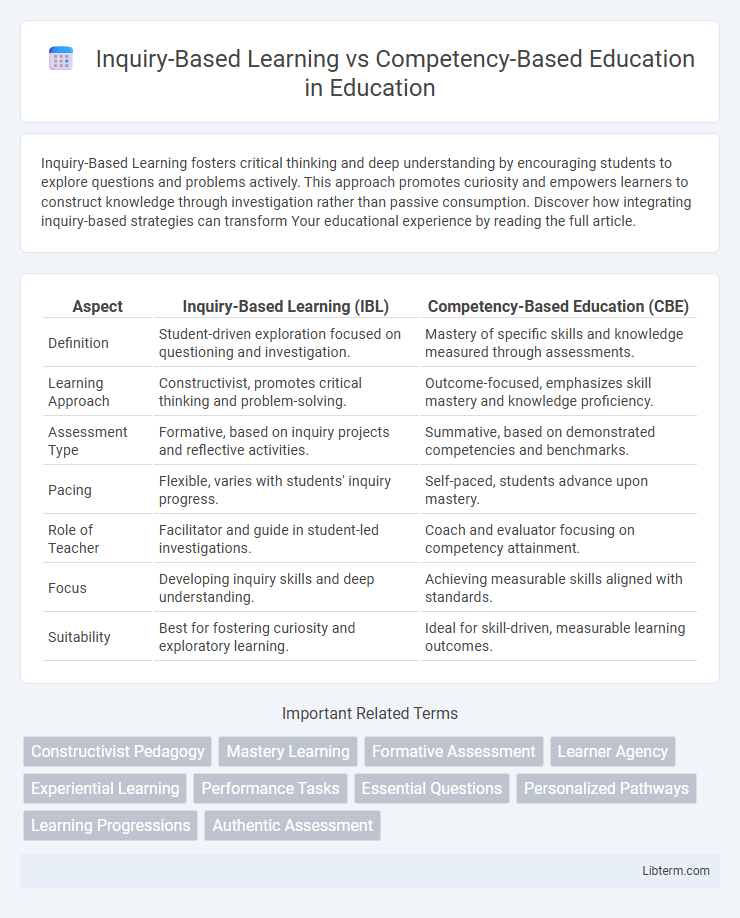
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning (IBL) | Competency-Based Education (CBE) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-driven exploration focused on questioning and investigation. | Mastery of specific skills and knowledge measured through assessments. |
| Learning Approach | Constructivist, promotes critical thinking and problem-solving. | Outcome-focused, emphasizes skill mastery and knowledge proficiency. |
| Assessment Type | Formative, based on inquiry projects and reflective activities. | Summative, based on demonstrated competencies and benchmarks. |
| Pacing | Flexible, varies with students' inquiry progress. | Self-paced, students advance upon mastery. |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and guide in student-led investigations. | Coach and evaluator focusing on competency attainment. |
| Focus | Developing inquiry skills and deep understanding. | Achieving measurable skills aligned with standards. |
| Suitability | Best for fostering curiosity and exploratory learning. | Ideal for skill-driven, measurable learning outcomes. |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning (IBL) centers on student-driven questioning, exploration, and critical thinking to deepen understanding and foster a hands-on approach to knowledge acquisition. Unlike traditional methods, IBL emphasizes active engagement and the development of investigative skills, encouraging learners to construct meaning through real-world problems. This educational framework aligns with modern pedagogical goals by promoting curiosity, self-direction, and analytical reasoning essential for lifelong learning.
Overview of Competency-Based Education
Competency-Based Education (CBE) emphasizes mastery of specific skills and knowledge, allowing learners to progress at their own pace upon demonstrating competence. This personalized approach aligns assessments directly with defined outcomes, ensuring that students achieve measurable proficiency before advancing. CBE is widely implemented in vocational training and higher education to enhance practical skills and workforce readiness.
Key Principles of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes student-driven exploration, fostering critical thinking through questioning, investigating, and reflecting on real-world problems. Its key principles include promoting curiosity, encouraging active learning, and developing problem-solving skills by allowing learners to construct knowledge independently. This approach contrasts with Competency-Based Education, which prioritizes mastery of specific skills and measurable outcomes over the exploratory process.
Core Components of Competency-Based Education
Competency-Based Education (CBE) centers on mastering specific skills and knowledge through personalized pacing, clear learning objectives, and measurable outcomes. Core components include flexible progression, where students advance upon demonstrating proficiency rather than seat time, comprehensive assessments targeting real-world skills, and individualized support tailored to learner needs. This contrasts with Inquiry-Based Learning's emphasis on open-ended questioning and exploration, as CBE prioritizes concrete competencies aligned with career and academic standards.
Comparing Goals: Curiosity vs Mastery
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes fostering curiosity by encouraging students to ask questions and explore topics deeply, promoting critical thinking and engagement. Competency-Based Education prioritizes mastery of specific skills and knowledge, ensuring learners achieve measurable proficiencies before progressing. The primary goal of Inquiry-Based Learning is cultivating intrinsic motivation and discovery, whereas Competency-Based Education focuses on demonstrable outcomes and skill acquisition.
Pedagogical Approaches and Classroom Strategies
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on student-driven questioning and exploration, promoting critical thinking through hands-on experiments and collaborative problem-solving activities. Competency-Based Education emphasizes mastery of specific skills and knowledge, using personalized learning paths, clear performance criteria, and frequent assessments to ensure students achieve defined competencies. Teachers in inquiry-based settings act as facilitators guiding inquiry processes, whereas in competency-based environments, educators provide targeted support and feedback aligned with individual learning progressions.
Assessment Methods in Both Models
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes formative assessments such as observations, reflective journals, and project presentations to gauge students' critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Competency-Based Education relies heavily on performance-based assessments, including skill demonstrations and mastery tests, to ensure students achieve specific learning outcomes. Both models prioritize authentic assessments but differ in their approach to measuring progress--Inquiry-Based Learning focuses on process and understanding, while Competency-Based Education centers on measurable competencies.
Benefits and Challenges of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking, creativity, and student engagement by encouraging exploration and questioning, which enhances deeper understanding and knowledge retention. However, challenges include the need for skilled facilitators, longer time requirements for curriculum completion, and potential difficulties in assessing student progress objectively. Despite these obstacles, maintaining a flexible learning environment and promoting collaborative problem-solving remain key benefits that drive meaningful educational experiences.
Advantages and Limitations of Competency-Based Education
Competency-Based Education (CBE) allows students to progress at their own pace by demonstrating mastery of specific skills and knowledge, offering personalized learning experiences and improved skill retention. It enhances workforce readiness by aligning curricula directly with industry standards and competency requirements but may limit creativity and critical thinking by focusing heavily on measurable outcomes. Challenges include the need for robust assessment systems and potential difficulties in standardizing competencies across diverse educational settings.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between inquiry-based learning and competency-based education depends on factors such as student autonomy, skill mastery, and assessment methods. Inquiry-based learning emphasizes critical thinking and exploration, ideal for fostering creativity and problem-solving skills. Competency-based education focuses on measurable skills and personalized pacing, making it suitable for clear learning outcomes and progress tracking.
Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com