A Content Management System (CMS) simplifies the process of creating, managing, and publishing digital content without requiring advanced technical skills. It offers customizable templates, efficient workflow management, and integration with various plugins to enhance website functionality. Explore the full article to discover how a CMS can transform your content strategy and boost online presence.
Table of Comparison
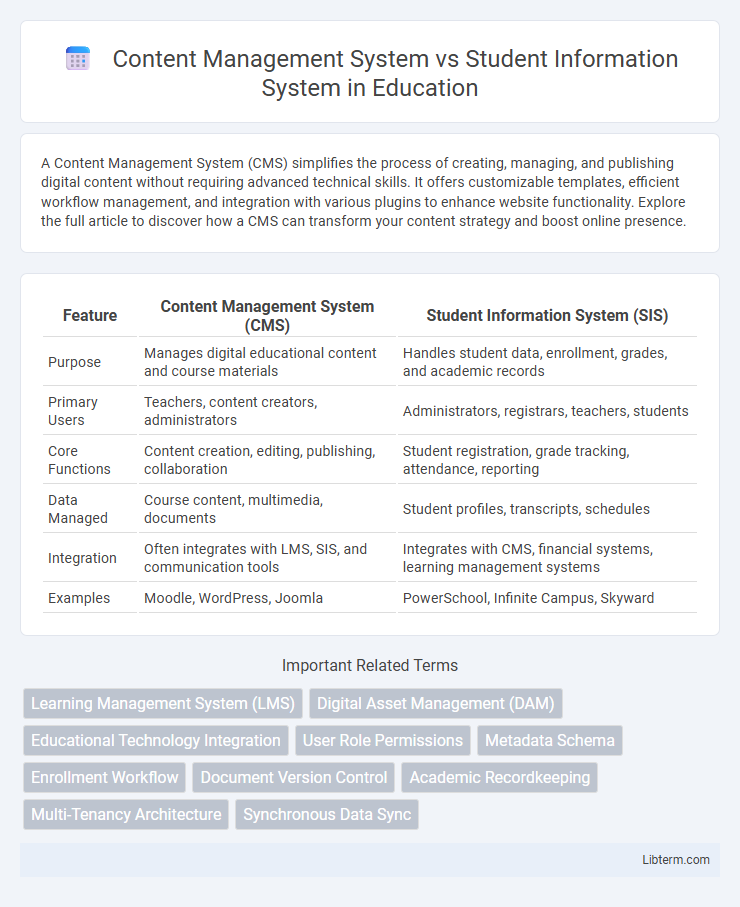
| Feature | Content Management System (CMS) | Student Information System (SIS) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Manages digital educational content and course materials | Handles student data, enrollment, grades, and academic records |
| Primary Users | Teachers, content creators, administrators | Administrators, registrars, teachers, students |
| Core Functions | Content creation, editing, publishing, collaboration | Student registration, grade tracking, attendance, reporting |
| Data Managed | Course content, multimedia, documents | Student profiles, transcripts, schedules |
| Integration | Often integrates with LMS, SIS, and communication tools | Integrates with CMS, financial systems, learning management systems |
| Examples | Moodle, WordPress, Joomla | PowerSchool, Infinite Campus, Skyward |
Understanding Content Management Systems (CMS)
Content Management Systems (CMS) facilitate the creation, management, and modification of digital content, enabling non-technical users to easily publish web pages and multimedia. A CMS offers tools such as content editing, version control, and workflow management, streamlining content collaboration and website maintenance. Unlike Student Information Systems (SIS), which handle academic records and student data, CMS platforms focus primarily on content organization and presentation across websites.
Defining Student Information Systems (SIS)
A Student Information System (SIS) is a specialized software platform designed to manage and streamline student data, including enrollment, attendance, grades, and academic records. Unlike Content Management Systems (CMS), which primarily handle digital content creation and distribution, SIS focuses on administrative tasks and institutional reporting. Effective SIS solutions integrate with learning management systems and enable real-time data access for educators, students, and administrators.
Core Features of CMS vs SIS
Content Management Systems (CMS) primarily offer features like content creation, editing, publishing workflows, and digital asset management tailored for managing websites and multimedia. Student Information Systems (SIS) focus on managing student data, including enrollment, attendance, grades, and scheduling, with specialized modules for academic tracking and reporting. CMS enables efficient content organization and user role management, while SIS ensures secure handling of sensitive educational records and compliance with institutional policies.
Primary Use Cases for CMS and SIS
Content Management Systems (CMS) primarily facilitate the creation, management, and distribution of digital content, supporting websites, blogs, and intranet portals with tools for editing, publishing, and collaboration. Student Information Systems (SIS) focus on managing student data, including enrollment, attendance, grades, and schedules, providing academic institutions with comprehensive administrative and reporting capabilities. While CMS enhances content delivery and user engagement, SIS streamlines educational operations and maintains secure, organized student records.
User Roles: Who Uses CMS and SIS?
Content Management Systems (CMS) primarily serve content creators, editors, administrators, and site visitors, facilitating tasks such as content publishing, editing, and website management. Student Information Systems (SIS) are designed for educational administrators, teachers, students, and parents, providing functionalities for managing student enrollment, grades, attendance, and academic records. The distinct user roles reflect the differing core purposes: CMS focuses on managing digital content and web presence, while SIS centers on organizing and accessing academic and administrative student data.
Integration Capabilities: CMS and SIS
Content Management Systems (CMS) and Student Information Systems (SIS) offer distinct integration capabilities essential for educational institutions. CMS platforms excel at seamlessly integrating with various third-party tools such as learning management systems, social media, and analytics software to enhance content delivery and user engagement. In contrast, SIS solutions prioritize robust integration with administrative and academic systems including enrollment databases, grading software, and financial management tools to streamline student records and operational workflows.
Data Security and Privacy Considerations
Content Management Systems (CMS) and Student Information Systems (SIS) differ significantly in data security and privacy considerations; SIS handles sensitive student records requiring stringent compliance with FERPA and GDPR regulations, while CMS primarily manages public or semi-private content with fewer regulatory constraints. Encryption protocols, role-based access controls, and secure authentication methods are critical in SIS to prevent unauthorized access to student grades, personal data, and attendance records. CMS security measures focus more on preventing content breaches and managing user permissions for editors and administrators to safeguard intellectual property and organizational information.
Customization and Scalability Comparison
Content Management Systems (CMS) offer extensive customization options through modular plugins and themes, enabling tailored user interfaces and workflows to meet diverse organizational needs. Student Information Systems (SIS) prioritize scalability to handle growing student populations and complex academic data, often featuring robust database structures optimized for educational environments. While CMS customization focuses on content presentation flexibility, SIS scalability emphasizes efficient data management and integration with institutional systems.
Cost and Implementation Factors
Content Management Systems (CMS) generally offer lower initial costs and faster implementation compared to Student Information Systems (SIS), which require more complex customization and integration with existing academic databases. CMS solutions often use open-source or subscription-based pricing models, while SIS implementations involve higher upfront investment due to specialized modules for enrollment, grading, and compliance. The total cost of ownership for SIS includes ongoing maintenance, training, and support, reflecting its critical role in managing sensitive student data and institutional workflows.
Choosing the Right Solution for Educational Institutions
Educational institutions must evaluate their primary needs when choosing between a Content Management System (CMS) and a Student Information System (SIS). A CMS excels in organizing, delivering, and managing educational content and resources, enhancing teaching and learning experiences, whereas an SIS focuses on managing student data, enrollment, grades, and administrative functions. Prioritizing features like data integration, user accessibility, and scalability ensures the selected solution effectively supports academic goals and operational efficiency.
Content Management System Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com