Segregated skill instruction isolates specific skills for focused learning, enabling targeted improvement and mastery. This method enhances your ability to concentrate on individual competencies without distraction, leading to more efficient knowledge acquisition. Explore the rest of the article to discover how segregated skill instruction can transform your learning approach.
Table of Comparison
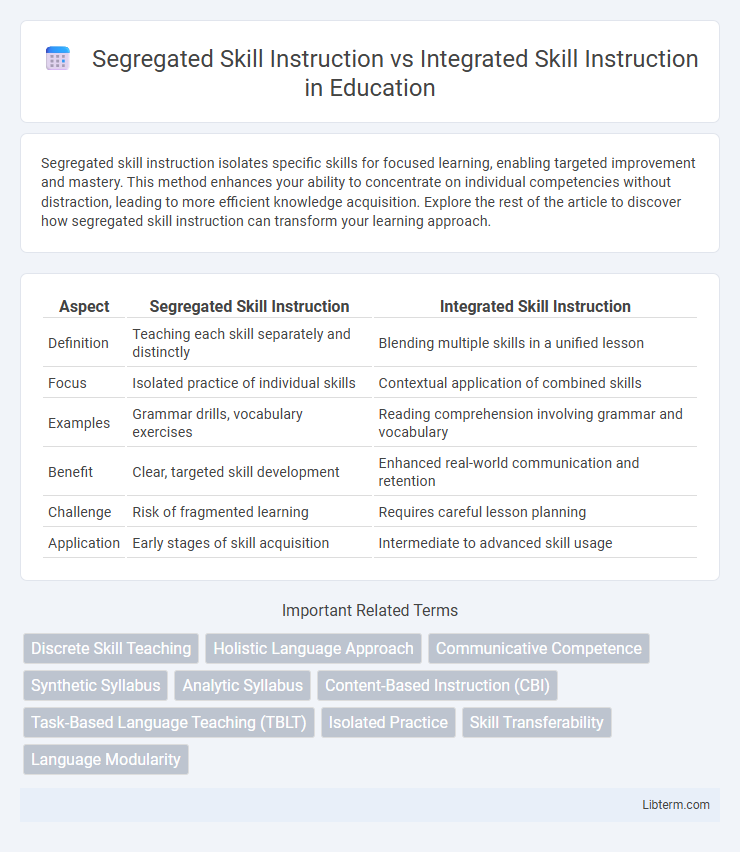
| Aspect | Segregated Skill Instruction | Integrated Skill Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teaching each skill separately and distinctly | Blending multiple skills in a unified lesson |
| Focus | Isolated practice of individual skills | Contextual application of combined skills |
| Examples | Grammar drills, vocabulary exercises | Reading comprehension involving grammar and vocabulary |
| Benefit | Clear, targeted skill development | Enhanced real-world communication and retention |
| Challenge | Risk of fragmented learning | Requires careful lesson planning |
| Application | Early stages of skill acquisition | Intermediate to advanced skill usage |
Introduction to Skill Instruction Approaches
Segregated Skill Instruction isolates individual language skills such as reading, writing, listening, or speaking, allowing focused practice and mastery of each skill independently. Integrated Skill Instruction combines multiple language skills within a single lesson, promoting the use of reading, writing, listening, and speaking in complementary contexts to enhance overall communicative competence. Both approaches serve distinct pedagogical purposes, with segregated instruction emphasizing skill-specific proficiency and integrated instruction fostering real-life language application and interaction.
Defining Segregated Skill Instruction
Segregated Skill Instruction isolates individual language skills such as reading, writing, listening, or speaking for focused practice without combining them in a single lesson. This approach allows learners to concentrate on mastering one specific skill by using targeted exercises and activities. Segregated instruction often enhances skill accuracy before learners apply them in integrated, real-world communication contexts.
Understanding Integrated Skill Instruction
Integrated Skill Instruction combines listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills within a single lesson to promote contextual learning and real-life communication. This approach enhances cognitive connections between language components, leading to improved retention and practical language use. Educators implementing integrated instruction often report increased student engagement and higher proficiency across multiple skill areas simultaneously.
Historical Context and Evolution
Segregated Skill Instruction emerged prominently in the early 20th century, reflecting the traditional educational model that prioritized isolated teaching of skills like reading, writing, and arithmetic for targeted mastery. Integrated Skill Instruction began gaining traction in the 1970s, influenced by constructivist theories and cognitive psychology, emphasizing multidisciplinary approaches to connect skills within meaningful contexts. The evolution from segregated to integrated methods highlights a shift towards holistic learning paradigms aimed at improving cognitive transfer and real-world application.
Benefits of Segregated Skill Instruction
Segregated Skill Instruction allows focused mastery of individual language components such as reading, writing, listening, or speaking, enhancing skill-specific accuracy and fluency. This method supports targeted assessment and remediation, enabling educators to identify and address particular skill deficits effectively. Learners often experience clearer skill progression and confidence-building by isolating skills before combining them in integrated tasks.
Advantages of Integrated Skill Instruction
Integrated Skill Instruction enhances language learning by combining listening, speaking, reading, and writing activities, promoting real-world communication and cognitive engagement. This approach improves retention and transfer of skills across contexts, aligning with communicative language teaching principles. Students develop fluency and accuracy simultaneously, fostering comprehensive language proficiency more effectively than segregated skill instruction.
Comparing Learning Outcomes
Segregated Skill Instruction isolates language components such as reading, writing, listening, and speaking to target mastery in each area, often resulting in improved foundational skills and clearer assessment benchmarks. Integrated Skill Instruction combines these components in authentic contexts, promoting cognitive connections and practical usage, which enhances communicative competence and long-term retention. Studies indicate that while segregated approaches may boost discrete skill accuracy, integrated instruction tends to yield superior overall communicative proficiency and learner engagement.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Segregated skill instruction often faces challenges like limited context transfer and fragmented learning, as students may struggle to apply isolated skills in real-world scenarios. Integrated skill instruction can encounter limitations such as cognitive overload and difficulty in designing cohesive lessons that balance multiple skill areas simultaneously. Both approaches demand tailored strategies to effectively address diverse learner needs and optimize skill acquisition outcomes.
Pedagogical Implications and Best Practices
Segregated Skill Instruction isolates language skills such as reading, writing, listening, and speaking to ensure focused, targeted practice, promoting clear skill acquisition and allowing educators to diagnose specific learner difficulties. Integrated Skill Instruction combines multiple language skills within a single lesson or activity, reflecting real-world language use and fostering holistic language competence through authentic communication contexts. Best practices suggest a balanced approach, where segregated instruction builds foundational skills and integrated instruction enhances fluency and practical application, supported by continuous formative assessment and adaptive scaffolding.
Choosing the Right Instructional Method
Choosing the right instructional method hinges on the learning objectives and student needs, where segregated skill instruction isolates specific skills for targeted mastery, and integrated skill instruction blends multiple skills within meaningful contexts to enhance real-world application. Research indicates segregated instruction benefits early skill acquisition and remediation, while integrated instruction supports higher-order thinking and transfer of knowledge across disciplines. Educators should assess curriculum goals, student proficiency, and content complexity to determine whether segmented practice or holistic engagement best promotes competency and long-term retention.
Segregated Skill Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com