Project-Based Learning engages students through hands-on experiences that foster critical thinking and real-world problem solving. This method encourages collaboration, creativity, and deeper understanding by allowing learners to apply concepts in practical contexts. Discover how Project-Based Learning can transform Your educational approach by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
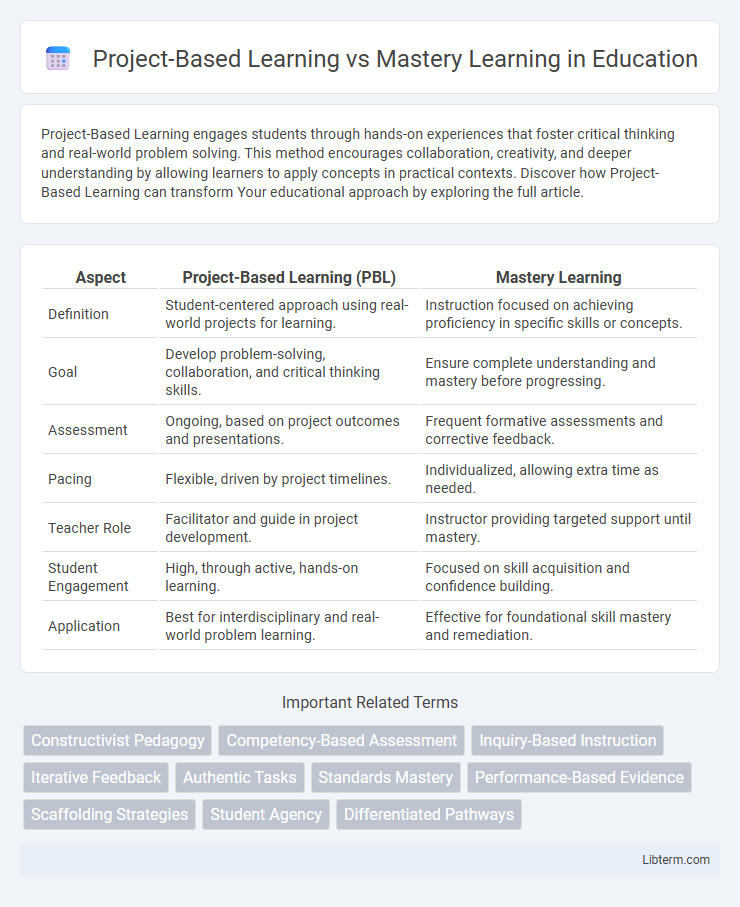
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Mastery Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach using real-world projects for learning. | Instruction focused on achieving proficiency in specific skills or concepts. |
| Goal | Develop problem-solving, collaboration, and critical thinking skills. | Ensure complete understanding and mastery before progressing. |
| Assessment | Ongoing, based on project outcomes and presentations. | Frequent formative assessments and corrective feedback. |
| Pacing | Flexible, driven by project timelines. | Individualized, allowing extra time as needed. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and guide in project development. | Instructor providing targeted support until mastery. |
| Student Engagement | High, through active, hands-on learning. | Focused on skill acquisition and confidence building. |
| Application | Best for interdisciplinary and real-world problem learning. | Effective for foundational skill mastery and remediation. |
Understanding Project-Based Learning (PBL)
Project-Based Learning (PBL) engages students in real-world challenges, promoting critical thinking, collaboration, and deep comprehension through hands-on projects. In PBL, learners apply knowledge to complex tasks, fostering skills such as problem-solving and creativity while connecting academic content to practical applications. This student-centered approach contrasts with Mastery Learning by emphasizing process and inquiry over discrete skill mastery.
Defining Mastery Learning
Mastery Learning is an instructional strategy emphasizing students' thorough understanding of specific topics before progressing to new content, ensuring retention and skill proficiency. This approach contrasts with Project-Based Learning, as it focuses on individualized pacing and mastery checkpoints rather than integrated, real-world problem-solving tasks. Mastery Learning employs formative assessments, corrective feedback, and targeted interventions to achieve consistent, high-level comprehension across diverse learners.
Core Principles of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) centers on active exploration and real-world problem-solving, engaging students in meaningful projects that promote critical thinking, collaboration, and creativity. Core principles include student-driven inquiry, sustained investigation, and authentic assessment through the creation of tangible products or presentations. This approach contrasts with Mastery Learning's emphasis on incremental skill acquisition and individualized pacing to ensure competency before progressing.
Key Features of Mastery Learning
Mastery Learning emphasizes achieving a high level of understanding before progressing, with students receiving tailored instruction and feedback until mastery is demonstrated. This approach incorporates frequent formative assessments and individual pacing, ensuring learners fully grasp concepts before moving on. Key features include clear learning objectives, focused corrective activities, and systematic progress tracking to support student success.
Comparing Teaching Approaches: PBL vs Mastery Learning
Project-Based Learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world problem solving where students engage in complex projects to develop critical thinking and collaboration skills, while Mastery Learning focuses on sequential skill acquisition and ensuring students achieve a high level of understanding before moving forward. PBL encourages interdisciplinary learning and creativity through sustained inquiry, whereas Mastery Learning employs formative assessments and personalized feedback to address individual learning gaps. Both approaches aim to improve student outcomes but differ in structure, with PBL fostering experiential learning and Mastery Learning prioritizing competency mastery.
Student Engagement and Motivation Differences
Project-Based Learning fosters high student engagement by involving learners in real-world tasks that promote collaboration, creativity, and practical problem-solving, which significantly boosts intrinsic motivation. Mastery Learning emphasizes personalized pacing and mastery of specific skills, leading to sustained motivation through clear progress tracking and achievable milestones. While Project-Based Learning thrives on dynamic interaction and hands-on experiences, Mastery Learning motivates students by ensuring comprehension and competence before advancing.
Assessment Methods: Project-Based vs Mastery Approaches
Project-Based Learning assessment predominantly involves performance tasks, presentations, and portfolios that evaluate students' ability to apply knowledge in real-world contexts and demonstrate collaboration and problem-solving skills. Mastery Learning assessment utilizes frequent formative evaluations, including quizzes and criterion-referenced tests, to ensure students achieve a thorough understanding of specific learning objectives before progressing. While Project-Based Learning emphasizes holistic, authentic assessment, Mastery Learning focuses on precise, data-driven measurement of individual competency and mastery.
Benefits and Challenges of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving skills by engaging students in complex, interdisciplinary projects over extended periods. Challenges include the need for significant instructor facilitation, potential uneven group participation, and difficulties in assessing individual mastery within a collaborative setting. Despite these challenges, PBL fosters deeper understanding and retention by connecting learning to tangible outcomes and authentic contexts.
Advantages and Limitations of Mastery Learning
Mastery Learning ensures students achieve a high level of understanding before moving on, resulting in improved retention and personalized pacing that addresses individual learning needs. Its advantages include increased student confidence and reduced achievement gaps, while limitations involve the potential for extended instructional time and challenges in curriculum planning within traditional time constraints. Effective implementation requires flexible scheduling and continuous formative assessment to balance mastery outcomes with educational efficiency.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Project-Based Learning emphasizes real-world problem solving and collaboration, fostering critical thinking and creativity through hands-on projects. Mastery Learning focuses on ensuring students achieve a high level of understanding before moving on, promoting personalized pacing and targeted feedback. Selecting the right approach depends on classroom goals, student needs, and subject matter complexity to maximize engagement and mastery.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com