A traditional curriculum emphasizes structured learning with a focus on core subjects like math, science, and language arts, following a teacher-centered approach. It prioritizes memorization, standardized testing, and a fixed scope of knowledge designed to build foundational skills. Explore the rest of the article to understand how traditional curriculum impacts Your education and alternatives that might better suit Your learning style.
Table of Comparison
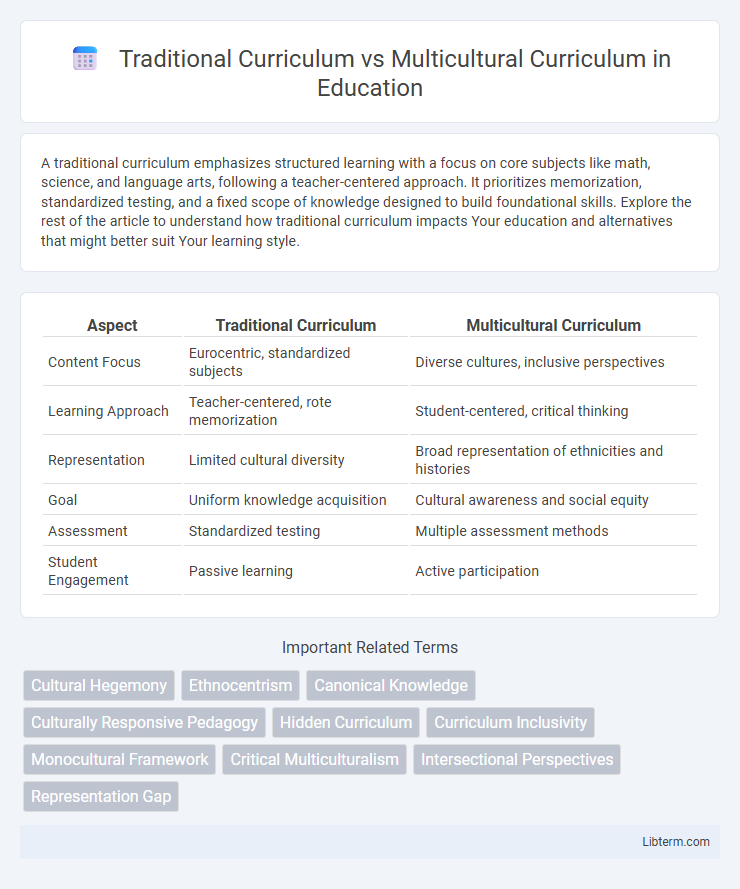
| Aspect | Traditional Curriculum | Multicultural Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Content Focus | Eurocentric, standardized subjects | Diverse cultures, inclusive perspectives |
| Learning Approach | Teacher-centered, rote memorization | Student-centered, critical thinking |
| Representation | Limited cultural diversity | Broad representation of ethnicities and histories |
| Goal | Uniform knowledge acquisition | Cultural awareness and social equity |
| Assessment | Standardized testing | Multiple assessment methods |
| Student Engagement | Passive learning | Active participation |
Introduction to Curriculum Models
Traditional curriculum models emphasize a standardized body of knowledge and skills, focusing on core subjects with a teacher-centered approach. Multicultural curriculum models integrate diverse cultural perspectives and experiences, promoting inclusivity and student engagement by reflecting various voices and histories. Understanding these curriculum models helps educators design effective teaching strategies that meet the needs of diverse student populations.
Defining Traditional Curriculum
The traditional curriculum centers on a fixed set of core subjects such as reading, writing, mathematics, science, and history, emphasizing foundational knowledge and standardized instruction. It typically follows a predetermined sequence designed to build academic skills systematically, often reflecting dominant cultural perspectives and values. This approach prioritizes uniform content delivery and measurable outcomes over cultural diversity and inclusivity.
Understanding Multicultural Curriculum
Understanding multicultural curriculum involves recognizing diverse cultural perspectives and integrating them into teaching materials to promote inclusivity and equitable learning. Unlike traditional curriculum that often centers on a dominant culture's narratives and knowledge, multicultural curriculum emphasizes representation from various ethnic, linguistic, and social backgrounds. This approach enhances critical thinking, cultural awareness, and prepares students for global citizenship by valuing multiple viewpoints and experiences.
Historical Context and Development
The traditional curriculum, rooted in Eurocentric perspectives, emerged during the 19th century with a focus on standardized knowledge and classical disciplines. In contrast, the multicultural curriculum developed in the late 20th century as a response to increasing cultural diversity and social movements advocating for inclusivity and representation. This shift emphasized integrating diverse cultural histories, experiences, and contributions to challenge dominant narratives and promote equity in education.
Core Values and Educational Goals
Traditional curriculum emphasizes core values such as discipline, standardized knowledge acquisition, and national cultural heritage, aiming to prepare students for structured societal roles and uniform assessments. Multicultural curriculum prioritizes inclusivity, cultural awareness, and social justice, with educational goals centered on fostering critical thinking, empathy, and global citizenship. Both approaches influence identity formation but differ in how they integrate diversity and address the needs of multicultural student populations.
Curriculum Content and Representation
Traditional curriculum emphasizes a standardized body of knowledge rooted in dominant cultural narratives, often limiting representation to Eurocentric perspectives and classical canon. Multicultural curriculum broadens content to include diverse voices, histories, and experiences, promoting inclusivity and cultural relevance for students from varied backgrounds. This approach enhances critical thinking by integrating multiple perspectives and addressing systemic biases inherent in traditional curriculum frameworks.
Teaching Methods and Approaches
Traditional curriculum employs teacher-centered methods emphasizing memorization and standardized testing, largely focusing on a fixed body of knowledge. Multicultural curriculum utilizes student-centered approaches that integrate diverse perspectives, critical thinking, and culturally responsive teaching to engage learners from varied backgrounds. This contrast in methods promotes inclusivity by adapting content and pedagogy to reflect cultural diversity and social equity.
Student Engagement and Outcomes
Traditional curriculum often centers on standardized content and teacher-led instruction, which can limit student engagement for diverse learners by not reflecting their cultural backgrounds. Multicultural curriculum integrates diverse perspectives and culturally relevant materials, enhancing student motivation and participation by validating their identities and experiences. Studies show that students exposed to multicultural curricula demonstrate higher academic achievement and critical thinking skills, leading to improved educational outcomes.
Addressing Diversity and Inclusion
Traditional curricula often prioritize a standardized, Eurocentric perspective that can marginalize diverse cultural viewpoints, limiting students' understanding of global experiences. Multicultural curricula actively incorporate diverse histories, languages, and perspectives, fostering an inclusive environment that respects and values differences among students. This approach enhances cultural competence, reduces biases, and prepares learners to engage in a pluralistic society.
Future Directions in Curriculum Design
Future directions in curriculum design emphasize integrating multicultural perspectives to foster inclusivity, critical thinking, and global awareness, moving beyond the content-centric focus of traditional curricula. Emerging trends prioritize culturally responsive teaching methods that adapt to diverse student backgrounds while promoting equity and social justice. Advancements in technology and interdisciplinary approaches support personalized learning experiences, preparing students for a dynamic, interconnected world.
Traditional Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com