Associate Professor is an academic rank signifying a faculty member who has demonstrated significant contributions to teaching, research, and service within a higher education institution. This position often serves as a bridge between assistant and full professor roles, highlighting your growing expertise and leadership in a specialized field. Explore the rest of the article to learn how becoming an Associate Professor can advance your academic career and influence.
Table of Comparison
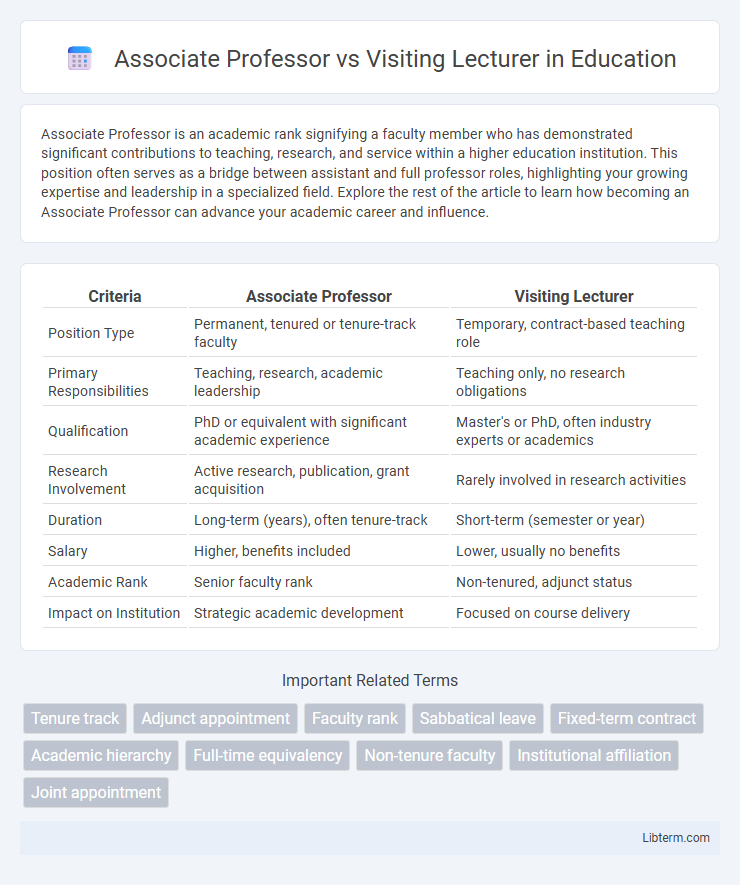
| Criteria | Associate Professor | Visiting Lecturer |
|---|---|---|
| Position Type | Permanent, tenured or tenure-track faculty | Temporary, contract-based teaching role |
| Primary Responsibilities | Teaching, research, academic leadership | Teaching only, no research obligations |
| Qualification | PhD or equivalent with significant academic experience | Master's or PhD, often industry experts or academics |
| Research Involvement | Active research, publication, grant acquisition | Rarely involved in research activities |
| Duration | Long-term (years), often tenure-track | Short-term (semester or year) |
| Salary | Higher, benefits included | Lower, usually no benefits |
| Academic Rank | Senior faculty rank | Non-tenured, adjunct status |
| Impact on Institution | Strategic academic development | Focused on course delivery |
Introduction to Academic Titles
An Associate Professor is a mid-level faculty member with a permanent or tenure-track position, recognized for significant academic contributions and research expertise. A Visiting Lecturer typically holds a temporary or part-time role, often invited to teach specific courses without long-term employment commitments. Academic titles reflect levels of responsibility, research involvement, and institutional affiliation within higher education institutions.
Definition of Associate Professor
An Associate Professor is a tenured or tenure-track faculty member who has demonstrated significant achievements in research, teaching, and service within a university or college. This academic rank is typically positioned between Assistant Professor and Full Professor, reflecting a higher level of experience and professional recognition. Unlike a Visiting Lecturer, whose appointment is usually temporary and primarily teaching-focused, an Associate Professor holds a more permanent status and participates in broader institutional responsibilities.
Definition of Visiting Lecturer
A Visiting Lecturer is an academic professional appointed temporarily, often for a specific term or semester, to teach courses without a permanent faculty position. Unlike an Associate Professor, who holds a tenured or tenure-track role with responsibilities in research, service, and curriculum development, a Visiting Lecturer primarily focuses on delivering lectures and contributing to teaching. This position is typically ideal for industry experts or academics on sabbatical seeking to share expertise without long-term commitments.
Key Responsibilities and Roles
Associate Professors lead advanced research projects, publish scholarly articles, and mentor graduate students while managing academic programs and serving on university committees. Visiting Lecturers primarily deliver specialized course instruction, contribute to curriculum development, and engage with students for a limited appointment period, often bringing industry or niche expertise. The Associate Professor role emphasizes sustained academic contributions and institutional leadership, whereas Visiting Lecturers focus on targeted teaching and practical knowledge dissemination.
Qualifications and Requirements
An Associate Professor typically holds a doctoral degree, extensive research experience, and a strong publication record, reflecting a permanent or tenure-track academic position with responsibilities in teaching, research, and service. A Visiting Lecturer usually requires at least a master's degree or equivalent professional experience, specializing primarily in teaching without the same research obligations or long-term employment security. The qualifications for an Associate Professor emphasize scholarly contributions and sustained academic leadership, whereas Visiting Lecturers focus on practical expertise and short-term instructional roles.
Employment Duration and Contract Types
Associate Professors typically hold long-term, tenure-track positions with permanent contracts, ensuring employment stability and opportunities for career advancement within academic institutions. Visiting Lecturers are engaged on short-term, fixed-duration contracts, often ranging from a single semester to a few years, primarily to address temporary teaching needs. The employment duration for Visiting Lecturers is significantly shorter and less secure compared to the stable, ongoing contracts associated with Associate Professors.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Associate Professors typically have tenure-track positions with clear pathways for promotion to full professorship, offering stable career advancement and increased academic responsibilities. Visiting Lecturers usually hold temporary or contract-based roles with limited opportunities for long-term career progression or institutional advancement. The associate professorship often includes research funding prospects and leadership roles, enhancing professional growth beyond teaching duties.
Workload and Teaching Expectations
Associate Professors typically have higher teaching loads combined with significant research, administrative duties, and mentorship responsibilities, often requiring full-time commitment. Visiting Lecturers generally focus primarily on teaching with limited or no research obligations, usually on a part-time or contract basis, allowing for more concentrated classroom engagement. The workload for Associate Professors is broader and more demanding, balancing academic scholarship and institutional service alongside teaching commitments.
Research and Publication Roles
Associate Professors typically lead research projects, secure funding, and publish extensively in peer-reviewed journals, reflecting a strong commitment to advancing their academic field. Visiting Lecturers primarily focus on teaching responsibilities with limited research obligations and fewer publication requirements. The distinction in research output and publication expectations significantly influences their roles within academic institutions.
Salary and Benefits Comparison
An Associate Professor typically receives a higher salary compared to a Visiting Lecturer, reflecting their permanent status and extensive academic experience. Benefits for Associate Professors often include health insurance, retirement plans, and research funding, which Visiting Lecturers may not fully access due to their temporary contracts. The salary range for Associate Professors generally spans from $70,000 to $120,000 annually, whereas Visiting Lecturers usually earn between $40,000 and $60,000 with limited benefits.
Associate Professor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com