Experiential learning immerses you in hands-on activities that foster deeper understanding through direct experience, enhancing knowledge retention and practical skills. This approach bridges theory and practice, making concepts more relatable and applicable in real-world scenarios. Discover how experiential learning can transform your educational journey by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
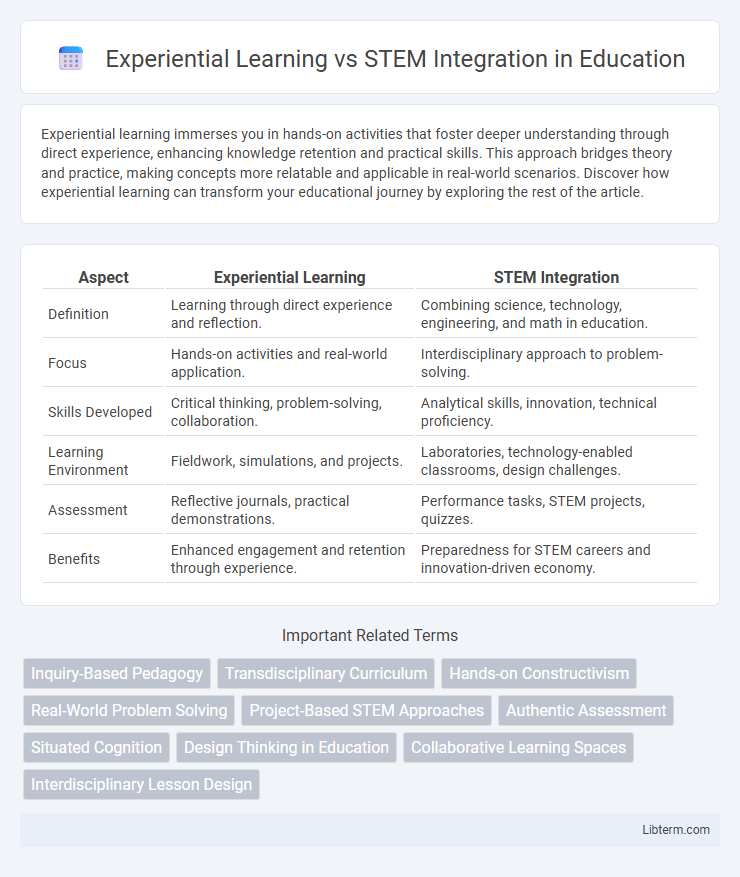
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | STEM Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection. | Combining science, technology, engineering, and math in education. |
| Focus | Hands-on activities and real-world application. | Interdisciplinary approach to problem-solving. |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, problem-solving, collaboration. | Analytical skills, innovation, technical proficiency. |
| Learning Environment | Fieldwork, simulations, and projects. | Laboratories, technology-enabled classrooms, design challenges. |
| Assessment | Reflective journals, practical demonstrations. | Performance tasks, STEM projects, quizzes. |
| Benefits | Enhanced engagement and retention through experience. | Preparedness for STEM careers and innovation-driven economy. |
Understanding Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes acquiring knowledge through direct experience, reflection, and active engagement, fostering deeper comprehension and critical thinking skills. This approach involves hands-on activities, real-world problem solving, and collaborative projects that promote meaningful connections between theory and practice. Understanding experiential learning is crucial for optimizing STEM integration, as it enhances student motivation, retention, and application of complex scientific and mathematical concepts.
Defining STEM Integration
STEM integration combines science, technology, engineering, and mathematics into a cohesive learning paradigm rather than teaching each discipline separately. This approach emphasizes real-world problem-solving and interdisciplinary collaboration, fostering critical thinking and innovation. Experiential learning supports STEM integration by engaging students in hands-on activities that deepen understanding and application of STEM concepts.
Core Principles of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning centers on active engagement, reflection, and the application of knowledge through direct experiences, fostering deeper understanding and retention. Core principles emphasize learner involvement, iterative feedback, and contextual problem-solving, which align closely with STEM education's hands-on approach. Integrating STEM with experiential learning enhances critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving skills by immersing students in authentic, interdisciplinary projects.
Key Components of STEM Integration
STEM integration involves the seamless blending of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics through interdisciplinary curricula that promote problem-solving and innovation. Key components include project-based learning, real-world applications, collaborative teamwork, and the use of technology to enhance critical thinking skills. Experiential learning complements STEM integration by engaging students in hands-on activities that reinforce theoretical concepts and foster deeper understanding.
Comparison: Goals and Objectives
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world experiences to deepen understanding and develop critical thinking skills, while STEM integration focuses on blending science, technology, engineering, and mathematics concepts to foster interdisciplinary problem-solving abilities. Goals of experiential learning prioritize personal engagement and reflection to enhance knowledge retention, whereas STEM integration aims to prepare students for future careers by promoting technical proficiency and collaborative innovation. Both approaches seek to improve educational outcomes but differ in targeting either holistic personal growth or specific academic and professional competencies.
Differences in Teaching Methodologies
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world experiences that engage students directly in the learning process through activities like simulations and fieldwork, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. STEM integration combines science, technology, engineering, and mathematics disciplines to create interdisciplinary lessons that emphasize conceptual connections and collaborative projects. While experiential learning centers on immersive activities to deepen understanding, STEM integration focuses on blending multiple subject areas to solve complex, real-world problems through a structured curriculum.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Experiential learning enhances student engagement by promoting hands-on activities that foster active participation and deeper understanding of STEM concepts. STEM integration connects real-world applications with interdisciplinary problem-solving, which significantly boosts motivation by making learning relevant and meaningful. Both approaches increase student interest and perseverance, but experiential learning particularly excels in cultivating intrinsic motivation through direct experience.
Real-World Application in Both Approaches
Experiential learning and STEM integration both emphasize real-world application by encouraging hands-on problem solving and critical thinking. Experiential learning immerses students in authentic scenarios, fostering practical skills through active participation and reflection. STEM integration combines science, technology, engineering, and mathematics concepts in project-based tasks, enabling learners to address complex challenges with interdisciplinary solutions.
Challenges and Limitations
Experiential learning faces challenges such as resource intensity, including the need for specialized materials, trained facilitators, and sufficient time to allow hands-on exploration. STEM integration encounters limitations in curriculum design complexity, balancing depth across disciplines while meeting standardized testing requirements and ensuring equitable access to technology. Both approaches require ongoing professional development for educators to effectively implement and sustain impactful student engagement.
Choosing the Right Approach for Educational Outcomes
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on activities and real-world problem-solving to foster deep understanding and retention, while STEM integration combines science, technology, engineering, and math concepts into interdisciplinary lessons that promote critical thinking and innovation. Selecting the right approach depends on educational goals, with experiential learning excelling in developing practical skills and STEM integration enhancing analytical abilities and collaboration. Tailoring the method to student needs and curriculum objectives ensures optimal engagement and measurable learning outcomes.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com