The opportunity gap refers to the unequal access to resources and opportunities that impact individuals' ability to succeed, often influenced by socioeconomic status, education, and environment. This disparity affects outcomes in areas like education, employment, and health, perpetuating cycles of inequality. Explore the rest of this article to understand how the opportunity gap shapes your community and what can be done to bridge it.
Table of Comparison
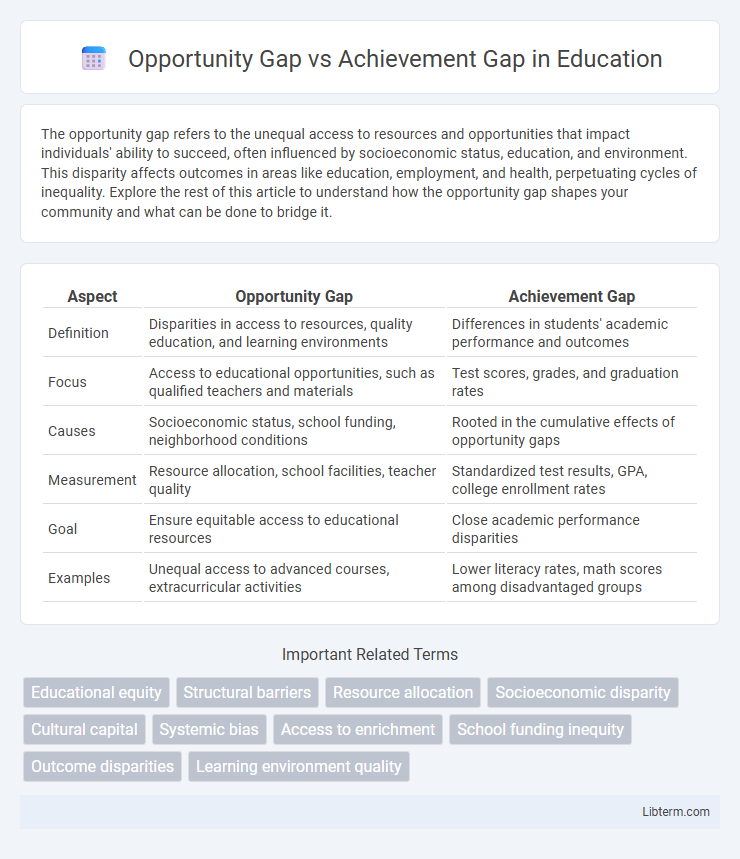
| Aspect | Opportunity Gap | Achievement Gap |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Disparities in access to resources, quality education, and learning environments | Differences in students' academic performance and outcomes |
| Focus | Access to educational opportunities, such as qualified teachers and materials | Test scores, grades, and graduation rates |
| Causes | Socioeconomic status, school funding, neighborhood conditions | Rooted in the cumulative effects of opportunity gaps |
| Measurement | Resource allocation, school facilities, teacher quality | Standardized test results, GPA, college enrollment rates |
| Goal | Ensure equitable access to educational resources | Close academic performance disparities |
| Examples | Unequal access to advanced courses, extracurricular activities | Lower literacy rates, math scores among disadvantaged groups |
Understanding the Opportunity Gap
The Opportunity Gap refers to the unequal access to resources, quality education, and learning environments that affect students' ability to succeed academically. This gap highlights disparities in school funding, experienced teachers, and extracurricular programs, which contribute to differences in student performance. Understanding the Opportunity Gap is crucial for addressing systemic inequalities and creating equitable educational opportunities for all learners.
Defining the Achievement Gap
The achievement gap refers to the persistent disparity in academic performance between groups of students, often defined by socioeconomic status, race, or ethnicity, measured through standardized test scores, graduation rates, and college enrollment. It quantifies differences in educational outcomes, highlighting inequities in knowledge acquisition and skill proficiency. Understanding the achievement gap is crucial for developing targeted interventions aimed at improving academic success for underperforming student populations.
Key Differences Between Opportunity and Achievement Gaps
The opportunity gap refers to disparities in access to resources such as quality education, extracurricular activities, and safe learning environments that affect students' chances for success, while the achievement gap focuses on measurable differences in academic performance outcomes among different student groups. Key differences include the opportunity gap emphasizing systemic inequities in input factors like funding and teacher quality, whereas the achievement gap highlights output disparities like test scores and graduation rates. Addressing the opportunity gap is essential for closing the achievement gap, as unequal opportunities often lead to unequal academic results.
Historical Context of Educational Disparities
The opportunity gap refers to the unequal access to resources, quality teaching, and learning environments shaped by historical segregation, discriminatory policies, and socioeconomic inequalities. The achievement gap reflects the measurable differences in academic performance often resulting from these systemic inequities rooted in historic underfunding of schools serving marginalized communities. Understanding the historical context of educational disparities reveals how enduring structural barriers continue to influence both access to opportunities and student outcomes.
Causes of the Opportunity Gap in Education
The opportunity gap in education stems primarily from systemic inequalities such as socioeconomic disparities, limited access to quality resources, and uneven distribution of experienced teachers. Factors like underfunded schools, neighborhood segregation, and insufficient early childhood education opportunities exacerbate these conditions. These causes create barriers that hinder students from low-income families and marginalized communities from attaining equitable educational outcomes.
Factors Contributing to the Achievement Gap
Factors contributing to the achievement gap include disparities in access to quality education, socioeconomic status, and resource availability. Differences in family support, school funding, and teacher effectiveness also significantly impact student performance. Health and nutrition, as well as exposure to chronic stress, further exacerbate learning inequalities among diverse student populations.
Impact of Opportunity Gap on Student Outcomes
The opportunity gap significantly affects student outcomes by limiting access to quality resources, experienced teachers, and enriching educational experiences, which directly hinders academic performance and long-term success. Students facing these disparities often exhibit lower test scores, higher dropout rates, and reduced college enrollment compared to peers with equal opportunities. Addressing the opportunity gap is essential to closing the achievement gap and fostering equity in education.
Addressing the Gaps: Strategies and Solutions
Addressing the opportunity gap requires equitable resource allocation, inclusive curricula, and access to quality early childhood education to ensure all students have the foundational support for success. To close the achievement gap, targeted interventions such as personalized learning, tutoring, and ongoing assessment help identify and support struggling students. Collaborative efforts among educators, families, and communities foster environments that promote high expectations and culturally responsive teaching, crucial for sustained academic improvement.
Equity vs. Equality in Bridging Educational Gaps
The opportunity gap refers to disparities in access to resources, quality instruction, and supportive learning environments, while the achievement gap measures differences in academic performance among student groups. Equity focuses on providing tailored support and resources to meet diverse student needs, addressing systemic barriers to success. Equality aims for uniform distribution but may fail to close gaps caused by historical and structural inequities in education.
Moving Forward: Policy Recommendations and Community Roles
Addressing the opportunity gap requires policies that ensure equitable access to quality education, including increased funding for underserved schools and expanded early childhood programs. Community roles involve fostering partnerships between families, local organizations, and educators to support student learning and well-being. Moving forward, integrated efforts targeting both resource allocation and community engagement are essential to close both opportunity and achievement gaps effectively.
Opportunity Gap Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com