Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online educational resources, enhancing flexibility and personalization in education. This approach enables You to engage with course material at your own pace while benefiting from direct interaction with instructors and peers. Explore the rest of the article to discover how blended learning can transform Your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
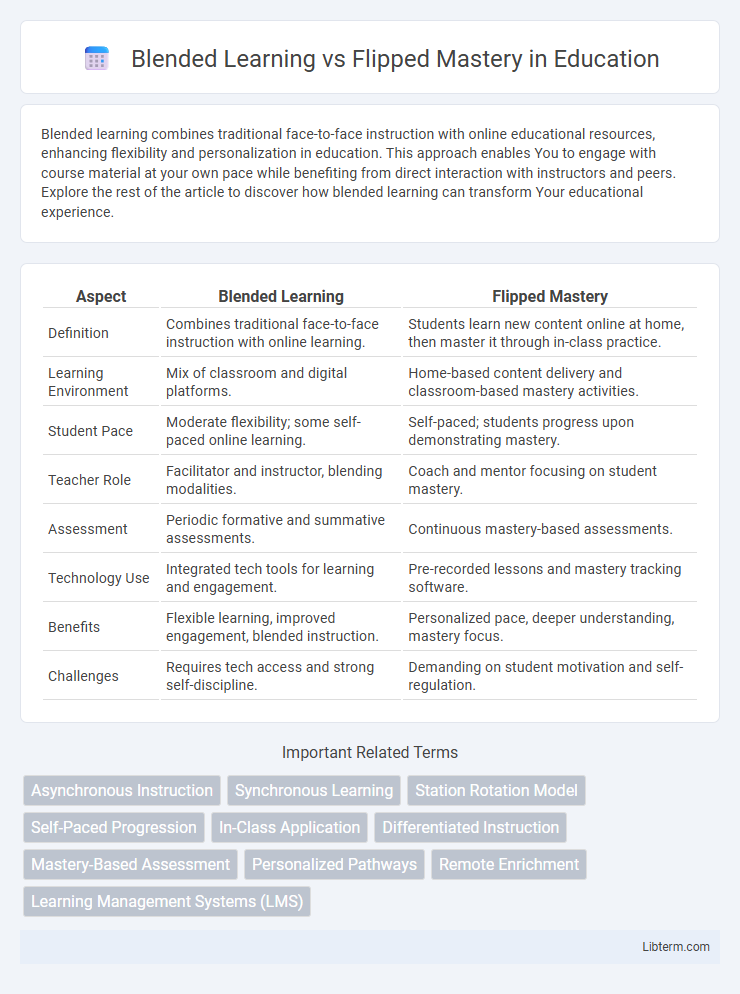
| Aspect | Blended Learning | Flipped Mastery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online learning. | Students learn new content online at home, then master it through in-class practice. |
| Learning Environment | Mix of classroom and digital platforms. | Home-based content delivery and classroom-based mastery activities. |
| Student Pace | Moderate flexibility; some self-paced online learning. | Self-paced; students progress upon demonstrating mastery. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and instructor, blending modalities. | Coach and mentor focusing on student mastery. |
| Assessment | Periodic formative and summative assessments. | Continuous mastery-based assessments. |
| Technology Use | Integrated tech tools for learning and engagement. | Pre-recorded lessons and mastery tracking software. |
| Benefits | Flexible learning, improved engagement, blended instruction. | Personalized pace, deeper understanding, mastery focus. |
| Challenges | Requires tech access and strong self-discipline. | Demanding on student motivation and self-regulation. |
Introduction to Blended Learning and Flipped Mastery
Blended Learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online digital media, allowing students to control the time, place, path, or pace of their learning. Flipped Mastery is a specific model within Blended Learning where students first engage with new material independently, often through video lessons, and then demonstrate mastery through activities or assessments before advancing. Both approaches aim to personalize education, but Flipped Mastery emphasizes mastery-based progression to ensure deeper understanding of content.
Key Definitions: Blended Learning vs Flipped Mastery
Blended Learning integrates traditional classroom instruction with online digital media, allowing students to control the time, place, path, or pace of their learning. Flipped Mastery is a specific model within Blended Learning where students first engage with new content independently, often through videos, then apply their knowledge through mastery-based activities during class time. The key distinction lies in Flipped Mastery's focus on student mastery demonstrated before progressing, contrasting with Blended Learning's broader approach to combining online and face-to-face education.
Core Principles of Blended Learning
Blended Learning integrates online digital media with traditional classroom methods, emphasizing personalized learning paths, flexible pacing, and student-centered instruction. Core principles include active learning through technology, continuous assessment to guide progress, and seamless integration of face-to-face and online environments. This approach leverages adaptive content and real-time feedback to enhance engagement and mastery of subjects.
Fundamentals of Flipped Mastery Approach
The Flipped Mastery approach centers on students mastering each concept at their own pace before progressing, using pre-recorded lessons and interactive assessments to reinforce understanding. This method contrasts with traditional Blended Learning by emphasizing mastery learning and individualized instruction rather than a fixed schedule of in-person and online activities. Core fundamentals include self-directed learning, ongoing formative assessments, and student accountability, which together promote deeper comprehension and skill retention.
Instructional Design: Blended vs Flipped Models
Blended learning integrates face-to-face instruction with online activities, allowing instructional designers to create flexible, multimodal content that adapts to diverse learner needs. Flipped mastery focuses on students mastering content at their own pace through pre-class videos and interactive exercises, emphasizing mastery-based progression and personalized feedback. The instructional design of blended models prioritizes varied engagement modes, while flipped mastery centers on student autonomy and competency-based learning within a structured framework.
Student Engagement and Interaction
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional face-to-face instruction, allowing students to engage with content at their own pace and interact with both instructors and peers during in-person sessions. Flipped mastery emphasizes students mastering material through pre-recorded lessons before attending class for hands-on activities, promoting deeper engagement through personalized feedback and collaborative problem-solving. Both models enhance student interaction by shifting the focus from passive listening to active participation and critical thinking.
Assessment Strategies and Outcomes
Blended Learning employs formative assessments combined with traditional tests to monitor student progress, enabling personalized feedback through both online and face-to-face interactions. Flipped Mastery emphasizes mastery-based assessments where students demonstrate proficiency before advancing, often using competency checkpoints and project-based evaluations to ensure deep understanding. Outcomes in Blended Learning generally show improved engagement and retention, while Flipped Mastery leads to higher mastery rates and self-paced progression tailored to individual learning speeds.
Technology Integration in Both Models
Blended learning integrates digital tools such as learning management systems and interactive content to combine online and face-to-face instruction, enhancing engagement and personalized pacing. Flipped mastery leverages technology to deliver video lectures and interactive assessments outside the classroom, enabling students to master concepts before advancing. Both models utilize adaptive software and real-time analytics to tailor learning experiences, though flipped mastery emphasizes competency-based progression through technology-enabled mastery tracking.
Advantages and Challenges of Each Method
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods, enhancing flexibility and personalized pacing while fostering student engagement through face-to-face interaction; however, it requires substantial technological infrastructure and can pose challenges in maintaining student motivation. Flipped mastery shifts direct instruction outside the classroom using videos and online resources, allowing students to learn at their own pace and enabling teachers to provide targeted support, but it demands high levels of self-discipline and access to reliable technology. Both approaches promote active learning and mastery of content, yet they necessitate careful planning to address potential disparities in student access and varying learning preferences.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Educational Goals
Blended learning integrates face-to-face instruction with online resources to create a flexible educational experience tailored to diverse learning styles and pacing. Flipped mastery reverses traditional teaching by having students engage with instructional content at home and demonstrate mastery through assessments before progressing. Selecting the right model depends on your educational goals: blended learning suits environments requiring balance between direct interaction and independent study, while flipped mastery emphasizes self-paced mastery and immediate feedback, ideal for competency-based education.
Blended Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com