Systematic instruction is a structured teaching approach that breaks down complex skills into smaller, manageable steps, ensuring consistent and effective learning outcomes. It emphasizes clear objectives, step-by-step guidance, and frequent assessments to monitor progress. Discover how this method can enhance Your learning or teaching experience by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
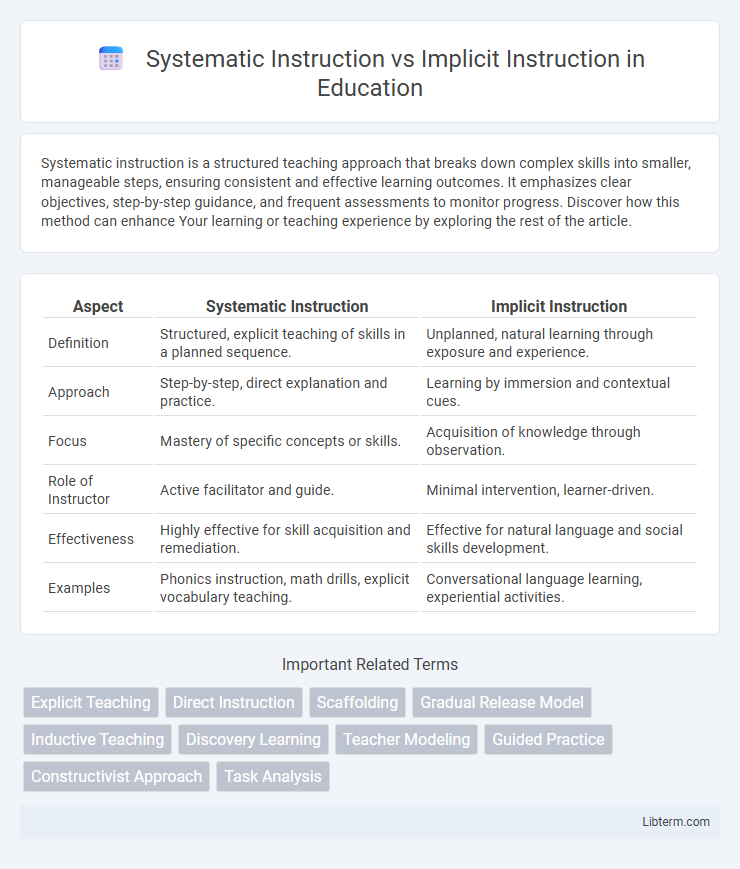
| Aspect | Systematic Instruction | Implicit Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured, explicit teaching of skills in a planned sequence. | Unplanned, natural learning through exposure and experience. |
| Approach | Step-by-step, direct explanation and practice. | Learning by immersion and contextual cues. |
| Focus | Mastery of specific concepts or skills. | Acquisition of knowledge through observation. |
| Role of Instructor | Active facilitator and guide. | Minimal intervention, learner-driven. |
| Effectiveness | Highly effective for skill acquisition and remediation. | Effective for natural language and social skills development. |
| Examples | Phonics instruction, math drills, explicit vocabulary teaching. | Conversational language learning, experiential activities. |
Understanding Systematic Instruction
Systematic instruction involves a structured, sequential teaching method emphasizing clear objectives, explicit teaching of skills, and consistent practice to ensure mastery. It enhances learning efficiency by breaking complex tasks into smaller, manageable components, facilitating better retention and application in diverse contexts. Research shows systematic instruction significantly improves outcomes in reading, math, and language acquisition, particularly for learners with special education needs.
What is Implicit Instruction?
Implicit instruction is a teaching approach that emphasizes learning through exposure and natural context rather than direct, explicit teaching of rules or concepts. It relies on learners' intuitive absorption of language patterns or skills from meaningful interactions, contributing to subconscious knowledge acquisition. This method contrasts with systematic instruction, which involves structured, step-by-step guidance to ensure mastery of specific competencies.
Key Principles of Systematic Instruction
Systematic instruction emphasizes a structured, sequential approach to teaching, incorporating clear objectives, step-by-step skills breakdown, and continuous progress monitoring to ensure mastery at each stage. It relies on explicit teaching methods with carefully designed lessons that build on prior knowledge and use consistent practice and feedback. This approach contrasts with implicit instruction, which depends on natural learning through exposure without overt guidance or structured reinforcement.
Core Characteristics of Implicit Instruction
Implicit instruction relies on natural language exposure and context to facilitate learning without explicit explanations or rules. It emphasizes intuition and pattern recognition through repeated encounters with language in meaningful situations. This approach supports acquisition by promoting subconscious absorption of grammatical structures and vocabulary within authentic communication.
Direct Comparison: Systematic vs Implicit Approaches
Systematic instruction involves structured, explicit teaching methods with clear objectives, step-by-step guidance, and consistent practice to ensure mastery of skills, primarily used in literacy and language learning. Implicit instruction relies on exposure and natural acquisition without overt explanations, promoting learning through context and immersion rather than direct teaching. Research shows systematic approaches yield faster, more reliable outcomes in skill acquisition, while implicit methods support intuitive understanding and long-term retention.
Effectiveness in Skill Acquisition
Systematic instruction employs explicit, structured teaching methods that enhance skill acquisition by breaking down tasks into sequential, manageable steps, leading to faster and more reliable learning outcomes. Implicit instruction relies on exposure and natural context, which may foster deeper understanding but often results in slower progress and less predictable skill mastery. Research in educational psychology consistently demonstrates that systematic instruction yields higher effectiveness in acquiring complex skills, particularly for learners requiring targeted interventions.
Applications in Diverse Learning Environments
Systematic instruction employs structured, sequential teaching methods ideal for learners requiring clear guidance, such as students with special needs or language learners in classroom settings. Implicit instruction, emphasizing natural exposure and context-driven learning, benefits immersive environments like language acquisition in bilingual programs or informal learning contexts. Educators tailor these approaches to optimize engagement and retention across diverse educational landscapes, enhancing adaptability and learner success.
Research Findings: Evidence-Based Outcomes
Research findings reveal systematic instruction consistently produces stronger outcomes in literacy and math skills compared to implicit instruction, especially for learners with disabilities. Studies show systematic instruction's structured, explicit teaching methods enhance retention, comprehension, and application of concepts due to clear, sequential steps. Implicit instruction may benefit incidental learning but lacks the reliable, measurable impacts evident in controlled trials favoring systematic approaches.
Choosing the Right Instructional Strategy
Choosing the right instructional strategy involves evaluating the benefits of systematic instruction, which provides structured, sequential teaching ideal for learners needing clear guidance and measurable progress. Implicit instruction suits environments where discovery and natural learning methods enhance critical thinking and adaptability, appealing to learners who thrive through exploration. Balancing these strategies depends on learner needs, content complexity, and desired outcomes to maximize engagement and retention.
Future Trends in Educational Practices
Future trends in educational practices emphasize a hybrid approach combining systematic instruction's structured curriculum and explicit skill-building with implicit instruction's emphasis on natural language acquisition and context-based learning. Advances in adaptive learning technologies and AI-driven personalized education platforms facilitate dynamic shifts between these methods, optimizing student engagement and mastery. Research increasingly supports integrating data-driven feedback to tailor instruction, promoting both foundational knowledge and creative problem-solving abilities for diverse learning needs.
Systematic Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com