Vocational training equips individuals with practical skills and knowledge tailored to specific trades or professions, enhancing employability and career prospects. This focused approach bridges the gap between theoretical education and real-world job demands, making it an essential path for those seeking hands-on experience. Explore the rest of the article to discover how vocational training can transform your professional future.
Table of Comparison
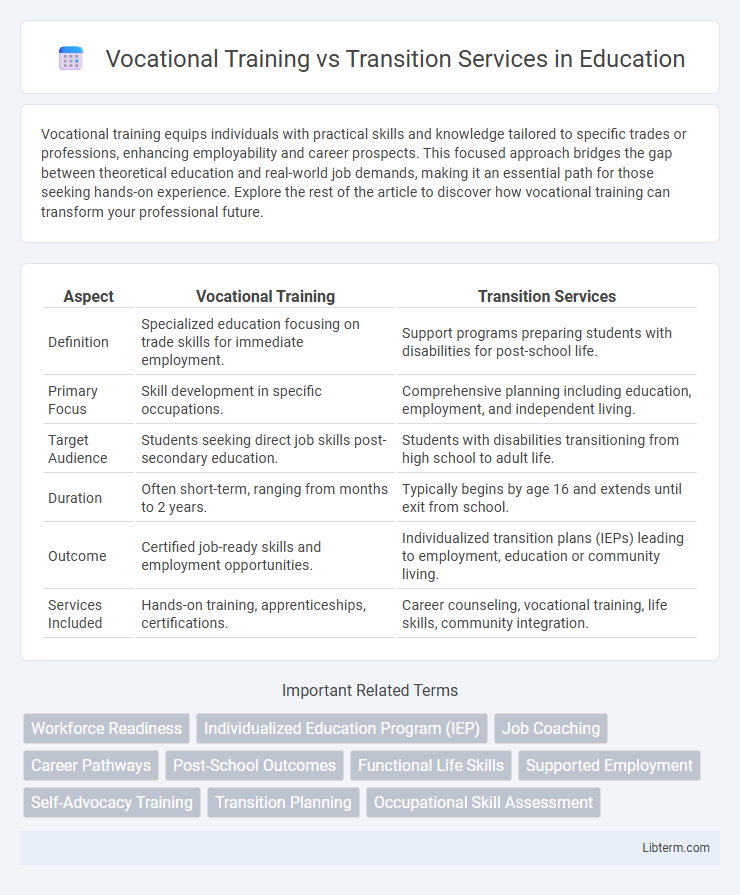
| Aspect | Vocational Training | Transition Services |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specialized education focusing on trade skills for immediate employment. | Support programs preparing students with disabilities for post-school life. |
| Primary Focus | Skill development in specific occupations. | Comprehensive planning including education, employment, and independent living. |
| Target Audience | Students seeking direct job skills post-secondary education. | Students with disabilities transitioning from high school to adult life. |
| Duration | Often short-term, ranging from months to 2 years. | Typically begins by age 16 and extends until exit from school. |
| Outcome | Certified job-ready skills and employment opportunities. | Individualized transition plans (IEPs) leading to employment, education or community living. |
| Services Included | Hands-on training, apprenticeships, certifications. | Career counseling, vocational training, life skills, community integration. |
Understanding Vocational Training
Vocational training provides practical skills and specialized knowledge tailored to specific trades or careers, enhancing employability and job readiness. It focuses on hands-on experience, technical expertise, and industry standards, preparing individuals for direct entry into the workforce. Effective vocational training programs align curriculum with labor market demands, ensuring relevant and up-to-date skill development for various vocational fields.
Defining Transition Services
Transition services encompass a coordinated set of activities designed to facilitate the movement of students with disabilities from school to post-school environments, including vocational training, higher education, employment, and independent living. These services are tailored to the individual's strengths, preferences, and interests, aiming to promote successful integration into adult life. Vocational training, as a component of transition services, provides hands-on skill development and job readiness specific to an industry or trade, supporting long-term employment outcomes.
Key Differences Between Vocational Training and Transition Services
Vocational training primarily focuses on developing specific job-related skills and technical competencies to prepare individuals for immediate employment in particular trades or professions. Transition services encompass a broader range of supports, including career counseling, job placement, life skills education, and community integration, aimed at helping students with disabilities move from school to post-school activities. Key differences include the scope of preparation--vocational training emphasizes skill acquisition for a specific job, whereas transition services provide comprehensive planning and support for various aspects of adult life and employment.
Core Objectives of Vocational Training
Vocational training centers on equipping individuals with specific trade skills and technical knowledge to enhance employability and job readiness. It emphasizes practical, hands-on experience and industry-relevant competencies tailored to meet labor market demands. Unlike transition services that assist broader life adjustments, vocational training's core objectives prioritize skill development, certification, and direct pathways to gainful employment.
Primary Goals of Transition Services
Transition services primarily aim to prepare students with disabilities for post-school life by developing skills for employment, education, and independent living. These services coordinate personalized planning, including job coaching, community experiences, and self-advocacy training, to support successful integration. Vocational training focuses more narrowly on skill development for specific trades or occupations, while transition services encompass a broader, multi-faceted approach to lifelong outcomes.
Target Populations: Who Benefits?
Vocational training primarily benefits individuals seeking specific job skills, including unemployed adults, youth entering the workforce, and people with disabilities aiming for competitive employment. Transition services target high school students with disabilities preparing to move from education to adult life, supporting career exploration, independent living skills, and post-secondary education. Both programs focus on enhancing employability but serve distinct groups, tailoring interventions to the unique needs of each population.
Curriculum and Program Components
Vocational training programs emphasize hands-on skill development in specific trades, incorporating technical instruction, work-based learning, and certification pathways to prepare students for immediate employment. Transition services integrate academic instruction with life skills, career exploration, and community-based experiences to support students with disabilities in moving from school to adult life. Curricula for vocational training are often trade-specific and competency-based, while transition services offer individualized plans combining educational goals, functional skills, and post-school outcomes.
Outcomes and Long-Term Impacts
Vocational training equips individuals with specific skills for immediate job placement, leading to higher employment rates and increased earning potential in the short term. Transition services emphasize comprehensive support, including career counseling and life skills, which contribute to sustained employment and improved quality of life over the long term. Data shows that combining both approaches results in the best outcomes, with greater job retention and enhanced independence for individuals with disabilities.
Collaboration with Employers and Community Partners
Vocational training emphasizes direct skill development through collaboration with employers to create hands-on learning opportunities, internships, and job placements that align with industry demands. Transition services integrate community partners such as local businesses, disability services, and social organizations to support students with disabilities in gaining workplace readiness and navigating employment challenges. Both approaches rely on strong employer engagement to foster career pathways and ensure seamless transitions from education to sustainable employment.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right path between vocational training and transition services involves evaluating individual career goals, skill levels, and support needs. Vocational training emphasizes skill acquisition for specific trades, while transition services focus on preparing students with disabilities for post-school employment and independent living. Key factors include the learner's readiness for workforce integration, access to specialized resources, and long-term career aspirations.
Vocational Training Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com