Student engagement is crucial for effective learning, as it directly influences motivation, retention, and academic success. Strategies that foster active participation and meaningful interaction with the material enhance critical thinking and deepen understanding. Discover practical methods to boost your student engagement and transform the educational experience in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
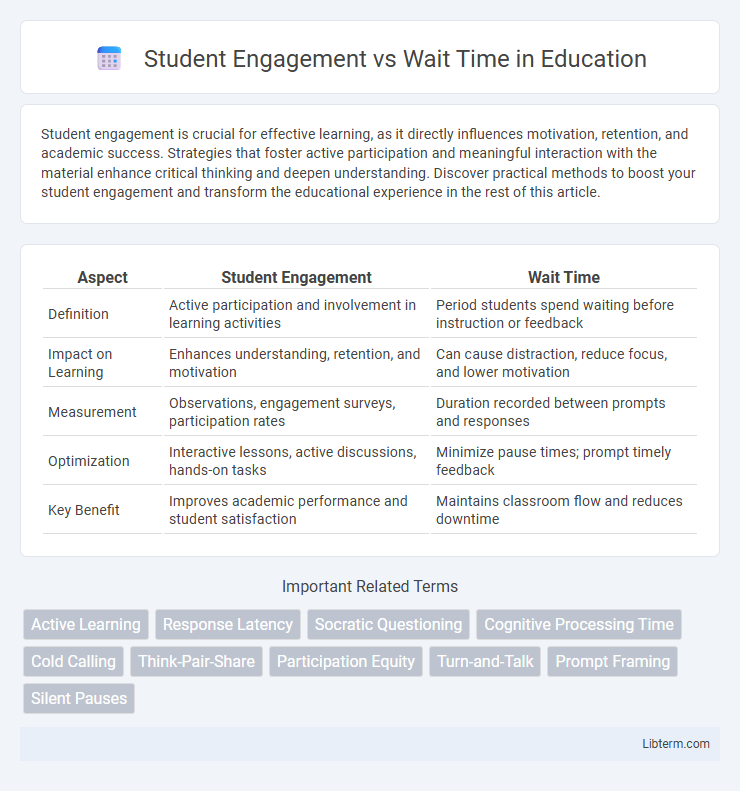
| Aspect | Student Engagement | Wait Time |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active participation and involvement in learning activities | Period students spend waiting before instruction or feedback |
| Impact on Learning | Enhances understanding, retention, and motivation | Can cause distraction, reduce focus, and lower motivation |
| Measurement | Observations, engagement surveys, participation rates | Duration recorded between prompts and responses |
| Optimization | Interactive lessons, active discussions, hands-on tasks | Minimize pause times; prompt timely feedback |
| Key Benefit | Improves academic performance and student satisfaction | Maintains classroom flow and reduces downtime |
Understanding Student Engagement in Modern Classrooms
Student engagement in modern classrooms significantly improves when teachers strategically manage wait time after posing questions, allowing students to process information and formulate thoughtful responses. Research shows that extending wait time to three to five seconds can increase student participation, critical thinking, and response quality, fostering deeper cognitive involvement. Effective wait time practices correlate with higher academic achievement and more dynamic, interactive learning environments.
Defining Wait Time in Educational Settings
Wait time in educational settings refers to the intentional pause a teacher allows after asking a question before soliciting student responses, typically ranging from 3 to 7 seconds. This strategic delay enhances student engagement by providing learners with sufficient processing time to formulate thoughtful answers, thereby improving comprehension and participation. Research indicates that increasing wait time positively influences student confidence, critical thinking, and classroom interaction quality.
The Relationship Between Student Engagement and Wait Time
Student engagement significantly increases when teachers implement strategic wait time after posing questions, allowing students sufficient processing opportunities to formulate thoughtful responses. Research indicates that extending wait times from the typical one second to three or more seconds can boost student participation rates and enhance cognitive processing. Longer wait times reduce anxiety, promote deeper thinking, and create a classroom environment conducive to active learning and higher student interaction.
The Science Behind Wait Time: Cognitive Processes Explained
Wait time significantly impacts student engagement by allowing cognitive processes such as information processing, memory consolidation, and critical thinking to occur effectively. Research in educational psychology shows that increased wait time after a question enhances students' ability to formulate thoughtful responses, leading to deeper comprehension and active participation. Neural studies corroborate that brief pauses facilitate synaptic activity related to learning and problem-solving, underscoring the cognitive foundation behind effective wait time strategies.
Best Practices for Increasing Student Engagement
Maximizing student engagement requires minimizing wait time during classroom interactions, ensuring students remain actively involved in learning activities. Effective strategies include using targeted questioning techniques that prompt immediate responses and incorporating interactive activities that sustain attention and participation. Research indicates that reducing wait time to less than three seconds significantly increases student motivation and cognitive processing, leading to better academic outcomes.
How Wait Time Influences Classroom Participation
Prolonged wait time after posing questions increases student engagement by allowing more thoughtful responses and encouraging participation from diverse learners. Short wait times often lead to quick, superficial answers, reducing opportunities for deeper cognitive processing and limiting classroom interaction. Research shows that extending wait time to 3-5 seconds significantly boosts the quantity and quality of student contributions, fostering a more inclusive and dynamic learning environment.
Strategies to Balance Wait Time and Active Learning
Effective strategies to balance wait time and active learning include using think-pair-share techniques, where students first reflect individually before discussing with peers, reducing downtime and increasing engagement. Incorporating quick formative assessments like polling or exit tickets allows instructors to gauge understanding while maintaining momentum. Structuring wait times with targeted prompts encourages deeper cognitive processing, turning pauses into productive learning opportunities and sustaining student attention.
Common Challenges with Implementing Wait Time
Common challenges with implementing wait time include teachers struggling to balance maintaining student engagement while allowing sufficient pauses for thoughtful responses. Extended pauses can lead to student anxiety or off-task behavior, making classroom management difficult. Additionally, educators often find it hard to consistently monitor and adjust wait times based on diverse student needs and participation levels.
Measuring the Impact of Wait Time on Student Outcomes
Measuring the impact of wait time on student outcomes reveals that longer wait times during classroom interactions significantly enhance student engagement and improve critical thinking skills. Research indicates that wait times of three to five seconds encourage deeper cognitive processing, leading to higher-quality student responses and greater retention of material. Quantitative studies show a positive correlation between increased wait time and improved academic performance, highlighting the importance of strategic pauses in teaching practices.
Practical Tips for Teachers to Optimize Engagement and Wait Time
Maximize student engagement by strategically balancing wait time after questions, allowing learners sufficient processing time to formulate thoughtful responses. Implement techniques such as varying question types, using think-pair-share activities, and incorporating wait times of 3 to 5 seconds to promote deeper cognitive processing and reduce off-task behavior. Monitor student reactions and adjust wait durations accordingly to maintain optimal engagement and encourage active participation in the classroom.
Student Engagement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com