Formative assessment is a critical teaching strategy designed to monitor student learning and provide ongoing feedback, enabling educators to identify strengths and areas for improvement. This approach supports personalized instruction, helping you tailor lessons to meet individual student needs effectively. Discover how formative assessment can transform your educational practice by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
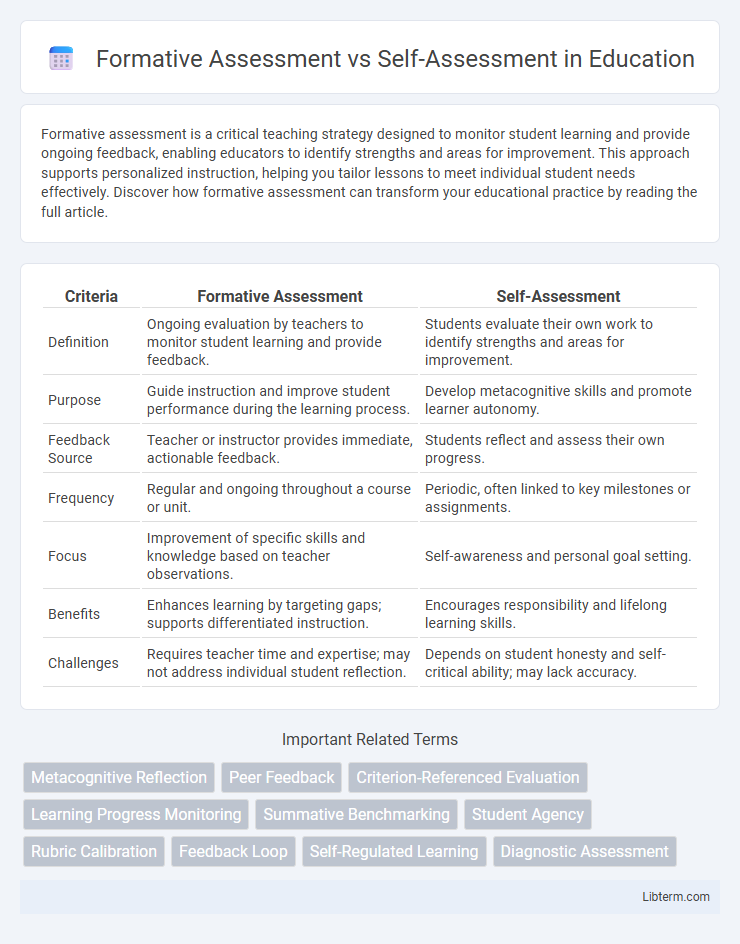
| Criteria | Formative Assessment | Self-Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing evaluation by teachers to monitor student learning and provide feedback. | Students evaluate their own work to identify strengths and areas for improvement. |
| Purpose | Guide instruction and improve student performance during the learning process. | Develop metacognitive skills and promote learner autonomy. |
| Feedback Source | Teacher or instructor provides immediate, actionable feedback. | Students reflect and assess their own progress. |
| Frequency | Regular and ongoing throughout a course or unit. | Periodic, often linked to key milestones or assignments. |
| Focus | Improvement of specific skills and knowledge based on teacher observations. | Self-awareness and personal goal setting. |
| Benefits | Enhances learning by targeting gaps; supports differentiated instruction. | Encourages responsibility and lifelong learning skills. |
| Challenges | Requires teacher time and expertise; may not address individual student reflection. | Depends on student honesty and self-critical ability; may lack accuracy. |
Introduction to Formative and Self-Assessment
Formative assessment involves ongoing evaluations during the learning process to provide immediate feedback that guides student improvement and instructional adjustments. Self-assessment empowers learners to independently evaluate their own understanding and skills, fostering metacognition and personal accountability. Both methods enhance educational outcomes by promoting active engagement and continuous reflection on learning progress.
Defining Formative Assessment
Formative assessment is a continuous process used by educators to monitor student learning and provide ongoing feedback that can be used to improve teaching strategies and student understanding. It involves a variety of informal methods such as quizzes, discussions, and observations aimed at identifying learning gaps and promoting active engagement. Unlike self-assessment, formative assessment is primarily conducted by teachers to guide instructional adjustments and support student progress.
Understanding Self-Assessment
Self-assessment empowers learners to critically evaluate their own progress and identify knowledge gaps, fostering deeper metacognitive skills and personalized learning strategies. Unlike formative assessment, which relies on feedback from instructors to guide improvement, self-assessment promotes autonomy by encouraging students to set goals and monitor their achievement against clear criteria. Mastery of self-assessment techniques enhances motivation, self-regulation, and the capacity for lifelong learning.
Key Differences Between Formative and Self-Assessment
Formative assessment involves teacher-led evaluations designed to monitor student learning and provide ongoing feedback, whereas self-assessment requires students to reflect on and evaluate their own understanding and progress. Teachers use formative assessments to identify learning gaps and adjust instruction, while self-assessment encourages learner autonomy and develops critical thinking skills. The key difference lies in the source of evaluation: formative assessment is externally driven by educators, and self-assessment is internally motivated by students.
Benefits of Formative Assessment
Formative assessment provides real-time feedback that helps educators identify student learning gaps and adjust instruction to improve outcomes. It promotes continuous engagement by allowing students to understand their progress and areas needing improvement before final evaluations. This method enhances learning retention and boosts academic achievement through targeted support and timely interventions.
Advantages of Self-Assessment
Self-assessment empowers learners to develop critical thinking and self-regulation skills by encouraging reflection on their own performance and progress. It promotes greater learner autonomy and motivation, fostering a personalized learning experience tailored to individual strengths and weaknesses. Research shows that self-assessment enhances metacognitive abilities, leading to improved academic outcomes and long-term retention of knowledge.
Challenges in Implementing Both Approaches
Formative assessment faces challenges such as variability in teacher expertise, time constraints, and ensuring consistent feedback that accurately guides student learning. Self-assessment struggles with issues like student bias, lack of metacognitive skills, and difficulty in objectively evaluating one's own performance. Both approaches require effective training and clear criteria to overcome implementation barriers and maximize their educational benefits.
Best Practices for Effective Assessment
Effective formative assessment requires clear learning objectives, timely feedback, and ongoing data collection to guide instruction and student progress. Self-assessment practices thrive when learners use reflective tools, such as rubrics or checklists, to evaluate their understanding and identify areas for improvement. Combining formative assessment with structured self-assessment encourages metacognition and active engagement, enhancing overall learning outcomes.
When to Use Formative vs. Self-Assessment
Formative assessment is most effective during the learning process to monitor student progress and provide immediate feedback for instructional adjustments. Self-assessment should be used when fostering learner autonomy and metacognitive skills, allowing students to reflect on their understanding and identify areas for improvement. Combining both methods enhances learning by supporting continuous feedback and promoting self-regulation.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Assessment Strategy
Selecting the appropriate assessment strategy depends on the learning objectives and student needs; formative assessment provides ongoing feedback to guide instructional adjustments, while self-assessment fosters student reflection and ownership of learning. Integrating both methods enhances student engagement and supports diverse learning styles, ultimately improving academic performance and metacognitive skills. Educators should evaluate context, goals, and resources to implement the most effective balance between formative assessment and self-assessment for optimal educational outcomes.
Formative Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com