Quoting involves repeating someone else's words exactly as they were originally stated, maintaining the original meaning and context. Proper quoting is essential to support your arguments, provide credibility, and avoid plagiarism in your writing. Explore the rest of this article to learn effective quoting techniques and best practices for your work.
Table of Comparison
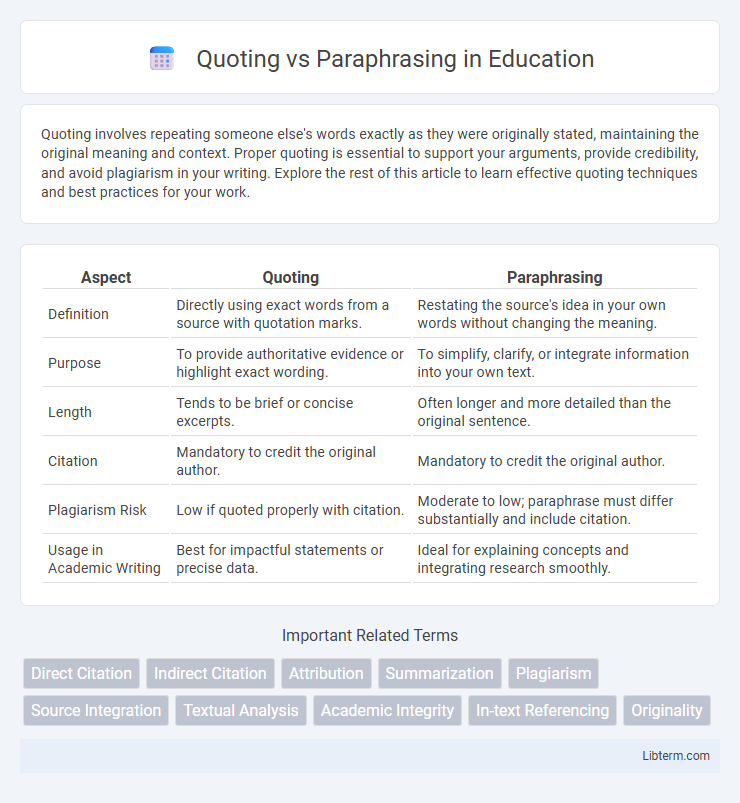
| Aspect | Quoting | Paraphrasing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Directly using exact words from a source with quotation marks. | Restating the source's idea in your own words without changing the meaning. |
| Purpose | To provide authoritative evidence or highlight exact wording. | To simplify, clarify, or integrate information into your own text. |
| Length | Tends to be brief or concise excerpts. | Often longer and more detailed than the original sentence. |
| Citation | Mandatory to credit the original author. | Mandatory to credit the original author. |
| Plagiarism Risk | Low if quoted properly with citation. | Moderate to low; paraphrase must differ substantially and include citation. |
| Usage in Academic Writing | Best for impactful statements or precise data. | Ideal for explaining concepts and integrating research smoothly. |
Understanding Quoting and Paraphrasing
Quoting involves directly using someone else's exact words within quotation marks to preserve the original meaning and emphasize authority or authenticity. Paraphrasing restates the same ideas in your own words, enhancing clarity and demonstrating comprehension while avoiding plagiarism. Effective understanding of quoting and paraphrasing ensures accurate representation of sources and strengthens academic integrity.
Key Differences Between Quoting and Paraphrasing
Quoting involves directly using another author's exact words enclosed in quotation marks, preserving the original phrasing and context. Paraphrasing rephrases the source material in your own words while maintaining the original meaning, enhancing clarity or conciseness without altering the idea. The key differences include the level of originality, with quoting being verbatim, whereas paraphrasing requires interpretation and restatement; proper citation remains essential in both to avoid plagiarism.
When to Use Direct Quotes
Direct quotes should be used when the original wording is especially clear, powerful, or authoritative, preserving the speaker's exact voice and intent. Quotations are essential when referencing legal documents, unique expressions, or when exact phrasing impacts the argument's credibility. Using direct quotes enhances trustworthiness, supports critical analysis, and provides concrete evidence from primary sources.
When to Paraphrase Source Material
Paraphrase source material when the goal is to simplify complex ideas, integrate information smoothly into your own writing style, or highlight specific points without overloading the text with direct quotes. Use paraphrasing to demonstrate understanding of the material while maintaining originality and avoiding plagiarism. This technique is especially useful in academic writing to convey evidence and support arguments with clarity and coherence.
Benefits of Quoting in Writing
Quoting preserves the original author's voice and authority, providing strong evidence and credibility to support arguments in academic or professional writing. Direct quotes capture precise wording, which enhances accuracy and ensures the original meaning is conveyed without alteration. Incorporating quotes can engage readers by introducing varied perspectives and reinforcing key points through reputable sources.
Advantages of Paraphrasing Information
Paraphrasing allows for the integration of information smoothly into your own writing style while demonstrating a deep understanding of the original material. It helps avoid excessive reliance on direct quotations, reducing the risk of plagiarism and enhancing originality. Effective paraphrasing also enables the customization of information to better suit the target audience and specific context.
How to Properly Quote Sources
Properly quoting sources requires exact replication of the original text within quotation marks, accompanied by a precise citation that includes the author's name, publication year, and page number if applicable. Integrating quotes seamlessly into your writing involves matching the quote's tone and context while providing clear attribution to avoid plagiarism. Maintaining the integrity of the source material and ensuring accurate formatting according to style guides such as APA, MLA, or Chicago is essential for effective quoting.
Effective Techniques for Paraphrasing
Effective techniques for paraphrasing involve thoroughly understanding the original text and expressing ideas using different vocabulary and sentence structures while maintaining the original meaning. Employing synonym substitution, changing sentence voice from active to passive or vice versa, and breaking complex information into simpler statements enhance clarity and originality. Proper attribution remains crucial to avoid plagiarism, even when the content is rephrased.
Common Mistakes in Quoting and Paraphrasing
Common mistakes in quoting and paraphrasing include failing to use quotation marks for direct quotes, leading to plagiarism, and inadequate citation of the original source. Paraphrasing errors often involve changing only a few words without altering sentence structure, resulting in insufficient originality. Properly distinguishing between quoting and paraphrasing ensures academic integrity and enhances the clarity of research writing.
Best Practices for Academic Integrity
Quoting involves directly using someone else's exact words with proper citation, while paraphrasing means restating ideas in your own words and requires accurate credit to the original source. Best practices for academic integrity include verifying that quotes are faithful to the original and ensuring paraphrased content reflects the source's intent without plagiarism. Proper use of quotation marks and referencing styles such as APA, MLA, or Chicago is essential to maintain transparency and uphold ethical standards in academic writing.
Quoting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com