Simulated tasks provide a realistic environment for practicing skills and decision-making without real-world consequences. These scenarios enhance learning and prepare you for actual challenges by replicating complex situations accurately. Explore the rest of this article to understand how simulated tasks can transform your training experience.
Table of Comparison
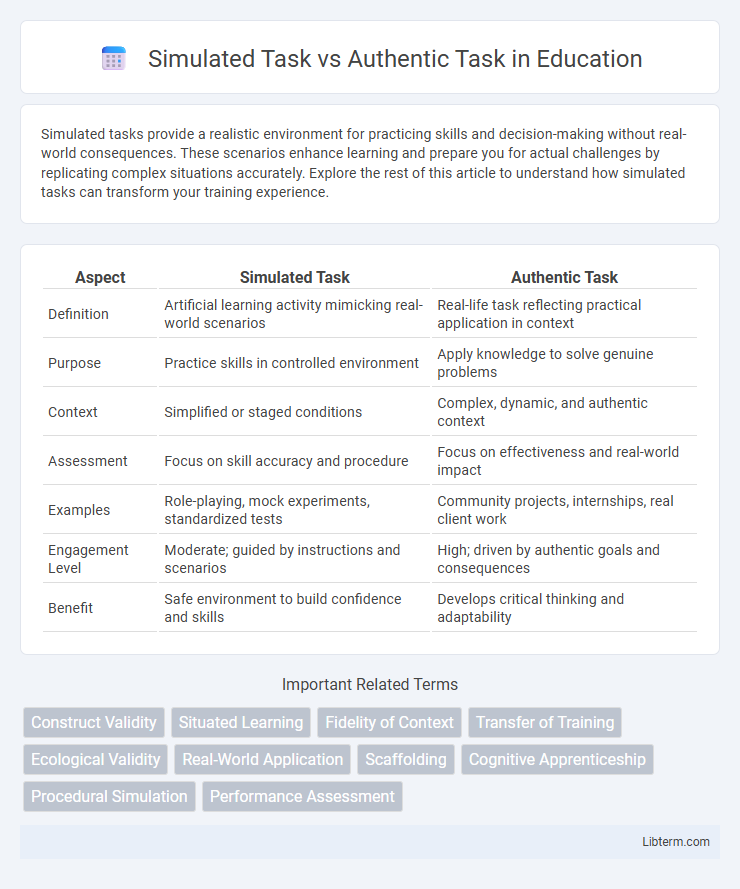
| Aspect | Simulated Task | Authentic Task |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artificial learning activity mimicking real-world scenarios | Real-life task reflecting practical application in context |
| Purpose | Practice skills in controlled environment | Apply knowledge to solve genuine problems |
| Context | Simplified or staged conditions | Complex, dynamic, and authentic context |
| Assessment | Focus on skill accuracy and procedure | Focus on effectiveness and real-world impact |
| Examples | Role-playing, mock experiments, standardized tests | Community projects, internships, real client work |
| Engagement Level | Moderate; guided by instructions and scenarios | High; driven by authentic goals and consequences |
| Benefit | Safe environment to build confidence and skills | Develops critical thinking and adaptability |
Introduction to Simulated and Authentic Tasks
Simulated tasks replicate real-world scenarios in controlled environments to enhance skill acquisition through practice and feedback, often used in training and education for professions like healthcare and aviation. Authentic tasks require learners to engage in complex, real-life challenges that demand critical thinking, problem-solving, and application of knowledge in genuine contexts, promoting deeper learning and transferability. Both approaches serve as essential strategies in experiential learning, each with unique benefits depending on the learning objectives and context.
Key Differences Between Simulated and Authentic Tasks
Simulated tasks replicate real-world scenarios in controlled environments, emphasizing skill practice without real consequences, while authentic tasks involve genuine, context-rich activities requiring practical application and critical thinking. Simulated tasks often focus on specific, measurable skills or knowledge, making them ideal for assessment and training, whereas authentic tasks integrate multiple skills and promote deeper understanding through real-life problem-solving. The key difference lies in authenticity and context: simulated tasks mimic reality for learning purposes, whereas authentic tasks engage learners in actual situations that demand meaningful, relevant outcomes.
Benefits of Simulated Tasks in Learning
Simulated tasks offer a controlled, risk-free environment that allows learners to practice complex skills repeatedly, improving retention and confidence. They enable real-time feedback and error correction without real-world consequences, fostering deeper understanding and skill refinement. Simulated tasks bridge theory and practice, enhancing critical thinking and decision-making abilities through realistic scenarios that mimic authentic challenges.
Advantages of Authentic Tasks for Skill Development
Authentic tasks enhance skill development by providing real-world contexts that promote critical thinking, problem-solving, and practical application. These tasks engage learners in meaningful activities that mirror professional environments, fostering deeper understanding and transferable skills. Exposure to authentic tasks also encourages collaboration and adaptability, essential abilities for success in dynamic work settings.
When to Use Simulated vs Authentic Tasks
Simulated tasks are ideal for early-stage learning when learners need a controlled environment to practice specific skills without real-world consequences. Authentic tasks should be used when the goal is to assess practical application and transfer of knowledge in real-life or workplace contexts. Choosing between simulated and authentic tasks depends on the learner's proficiency level and the complexity of skills required for performance evaluation.
Challenges of Implementing Authentic Tasks
Implementing authentic tasks presents challenges such as aligning real-world complexity with curriculum standards and ensuring access to appropriate resources and technology. Educators face difficulties in assessing open-ended, context-rich activities that lack standardized scoring, complicating reliable evaluation. Time constraints and varying student readiness also hinder the consistent integration of authentic tasks into diverse learning environments.
The Role of Technology in Task Simulation
Technology enhances simulated tasks by creating immersive, interactive environments that closely mimic real-world scenarios, improving skill acquisition and decision-making accuracy. Advanced tools such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and AI-driven simulations enable users to practice complex tasks safely and repeatedly without real-world consequences. These technological advancements bridge the gap between simulated and authentic tasks by providing realistic feedback and adaptive challenges that replicate authentic task demands.
Assessment Methods for Simulated and Authentic Tasks
Assessment methods for simulated tasks typically involve controlled environments where specific skills are tested using standardized scenarios and tools, enabling precise measurement of learner performance and error rates. Authentic task assessments prioritize real-world application by evaluating learners through practical activities or projects that replicate workplace conditions, emphasizing problem-solving, critical thinking, and the ability to transfer knowledge to complex, dynamic situations. Effective assessment strategies balance objectivity and contextual relevance, often incorporating rubrics, direct observation, peer reviews, and reflective self-assessments to capture both competency and practical effectiveness.
Case Studies: Simulated vs Authentic Tasks in Practice
Case studies comparing simulated and authentic tasks highlight the fidelity and contextual relevance of authentic tasks, which often lead to higher learner engagement and better transfer of skills in real-world settings. Simulated tasks, while controlled and replicable, may lack the dynamic complexity present in authentic scenarios, limiting their effectiveness for deep skill acquisition. Research indicates that integrating authentic tasks aligned with real-world case studies enhances critical thinking and problem-solving abilities more effectively than purely simulated exercises.
Future Trends in Task Design for Education
Future trends in task design for education emphasize the integration of simulated tasks with authentic tasks to enhance experiential learning and skill transferability. Advances in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technology enable immersive simulated environments that replicate real-world scenarios, while data analytics help tailor authentic tasks for individualized learning outcomes. The convergence of AI-driven assessment tools and adaptive learning systems will further refine the balance between simulated and authentic tasks, promoting deeper engagement and competency development.
Simulated Task Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com