Inquiry-based learning fosters critical thinking and deeper understanding by encouraging students to ask questions and explore topics independently. This approach promotes active engagement and develops problem-solving skills essential for academic success. Discover how incorporating inquiry-based learning can transform your educational experience in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
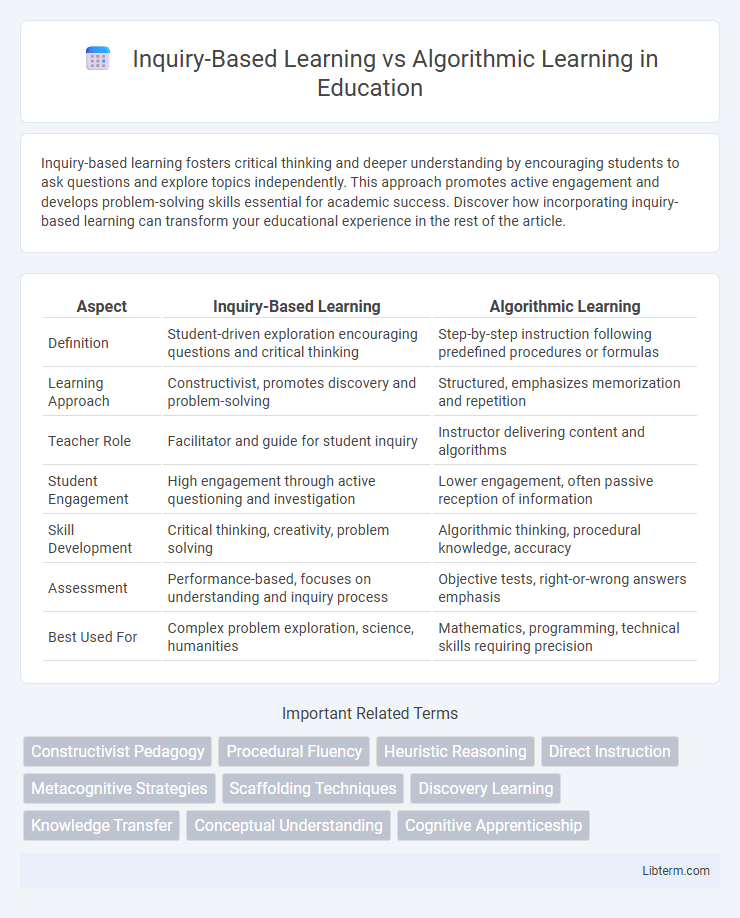
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Algorithmic Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-driven exploration encouraging questions and critical thinking | Step-by-step instruction following predefined procedures or formulas |
| Learning Approach | Constructivist, promotes discovery and problem-solving | Structured, emphasizes memorization and repetition |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and guide for student inquiry | Instructor delivering content and algorithms |
| Student Engagement | High engagement through active questioning and investigation | Lower engagement, often passive reception of information |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, creativity, problem solving | Algorithmic thinking, procedural knowledge, accuracy |
| Assessment | Performance-based, focuses on understanding and inquiry process | Objective tests, right-or-wrong answers emphasis |
| Best Used For | Complex problem exploration, science, humanities | Mathematics, programming, technical skills requiring precision |
Understanding Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes active exploration, critical thinking, and problem-solving by encouraging students to ask questions and investigate real-world scenarios. This approach fosters deeper comprehension through hands-on experiences and reflective analysis rather than following predetermined steps. Research shows that Inquiry-Based Learning improves conceptual understanding and retention compared to traditional algorithmic methods that rely on memorization and repetitive practice.
Defining Algorithmic Learning
Algorithmic learning involves following a set of predefined, step-by-step procedures or rules to solve problems, emphasizing systematic and reproducible methods. This approach contrasts with inquiry-based learning, which encourages exploration and critical thinking through questioning and investigation. Algorithmic learning is essential in disciplines like mathematics and computer science where precise, logical sequences are crucial for problem-solving.
Core Principles of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on fostering curiosity, promoting student-driven questioning, and encouraging exploration to construct knowledge actively. It prioritizes critical thinking, problem-solving, and the development of deeper understanding through hands-on experiences and investigation. This approach contrasts with Algorithmic Learning, which relies on step-by-step procedures and memorization rather than conceptual engagement.
Core Principles of Algorithmic Learning
Algorithmic Learning relies on step-by-step procedures, predefined rules, and systematic problem-solving techniques designed to achieve specific outcomes efficiently. It emphasizes replicability, consistency, and the use of algorithms to process input data and generate solutions, often leveraging computational methods or decision trees. This approach contrasts with Inquiry-Based Learning by focusing on structured, rule-based knowledge acquisition rather than exploratory or experimental discovery.
Engagement and Motivation in the Classroom
Inquiry-Based Learning significantly boosts student engagement and motivation by encouraging curiosity, critical thinking, and active participation, fostering a deeper connection with the subject matter. Algorithmic Learning, while efficient for mastering procedural skills and providing structured feedback, often results in lower intrinsic motivation due to its repetitive and predictable nature. Empirical studies show that classrooms implementing Inquiry-Based Learning report higher student enthusiasm, sustained attention, and improved problem-solving abilities compared to those relying primarily on Algorithmic Learning methods.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking by encouraging students to ask questions, explore problems, and develop solutions independently, enhancing analytical and evaluative skills. Algorithmic Learning relies on step-by-step procedures and repetitive practice, which strengthens pattern recognition and procedural knowledge but may limit deeper reasoning abilities. Emphasizing inquiry in education leads to improved critical thinking skills essential for problem-solving in complex, real-world situations.
Application in Real-World Scenarios
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and problem-solving by encouraging students to explore real-world scenarios through questioning and investigation, enhancing adaptability in dynamic environments. Algorithmic Learning emphasizes step-by-step procedures and repetitive practice, which is effective in fields requiring precision and consistency, such as computer programming and data analysis. Combining both approaches can maximize practical application by developing both analytical reasoning and procedural skills essential for complex, real-world challenges.
Assessment and Evaluation Methods
Inquiry-based learning emphasizes formative assessments such as reflective journals, project presentations, and open-ended questions that evaluate critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Algorithmic learning relies heavily on summative assessments including multiple-choice tests, quizzes, and standardized exams that measure procedural accuracy and memorization. Effective evaluation in inquiry-based learning captures conceptual understanding, while algorithmic learning focuses on correctness and speed in executing predefined procedures.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Approaches
Inquiry-based learning often faces challenges in maintaining student engagement and ensuring consistent knowledge acquisition due to its open-ended nature and reliance on student-led exploration. Algorithmic learning's limitations include reduced critical thinking development and overdependence on rote memorization, which can hinder problem-solving adaptability. Both methods struggle with balancing depth of understanding and scalability in diverse educational settings, impacting overall effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Learners
Inquiry-Based Learning promotes critical thinking and creativity by encouraging students to explore concepts through questions and hands-on activities, making it ideal for learners who thrive in open-ended environments. Algorithmic Learning emphasizes structured, step-by-step problem solving, benefiting students who prefer clear guidelines and repetitive practice to master skills. Selecting the right approach depends on assessing learner preferences, cognitive styles, and educational goals to tailor instruction that supports diverse needs effectively.
Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com