Discovery learning empowers you to build knowledge through active exploration and problem-solving, fostering deeper understanding and retention. This approach emphasizes hands-on experiences that stimulate curiosity and critical thinking skills. Explore the rest of the article to uncover practical strategies for implementing discovery learning in your educational setting.
Table of Comparison
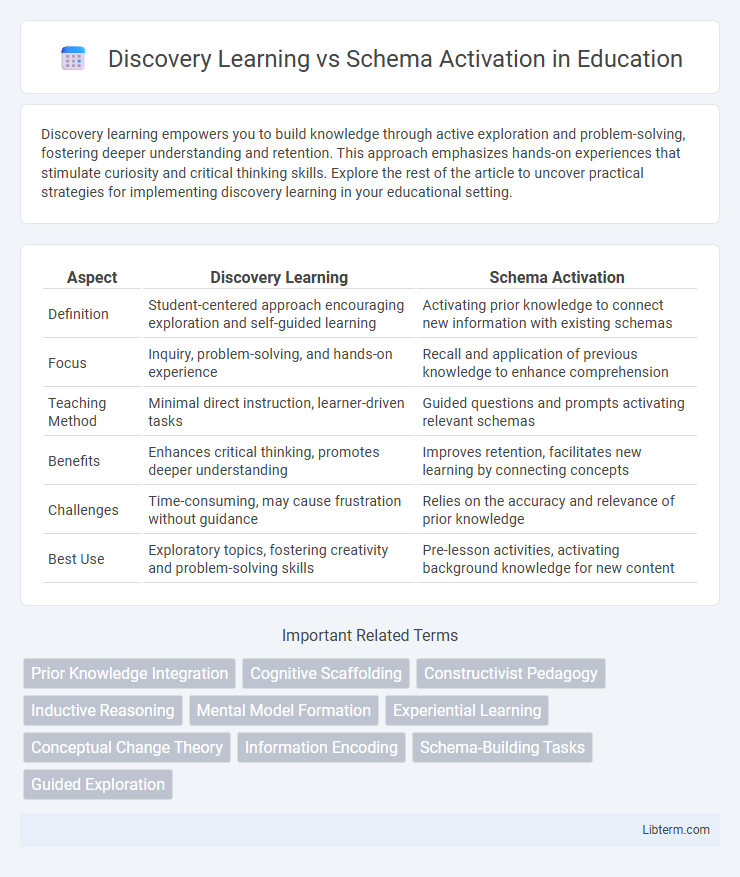
| Aspect | Discovery Learning | Schema Activation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach encouraging exploration and self-guided learning | Activating prior knowledge to connect new information with existing schemas |
| Focus | Inquiry, problem-solving, and hands-on experience | Recall and application of previous knowledge to enhance comprehension |
| Teaching Method | Minimal direct instruction, learner-driven tasks | Guided questions and prompts activating relevant schemas |
| Benefits | Enhances critical thinking, promotes deeper understanding | Improves retention, facilitates new learning by connecting concepts |
| Challenges | Time-consuming, may cause frustration without guidance | Relies on the accuracy and relevance of prior knowledge |
| Best Use | Exploratory topics, fostering creativity and problem-solving skills | Pre-lesson activities, activating background knowledge for new content |
Introduction to Discovery Learning and Schema Activation
Discovery Learning emphasizes active, hands-on engagement where learners explore concepts independently, fostering deeper understanding and long-term retention. Schema Activation involves connecting new information to existing knowledge frameworks, enhancing comprehension by priming relevant background concepts. Both methods stimulate cognitive processes but differ in approach: Discovery Learning encourages self-guided inquiry, while Schema Activation relies on tapping into prior knowledge to scaffold learning.
Core Principles of Discovery Learning
Discovery learning centers on active engagement and exploration, encouraging learners to construct knowledge through experience rather than direct instruction. Key principles include fostering curiosity, promoting problem-solving skills, and facilitating the learner's ability to develop mental models independently. This approach contrasts with schema activation, which primarily involves recalling and connecting prior knowledge to new information to enhance comprehension.
Fundamentals of Schema Activation
Schema activation involves tapping into learners' prior knowledge structures to prepare the mind for new information, enhancing comprehension and retention. By linking new content to existing mental frameworks, schema activation facilitates deeper understanding through meaningful connections. This cognitive strategy contrasts with discovery learning, which emphasizes exploration and self-guided problem-solving rather than structured knowledge integration.
Key Differences Between Discovery Learning and Schema Activation
Discovery Learning emphasizes active exploration where learners construct knowledge through direct experience and problem-solving, fostering deep understanding and retention. Schema Activation involves priming prior knowledge frameworks to facilitate comprehension and integration of new information, enhancing cognitive connections and recall. The key difference lies in Discovery Learning's inductive, learner-centered approach versus Schema Activation's reliance on existing mental structures to support learning.
Cognitive Processes Involved in Both Approaches
Discovery Learning engages cognitive processes such as hypothesis generation, problem-solving, and inductive reasoning, allowing learners to actively construct knowledge through exploration and experimentation. Schema Activation involves recognizing and retrieving existing cognitive frameworks, which facilitates comprehension and integration of new information by connecting it to prior knowledge. Both approaches stimulate metacognitive skills, but Discovery Learning emphasizes active inquiry, whereas Schema Activation focuses on framework recall and assimilation.
Advantages and Challenges of Discovery Learning
Discovery learning promotes active engagement and deeper understanding by encouraging learners to explore concepts independently, which enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills. It fosters long-term retention through experiential learning but can pose challenges such as increased cognitive load and potential frustration for learners lacking prior knowledge or effective guidance. Educators must balance scaffolding and autonomy to maximize the benefits of discovery learning while minimizing confusion and inefficiency.
Benefits and Limitations of Schema Activation
Schema activation enhances comprehension by connecting new information to learners' existing knowledge frameworks, facilitating deeper understanding and retention. It enables efficient organization of material, aiding retrieval and critical thinking but may limit creativity if learners overly rely on preconceived schemas. Challenges include potential reinforcement of misconceptions and difficulty adapting schema to novel or complex content, highlighting the importance of guided activation in diverse learning contexts.
Classroom Strategies for Implementing Discovery Learning
Discovery learning in classrooms emphasizes student-centered exploration, encouraging learners to construct knowledge through hands-on activities and problem-solving tasks that foster critical thinking and deep understanding. Effective strategies include providing open-ended questions, facilitating collaborative group work, and integrating real-world scenarios to promote inquiry and self-discovery while subtly guiding students with well-designed scaffolds. Unlike schema activation, which builds on prior knowledge by explicitly linking new information to existing mental frameworks, discovery learning prioritizes active engagement and experiential learning to develop autonomous knowledge construction skills.
Techniques for Enhancing Schema Activation
Techniques for enhancing schema activation include the use of graphic organizers, such as mind maps and KWL charts, which help learners visually connect new information to existing knowledge structures. Pre-reading strategies like guided questioning and previewing key vocabulary activate relevant schemas, facilitating deeper comprehension. Incorporating real-life contexts and examples also strengthens schema activation by making new content more relatable and accessible to the learner's prior experience.
Choosing the Right Approach: Contexts and Recommendations
Choosing the right approach between Discovery Learning and Schema Activation depends on the learners' prior knowledge and learning objectives. Discovery Learning suits exploratory contexts where fostering problem-solving skills and critical thinking is essential, while Schema Activation is optimal for activating existing knowledge structures to enhance comprehension and retention. Educators should recommend Discovery Learning for open-ended tasks and Schema Activation for structured content acquisition to maximize learning outcomes.
Discovery Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com