Experiential learning immerses you in hands-on activities, enabling deeper understanding through real-world experience rather than passive study. This approach enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by engaging actively with the material. Explore the rest of the article to discover how experiential learning can transform your educational journey.
Table of Comparison
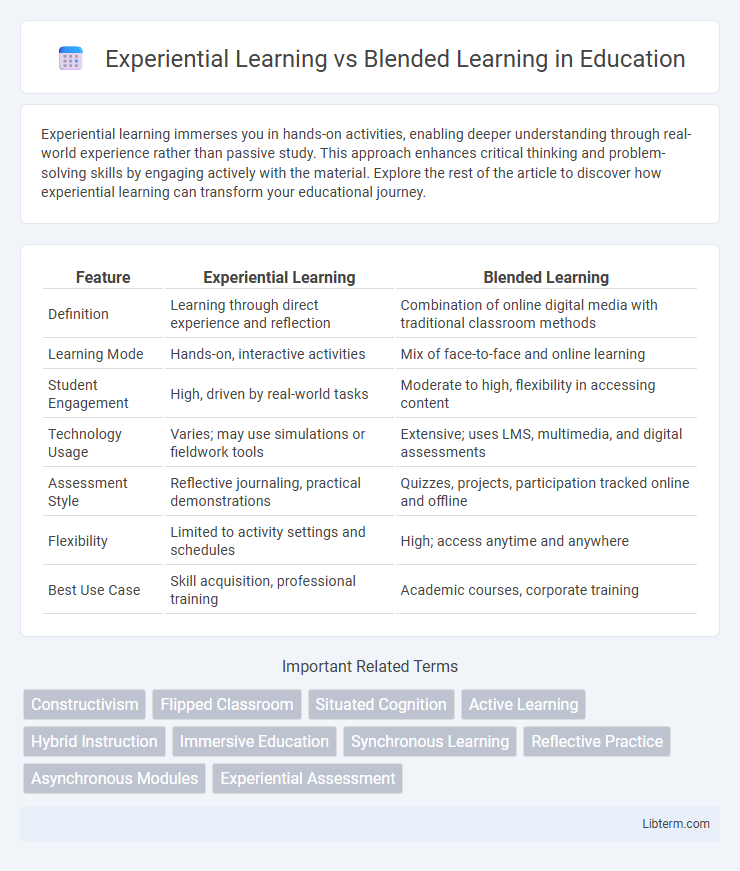
| Feature | Experiential Learning | Blended Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection | Combination of online digital media with traditional classroom methods |
| Learning Mode | Hands-on, interactive activities | Mix of face-to-face and online learning |
| Student Engagement | High, driven by real-world tasks | Moderate to high, flexibility in accessing content |
| Technology Usage | Varies; may use simulations or fieldwork tools | Extensive; uses LMS, multimedia, and digital assessments |
| Assessment Style | Reflective journaling, practical demonstrations | Quizzes, projects, participation tracked online and offline |
| Flexibility | Limited to activity settings and schedules | High; access anytime and anywhere |
| Best Use Case | Skill acquisition, professional training | Academic courses, corporate training |
Introduction to Experiential and Blended Learning
Experiential learning involves active participation and reflection, emphasizing hands-on experiences to foster deeper understanding and skill development. Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with digital tools, creating a flexible and personalized educational environment. Integrating experiential methods within blended learning frameworks enhances engagement, retention, and practical application of knowledge.
Defining Experiential Learning
Experiential learning is a hands-on educational approach where learners actively engage in real-world tasks and reflect on their experiences to gain deeper understanding. This method emphasizes learning through direct involvement, critical thinking, and problem-solving rather than passive absorption of information. Unlike blended learning, which combines online and face-to-face instruction, experiential learning focuses on immersive activities that promote practical skills and personal growth.
Understanding Blended Learning
Blended learning integrates traditional face-to-face instruction with digital and online resources, creating a hybrid educational environment that enhances flexibility and accessibility. This approach leverages technology to personalize learning experiences, promote interactive engagement, and support diverse learning styles. By combining experiential activities with virtual tools, blended learning offers a comprehensive framework that fosters deeper comprehension and practical application of knowledge.
Key Differences Between Experiential and Blended Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world experiences where learners actively engage with tasks to deepen understanding and develop practical skills, often through simulations, internships, or project-based activities. Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with digital tools and online resources to create a flexible, hybrid educational model that enhances accessibility and personalization. Key differences lie in the mode of engagement--experiential learning prioritizes immersive, activity-based learning, while blended learning integrates multiple delivery methods to balance direct teaching with technological interactivity.
Benefits of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by engaging learners directly in hands-on activities, fostering deeper understanding and retention. This method promotes active participation and real-world application, which increases learner motivation and confidence. Experiential learning also supports collaboration and adaptability, making it highly effective for developing practical skills and emotional intelligence.
Advantages of Blended Learning
Blended learning combines in-person experiential activities with online educational resources, providing flexibility and accessibility that enhances student engagement and retention. This approach allows for personalized pacing and immediate feedback through digital tools, supporting diverse learning styles and improving overall academic performance. The integration of technology also facilitates continuous assessment and data-driven instruction, optimizing learning outcomes in various educational settings.
Challenges in Implementing Both Methods
Implementing experiential learning faces challenges such as logistical constraints, high resource demands, and the need for skilled facilitators to guide real-world activities effectively. Blended learning struggles with ensuring seamless integration between online and face-to-face components, maintaining student engagement across platforms, and addressing technological disparities among learners. Both methods require careful curriculum design and continuous instructor training to overcome barriers related to adaptability and assessment accuracy.
Comparing Outcomes: Student Engagement and Retention
Experiential learning enhances student engagement by immersing learners in hands-on activities that foster deeper understanding and critical thinking, leading to higher retention rates compared to traditional methods. Blended learning combines online digital media with face-to-face instruction, offering flexibility and personalized pace, which also improves retention but may vary based on implementation quality. Research from institutions like the University of Colorado shows that experiential learning environments often result in 10-20% greater knowledge retention and increased motivation than blended learning settings.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Educational Goals
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world experiences that enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills, making it ideal for skill-based and vocational education. Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with digital tools, offering flexibility and personalized pacing suited for diverse learning styles and academic subjects. Selecting the right approach depends on educational goals, resource availability, and the desired balance between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Future Trends in Experiential and Blended Learning
Future trends in experiential and blended learning emphasize immersive technologies such as virtual and augmented reality to create realistic, hands-on experiences that enhance student engagement and skill acquisition. Artificial intelligence-driven adaptive learning systems personalize blended learning pathways, optimizing outcomes by integrating experiential activities with digital content. The rise of data analytics facilitates continuous assessment and refinement of both experiential and blended learning models, ensuring they remain responsive to evolving educational needs and workforce demands.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com