Effective teacher feedback plays a crucial role in improving student learning by providing clear, specific, and actionable insights. Constructive feedback helps learners understand their strengths and areas for growth, fostering motivation and self-reflection. Explore the rest of the article to discover strategies for delivering impactful feedback that enhances your students' educational experience.
Table of Comparison
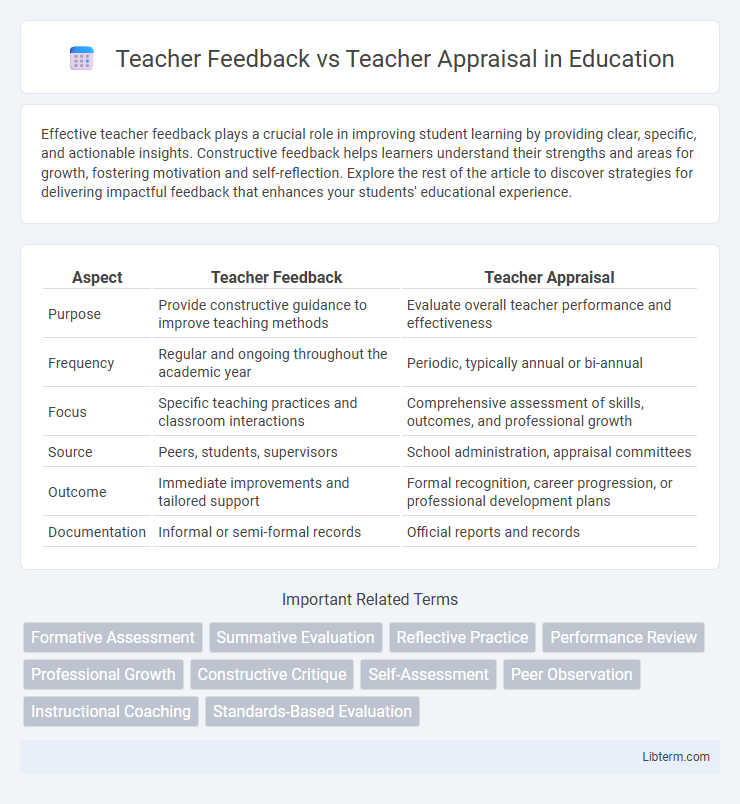
| Aspect | Teacher Feedback | Teacher Appraisal |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provide constructive guidance to improve teaching methods | Evaluate overall teacher performance and effectiveness |
| Frequency | Regular and ongoing throughout the academic year | Periodic, typically annual or bi-annual |
| Focus | Specific teaching practices and classroom interactions | Comprehensive assessment of skills, outcomes, and professional growth |
| Source | Peers, students, supervisors | School administration, appraisal committees |
| Outcome | Immediate improvements and tailored support | Formal recognition, career progression, or professional development plans |
| Documentation | Informal or semi-formal records | Official reports and records |
Understanding Teacher Feedback
Teacher feedback centers on providing specific, actionable insights to educators for improving their instructional methods and student engagement, emphasizing formative support rather than summative judgment. It involves observational data, peer reviews, and student performance metrics to guide professional development tailored to individual teacher needs. Understanding teacher feedback requires recognizing its role in fostering continuous growth and reflective practice within educational environments.
Defining Teacher Appraisal
Teacher appraisal is a systematic evaluation process designed to assess a teacher's performance, effectiveness, and professional development needs within an educational institution. It typically involves criteria such as lesson planning, classroom management, student engagement, and adherence to curriculum standards. Unlike teacher feedback, which provides informal or formative input for immediate improvement, teacher appraisal serves as a formal, summative assessment that informs career progression, training requirements, and accountability measures.
Key Differences: Feedback vs Appraisal
Teacher feedback is ongoing, formative, and aimed at improving teaching practices through constructive comments and suggestions, whereas teacher appraisal is a summative evaluation conducted periodically to assess overall performance against set standards. Feedback focuses on specific behaviors and instructional techniques, providing immediate insights for growth, while appraisal measures outcomes, professional competencies, and contributions to the educational institution. Appraisals often influence career progression and compensation, making them more formal and standardized compared to the more personalized and developmental nature of feedback.
Purposes of Teacher Feedback
Teacher feedback primarily aims to improve instructional practices by providing specific, actionable insights that help educators refine their teaching strategies and enhance student learning outcomes. It fosters professional growth through continuous reflection and adjustment based on real-time classroom interactions. Unlike teacher appraisal, which evaluates overall performance for administrative decisions, feedback is developmental, focusing on supporting teacher effectiveness and motivation.
Objectives of Teacher Appraisal
Teacher appraisal aims to evaluate educators' performance systematically, focusing on enhancing teaching quality, professional development, and accountability within educational institutions. Its objectives include identifying strengths and areas for improvement, guiding career progression, and ensuring alignment with curriculum standards and school goals. Unlike teacher feedback, which is often informal and ongoing, teacher appraisal is a formal, periodic process designed to inform administrative decisions and improve overall instructional effectiveness.
Impact on Teacher Development
Teacher feedback provides ongoing, personalized insights that directly influence teacher growth by identifying strengths and areas for improvement, fostering reflective practice and skill enhancement. Teacher appraisal typically involves formal evaluations that assess performance against set standards, contributing to career progression and accountability but may be less frequent and comprehensive. The combination of formative feedback and summative appraisal maximizes teacher development by aligning continuous learning with clear professional benchmarks.
Methods of Delivering Feedback
Teacher feedback is often delivered through personalized, formative methods such as one-on-one meetings, written comments on lesson plans, or digital platforms like video analysis, enabling immediate, constructive guidance. Teacher appraisal typically employs summative methods including formal observations, standardized evaluation forms, and performance reviews conducted by administrators to assess overall effectiveness. Integrating real-time feedback tools with structured appraisal processes enhances teacher development and instructional quality.
Appraisal Processes and Criteria
Teacher appraisal processes involve systematic evaluation methods that assess educators based on predefined criteria such as instructional effectiveness, classroom management, student engagement, and professional development. Appraisal criteria frequently include quantitative data like student performance metrics and qualitative inputs like peer observations and self-reflections to ensure a comprehensive performance review. These structured appraisal systems aim to identify areas for improvement, guide professional growth, and support accountability within educational institutions.
Challenges in Implementing Feedback and Appraisal
Teacher feedback faces challenges such as subjectivity and inconsistency, which can hinder accurate professional growth assessments. Teacher appraisal systems often struggle with balancing standardized evaluation metrics and personalized development goals, leading to potential demotivation or biased outcomes. Limited training for evaluators and resistance from educators further complicate effective implementation of both feedback and appraisal processes.
Best Practices for Effective Evaluation
Teacher feedback emphasizes ongoing, specific, and constructive input to support professional growth and improve classroom practices, while teacher appraisal involves formal, summative assessment based on performance criteria and standards. Best practices for effective evaluation include using clear rubrics, fostering a collaborative environment, focusing on student outcomes, and integrating self-reflection tools to align feedback with appraisal objectives. Combining qualitative observations with quantitative data enhances accuracy and promotes a growth-oriented culture in educational settings.
Teacher Feedback Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com