Bilingual education enhances cognitive abilities and improves academic performance by immersing students in two languages simultaneously. This approach fosters cultural awareness and better prepares learners for a globalized world. Discover how bilingual education can transform your learning experience by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
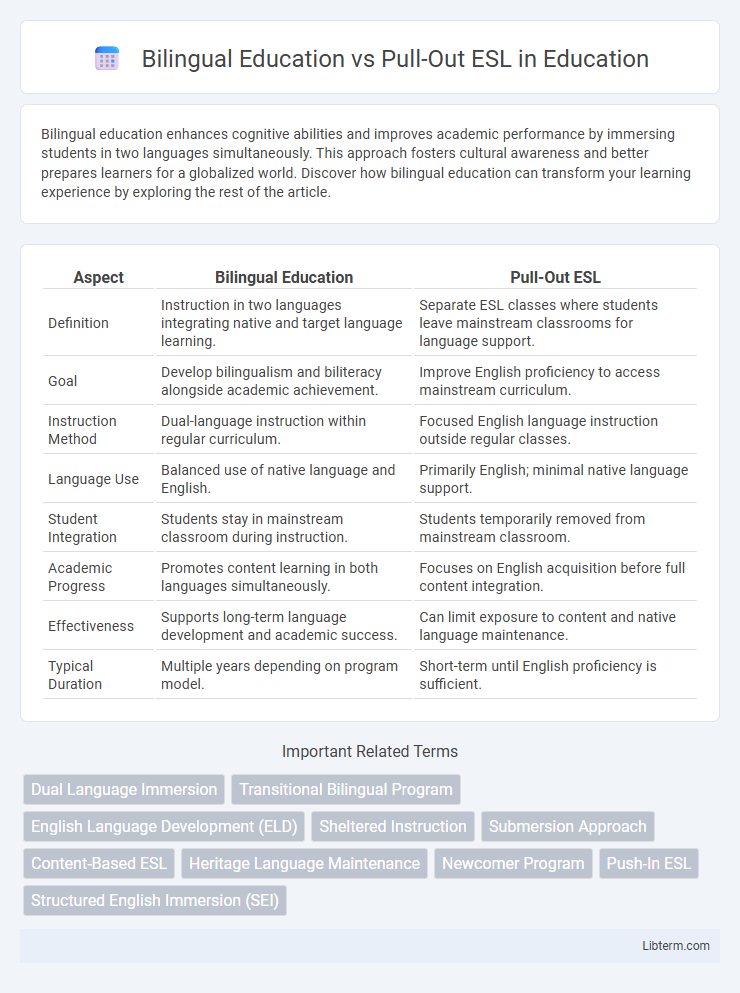
| Aspect | Bilingual Education | Pull-Out ESL |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instruction in two languages integrating native and target language learning. | Separate ESL classes where students leave mainstream classrooms for language support. |
| Goal | Develop bilingualism and biliteracy alongside academic achievement. | Improve English proficiency to access mainstream curriculum. |
| Instruction Method | Dual-language instruction within regular curriculum. | Focused English language instruction outside regular classes. |
| Language Use | Balanced use of native language and English. | Primarily English; minimal native language support. |
| Student Integration | Students stay in mainstream classroom during instruction. | Students temporarily removed from mainstream classroom. |
| Academic Progress | Promotes content learning in both languages simultaneously. | Focuses on English acquisition before full content integration. |
| Effectiveness | Supports long-term language development and academic success. | Can limit exposure to content and native language maintenance. |
| Typical Duration | Multiple years depending on program model. | Short-term until English proficiency is sufficient. |
Understanding Bilingual Education: An Overview
Bilingual education integrates content instruction with language development, enabling students to learn academic subjects in both their native language and English, which supports cognitive growth and cultural identity. Pull-out ESL programs separate English language learners from mainstream classrooms for targeted language instruction, often limiting exposure to academic content in the native language. Understanding bilingual education reveals its emphasis on dual-language proficiency and academic achievement, contrasting with pull-out ESL's narrower focus on English language acquisition.
What Is Pull-Out ESL? Key Features
Pull-Out ESL is an instructional model where English Language Learners (ELLs) are temporarily removed from mainstream classrooms to receive specialized English language support from certified ESL teachers. Key features include individualized or small group instruction targeting language skills like vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation. This method emphasizes direct language development while allowing students to participate in content-area learning with their peers.
Language Development in Bilingual Education
Bilingual education fosters simultaneous development of both the native language and English, enhancing cognitive flexibility and academic achievement. Research shows students in bilingual programs demonstrate stronger metalinguistic awareness and higher proficiency in both languages compared to those in pull-out ESL, who receive limited and fragmented English instruction. This integrated approach supports continuous language growth within meaningful content, promoting long-term bilingual competence.
Language Learning Outcomes in Pull-Out ESL
Pull-Out ESL programs provide targeted language instruction by temporarily removing students from mainstream classes, enabling focused skill development in listening, speaking, reading, and writing English. Research shows that Pull-Out ESL can improve students' basic interpersonal communication skills quickly but may limit exposure to academic language necessary for content mastery. Consequently, students in Pull-Out ESL often demonstrate slower progress in academic achievement compared to peers in bilingual education settings where content and language are integrated.
Academic Achievement: A Comparative Analysis
Bilingual education programs enhance academic achievement by promoting language proficiency in both the native language and English, leading to higher standardized test scores and better content comprehension. Pull-out ESL services primarily focus on English language acquisition but often result in fragmented learning experiences, which may hinder overall academic performance. Comparative studies show students in bilingual education exhibit stronger cognitive development and long-term academic gains compared to those receiving pull-out ESL instruction.
Cultural Integration and Student Identity
Bilingual education fosters cultural integration by maintaining students' native languages while promoting English proficiency, reinforcing a strong sense of cultural identity and community belonging. Pull-out ESL programs often isolate non-native speakers from mainstream classrooms, which can hinder cultural exchange and may lead to fragmented student identity development. Research indicates that sustaining native language in bilingual settings supports both academic achievement and the preservation of students' cultural heritage.
Teacher Roles and Instructional Strategies
Bilingual education teachers serve as language and content instructors, facilitating dual-language proficiency through integrated curricula that promote both academic and linguistic development, whereas pull-out ESL teachers primarily provide focused, intensive language instruction outside the mainstream classroom. Bilingual educators employ culturally responsive pedagogy and scaffolding techniques that build on students' native languages to enhance comprehension and engagement, while pull-out ESL instructors use targeted, skill-based interventions tailored to students' specific language deficits. Collaboration between bilingual and ESL teachers ensures coherent instructional planning, leveraging varied strategies to address diverse learner needs and optimize English language acquisition.
Family and Community Involvement
Bilingual education programs actively engage families and communities by incorporating cultural values and promoting language preservation, which enhances parental participation and supports students' linguistic development in both languages. In contrast, pull-out ESL programs often isolate students from their peers and limit family involvement due to fragmented instructional time and lack of cultural integration. Research indicates that sustained family engagement in bilingual settings fosters stronger academic outcomes and community connections compared to the more segmented approach of pull-out ESL.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Model
Bilingual education faces challenges such as limited resources for qualified teachers and potential delays in English proficiency development due to dual language instruction. Pull-out ESL programs often struggle with fragmented learning experiences and social isolation, which can hinder students' academic progress and language immersion. Both models encounter limitations in addressing diverse student needs, with bilingual education sometimes lacking sufficient support for content mastery and pull-out ESL missing opportunities for integrated language use within the mainstream classroom.
Choosing the Best Approach for Diverse Learners
Bilingual education fosters academic success by integrating content learning with language development in students' native languages, which supports cognitive growth and cultural identity. Pull-out ESL programs provide targeted language instruction outside the mainstream classroom, emphasizing English proficiency but often limiting content access. Selecting the best approach requires evaluating student language proficiency, cultural background, educational goals, and available resources to tailor instruction that promotes both language acquisition and academic achievement for diverse learners.
Bilingual Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com