Competency-based assessment focuses on evaluating your practical skills and knowledge against predefined standards to ensure real-world proficiency. This method offers a clear measurement of your ability to perform specific tasks effectively in professional settings. Discover how competency-based assessment can transform your learning and career by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
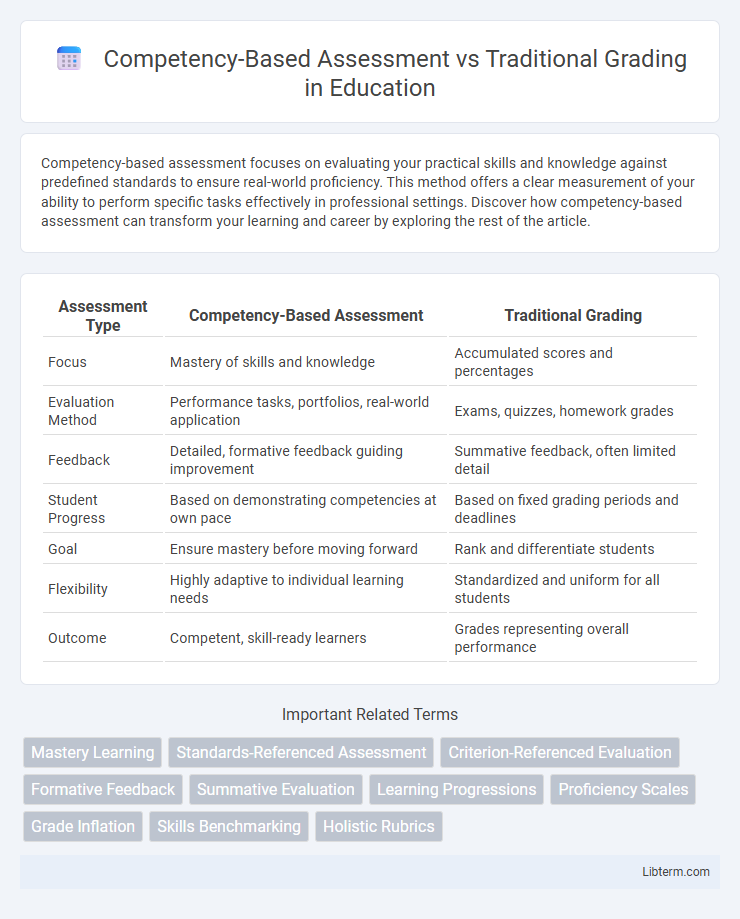
| Assessment Type | Competency-Based Assessment | Traditional Grading |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Mastery of skills and knowledge | Accumulated scores and percentages |
| Evaluation Method | Performance tasks, portfolios, real-world application | Exams, quizzes, homework grades |
| Feedback | Detailed, formative feedback guiding improvement | Summative feedback, often limited detail |
| Student Progress | Based on demonstrating competencies at own pace | Based on fixed grading periods and deadlines |
| Goal | Ensure mastery before moving forward | Rank and differentiate students |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptive to individual learning needs | Standardized and uniform for all students |
| Outcome | Competent, skill-ready learners | Grades representing overall performance |
Introduction to Competency-Based Assessment
Competency-Based Assessment measures students' mastery of specific skills and knowledge through clear, predefined competencies, offering a personalized learning pace unlike Traditional Grading which typically relies on cumulative scores and letter grades. This approach emphasizes real-world application and continuous feedback, fostering deeper understanding and skill development. By aligning assessment with individual learning goals, Competency-Based Assessment supports tailored instruction and more accurate reflection of student abilities.
Understanding Traditional Grading Systems
Traditional grading systems rely on numeric or letter scores to evaluate student performance, often emphasizing memorization and standardized testing results. These systems typically assess knowledge retention and task completion rather than mastery of specific skills or competencies. Consequently, traditional grading may not fully capture a student's practical abilities or growth over time.
Key Differences Between the Two Approaches
Competency-Based Assessment measures students' proficiency by evaluating their mastery of specific skills and knowledge, focusing on individual learning progress rather than time spent in class. Traditional grading relies on cumulative scores from exams, assignments, and participation, often emphasizing relative performance and letter grades over demonstrated competency. While competency-based systems provide personalized feedback and promote self-paced learning, traditional grading offers standardized benchmarks that facilitate easy comparison across students and institutions.
Measuring Student Mastery: Competency vs. Grades
Competency-based assessment emphasizes measuring student mastery through clearly defined skills and knowledge, allowing personalized pacing and deeper understanding. Traditional grading often relies on aggregated scores and percentage points, which may not accurately reflect individual proficiency or learning progress. This approach ensures targeted feedback and meaningful evaluation aligned with real-world competencies rather than arbitrary grade boundaries.
Impact on Student Motivation and Engagement
Competency-Based Assessment (CBA) enhances student motivation by focusing on mastering specific skills and knowledge, allowing personalized pacing that fosters deeper engagement. Traditional grading often prioritizes cumulative scores and letter grades, which can lead to anxiety and surface-level learning, reducing intrinsic motivation. Research indicates that CBA's emphasis on feedback and mastery encourages students to take ownership of their learning, resulting in higher sustained engagement compared to traditional grading methods.
Teacher Roles and Responsibilities
Teachers in competency-based assessment systems primarily act as facilitators, guiding students through individualized learning paths and providing targeted feedback to support mastery of specific skills. In contrast, traditional grading often requires teachers to assign scores based on cumulative performance, emphasizing standardized testing and broad evaluation criteria. The shift to competency-based models redefines teacher responsibilities to include continuous monitoring, personalized instruction, and detailed documentation of student progress toward clearly defined competencies.
Flexibility and Personalization in Learning
Competency-based assessment offers greater flexibility by allowing students to progress at their own pace, demonstrating mastery of specific skills before moving forward. This personalized approach adapts to individual learning needs, unlike traditional grading systems that rely on fixed schedules and uniform benchmarks. As a result, competency-based models foster deeper understanding and tailor education to each student's unique strengths and challenges.
Challenges in Implementation
Competency-based assessment faces challenges such as the need for extensive teacher training and the development of precise rubrics to measure mastery effectively. Traditional grading systems often pose resistance due to their simplicity and long-established use, making the transition difficult for institutions. Integrating personalized learning paths and ensuring consistent standards across diverse subjects further complicate the implementation of competency-based frameworks.
Success Stories and Case Studies
Competency-based assessment has shown success in improving student mastery and real-world skill application, as evidenced by case studies from institutions like Western Governors University, where personalized pacing and mastery requirements led to higher graduation rates and employer satisfaction. Traditional grading systems, while widely used, often receive criticism in studies for not accurately reflecting students' practical competencies or readiness for the workforce, highlighting gaps addressed by competency-based models. Schools adopting competency-based frameworks report increased student engagement and equitable evaluation outcomes, proving its effectiveness through empirical success stories across diverse educational settings.
Future Trends in Educational Assessment
Future trends in educational assessment emphasize Competency-Based Assessment (CBA) as a more personalized and mastery-focused approach, moving beyond Traditional Grading's reliance on cumulative scores and time-based progression. CBA leverages digital platforms and data analytics to provide real-time feedback and adaptive learning paths tailored to individual student skills and knowledge gaps. These innovations support lifelong learning and align assessments with workforce demands, promoting skills verification rather than mere grade accumulation.
Competency-Based Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com