Visual literacy enhances your ability to interpret and create meaning from images, empowering communication beyond words. Developing this skill improves critical thinking and supports learning across various disciplines. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical strategies for boosting your visual literacy.
Table of Comparison
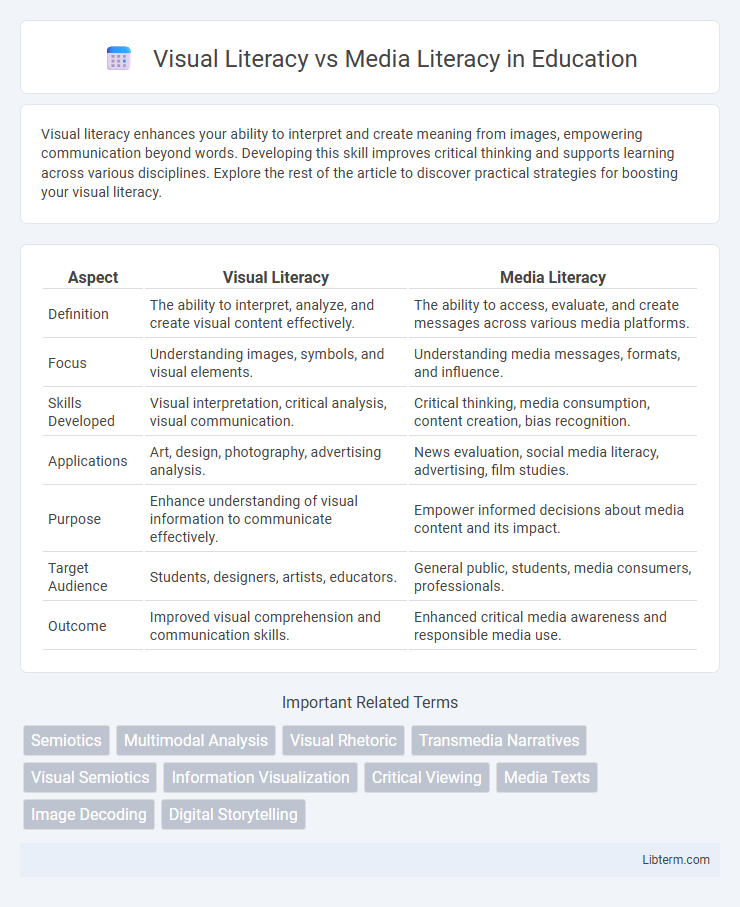
| Aspect | Visual Literacy | Media Literacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The ability to interpret, analyze, and create visual content effectively. | The ability to access, evaluate, and create messages across various media platforms. |
| Focus | Understanding images, symbols, and visual elements. | Understanding media messages, formats, and influence. |
| Skills Developed | Visual interpretation, critical analysis, visual communication. | Critical thinking, media consumption, content creation, bias recognition. |
| Applications | Art, design, photography, advertising analysis. | News evaluation, social media literacy, advertising, film studies. |
| Purpose | Enhance understanding of visual information to communicate effectively. | Empower informed decisions about media content and its impact. |
| Target Audience | Students, designers, artists, educators. | General public, students, media consumers, professionals. |
| Outcome | Improved visual comprehension and communication skills. | Enhanced critical media awareness and responsible media use. |
Introduction to Visual Literacy and Media Literacy
Visual literacy involves the ability to interpret, analyze, and create meaning from images by understanding visual elements like color, composition, and symbolism. Media literacy encompasses critical thinking skills needed to evaluate and produce content across various platforms, including text, audio, video, and digital media. Both literacies empower individuals to navigate and communicate effectively in an increasingly visual and media-rich environment.
Defining Visual Literacy: Key Concepts
Visual literacy involves the ability to interpret, negotiate, and make meaning from information presented in the form of images, encompassing skills such as recognizing symbols, understanding visual narratives, and analyzing design elements. Key concepts include visual cognition, comprehension of color theory, spatial relationships, and semiotics to decode messages embedded in visuals. Mastery of visual literacy enables critical evaluation of images in various contexts, facilitating deeper understanding beyond mere observation.
Understanding Media Literacy: Core Principles
Media literacy encompasses critical analysis skills that enable individuals to interpret, evaluate, and create messages in various forms of media, emphasizing the understanding of intent, context, and audience. It involves recognizing biases, distinguishing between credible sources and misinformation, and decoding persuasive techniques used by media producers. Visual literacy, a subset of media literacy, specifically focuses on the ability to comprehend and critically assess visual elements such as images, symbols, and layouts within media content.
Historical Development of Visual and Media Literacy
Visual literacy emerged in the early 20th century with the rise of photographic technologies and film, emphasizing the ability to interpret and create meaning from images. Media literacy developed later in the 1960s and 1970s, expanding the focus to include critical analysis of diverse media forms like television, radio, and digital content. Both fields evolved in response to technological advancements and increasing media saturation, shaping educational frameworks that address information interpretation and critical thinking skills.
Comparing Visual and Media Literacy: Fundamental Differences
Visual literacy centers on the ability to interpret, create, and communicate through images, emphasizing understanding visual elements such as color, composition, and symbolism. Media literacy encompasses a broader skill set that includes analyzing, evaluating, and creating messages across various media platforms like television, internet, and print, focusing on content, context, and purpose. The fundamental difference lies in visual literacy's focus on visual content specifically, while media literacy addresses multiple forms of media, incorporating critical thinking about both visual and non-visual messages.
Interconnection Between Visual and Media Literacy
Visual literacy enhances the ability to interpret and analyze images, symbols, and visual media, while media literacy broadens this skill set to include critical understanding of various media formats and messages. The interconnection between visual and media literacy lies in their shared emphasis on decoding meaning, evaluating sources, and recognizing persuasive techniques across both visual and textual content. Mastery of this combined skill set is crucial for navigating digital environments where visual and media messages are increasingly integrated and influential.
Role of Technology in Shaping Literacies
Technology plays a pivotal role in shaping both visual literacy and media literacy by providing diverse digital platforms and tools that demand critical analysis and interpretation skills. Advanced software and multimedia technologies enable users to create, manipulate, and disseminate visual and media content, fostering deeper understanding of visual cues, symbols, and media messages. The integration of artificial intelligence and augmented reality further enhances the interactive experience, requiring users to develop sophisticated literacy to navigate and evaluate complex digital environments effectively.
Educational Approaches to Teaching Both Literacies
Educational approaches to teaching visual literacy emphasize analyzing and interpreting images, symbols, and visual media to enhance critical thinking and communication skills. Media literacy education focuses on understanding and evaluating diverse media content, including digital and traditional platforms, to foster informed and responsible media consumption. Integrating both literacies in curricula develops students' ability to decode visual and media messages, promoting comprehensive analysis and creative expression.
Challenges in Developing Visual and Media Literacy Skills
Developing visual literacy skills faces challenges such as the overwhelming volume of complex images and the need for critical analysis to discern meaning and bias, while media literacy hurdles include navigating misinformation and understanding diverse media formats across digital platforms. Both require educators to implement adaptive teaching strategies that address varying cognitive abilities and the rapid evolution of visual and media landscapes. Limited access to technology and insufficient curriculum integration further complicate efforts to enhance these essential skills in students and adults alike.
Future Trends in Visual and Media Literacy
Future trends in visual and media literacy emphasize the integration of immersive technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to enhance critical analysis skills. Increasing reliance on artificial intelligence (AI) for content creation necessitates advanced literacy for identifying deepfakes and misinformation. Educational frameworks are evolving to prioritize multimodal communication and digital citizenship to equip learners with adaptive media evaluation capabilities.
Visual Literacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com